Abstract
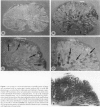
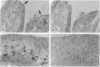
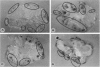
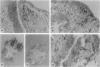
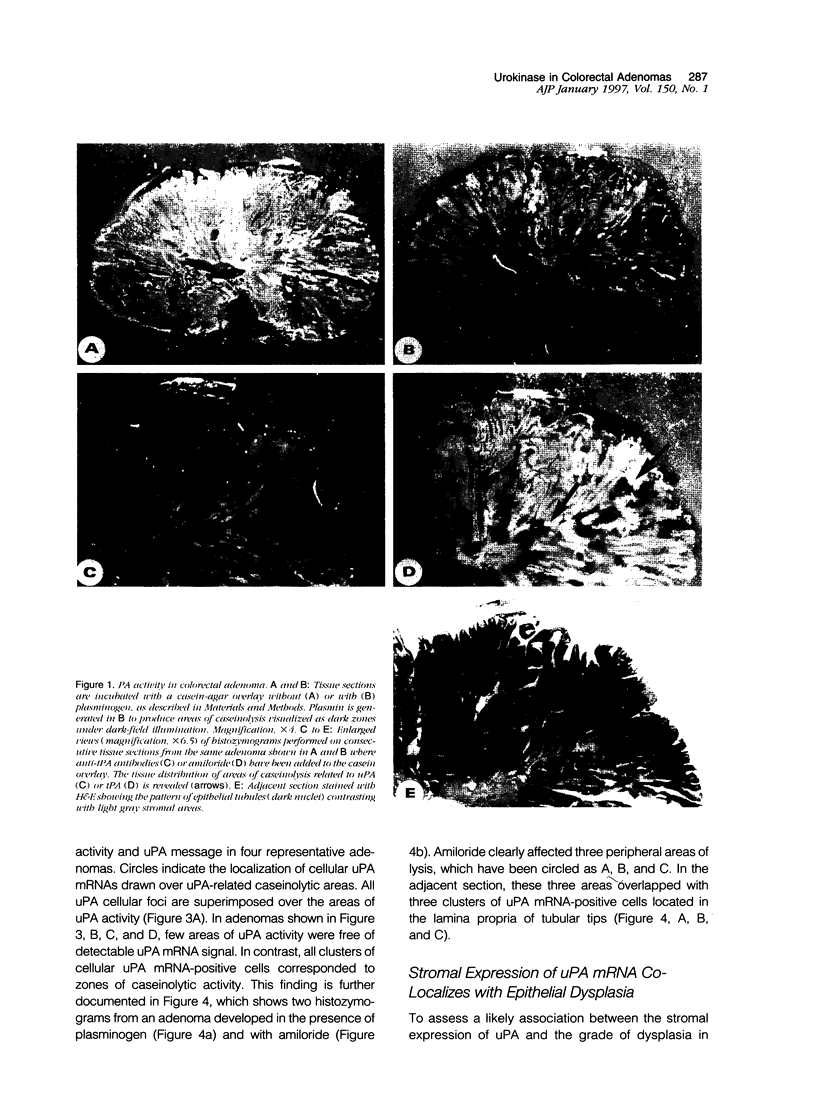
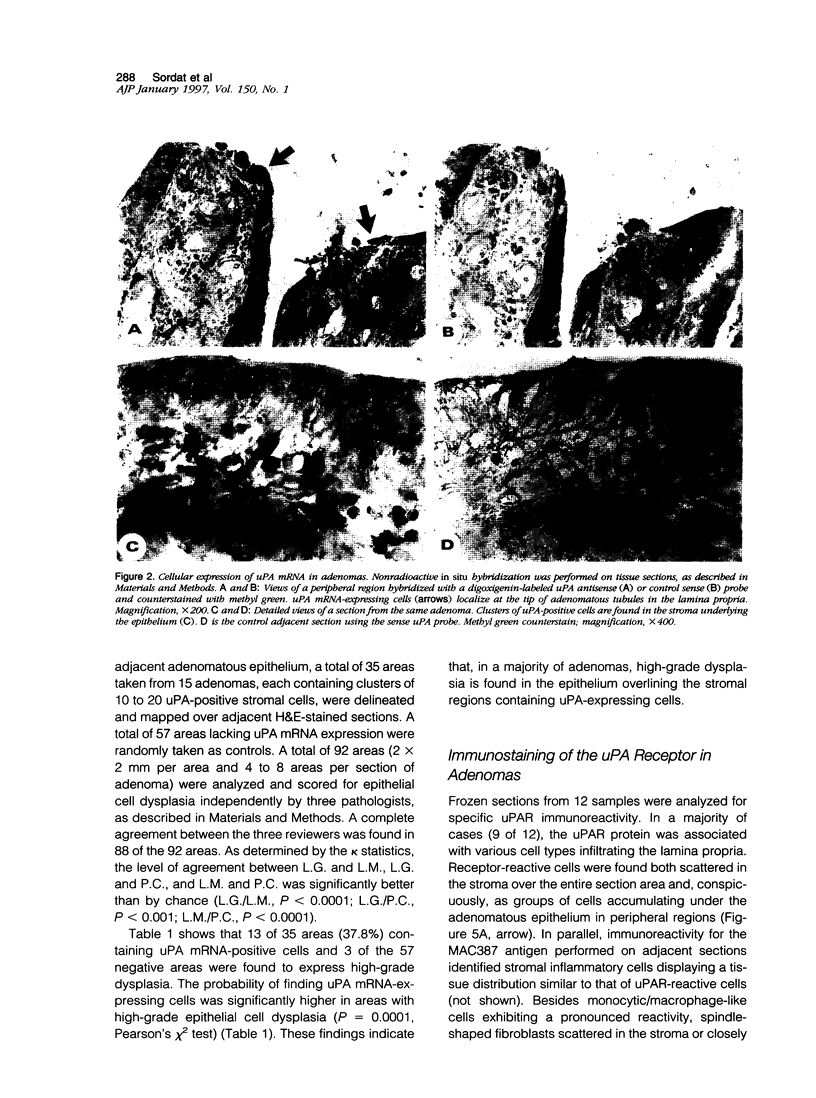
An increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and a decrease of tissue-type PA (tPA) have been associated with the transition from normal to adenomatous colorectal mucosa. Serial sections from 25 adenomas were used to identify PA-related caseinolytic activities by in situ zymography, blocking selectively uPA or tPA. The distribution of uPA, tPA, and type 1 PA inhibitor mRNAs was investigated by nonradioactive in situ hybridization, and the receptor for uPA was detected by immunostaining. Low- and high-grade epithelial cell dysplasia was mapped histologically. Results show that 23 of 25 adenomas expressed uPA-related lytic activity located predominantly in the periphery whereas tPA-related activity was mainly in central areas of adenomas. In 15 of 25 adenomas, uPA mRNA was expressed in stromal cells clustered in foci that coincided with areas of uPA lytic activity. The probability of finding uPA mRNA-reactive cells was significantly higher in areas with high-grade epithelial dysplasia. uPA receptor was mainly stromal and expressed at the periphery. Type 1 PA inhibitor mRNA cellular expression was diffuse in the stroma, in endothelial cells, and in a subpopulation of alpha-smooth muscle cell actin-reactive cells. These results show that a stromal up-regulation of the uPA/plasmin system is associated with foci of severe dysplasia in a subset of colorectal adenomas.
Full text
PDF



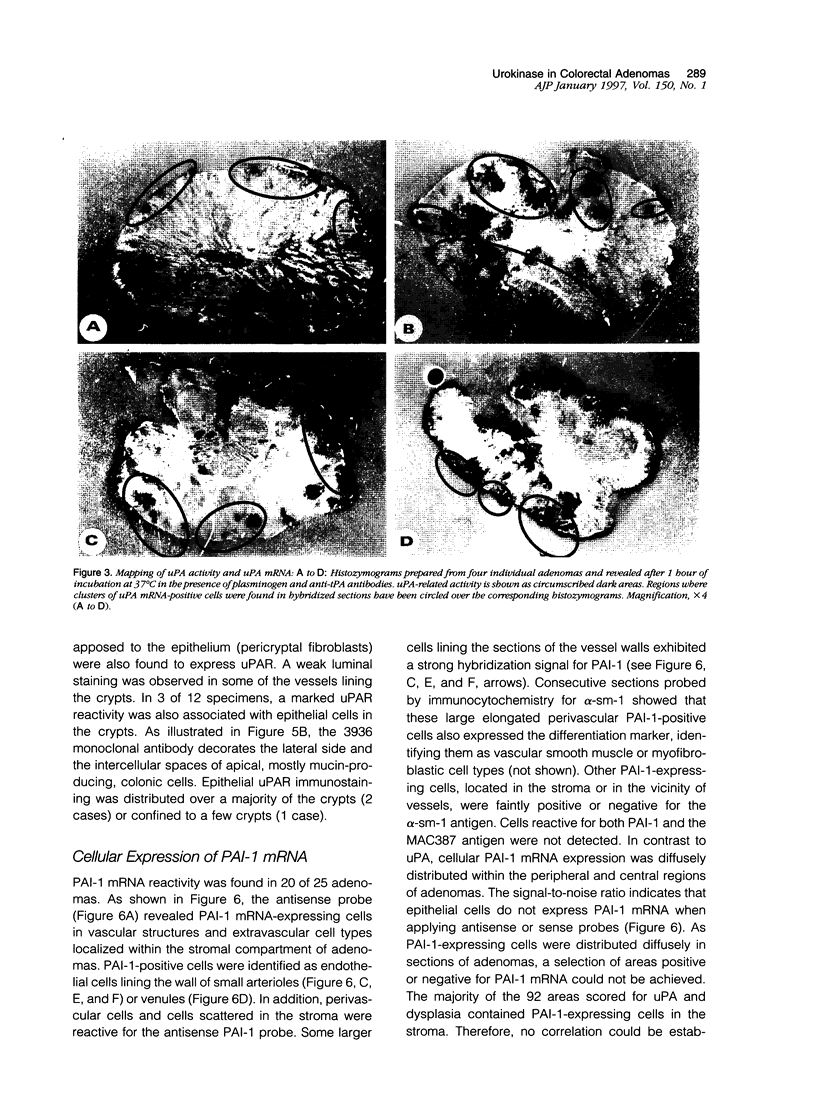
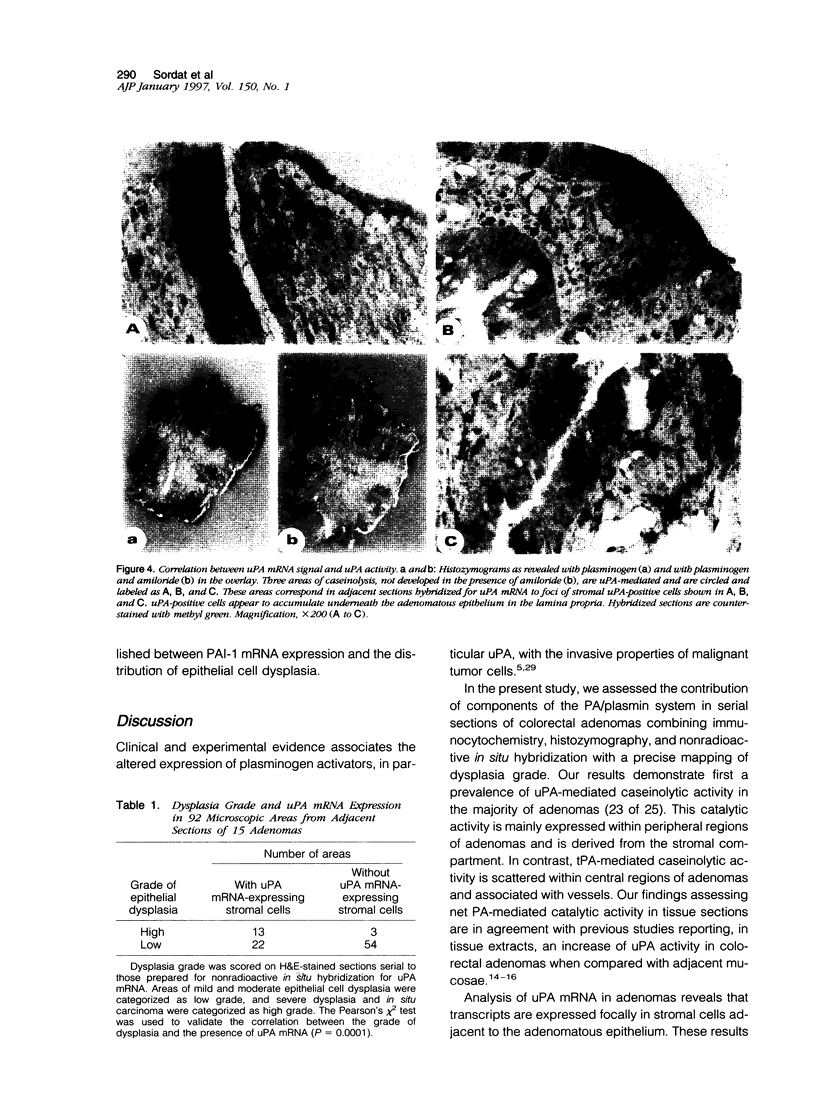

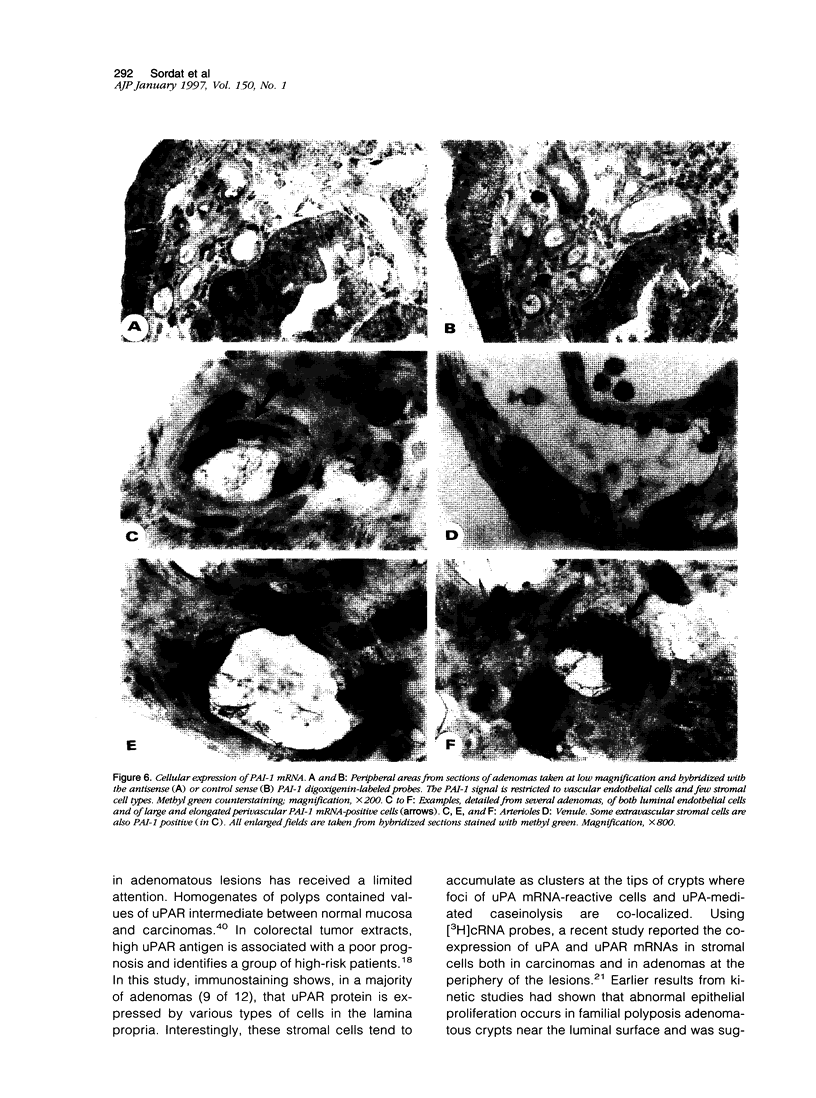



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt N., Rønne E., Danø K. The structure and function of the urokinase receptor, a membrane protein governing plasminogen activation on the cell surface. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1995 May;376(5):269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. T., Hall N. R. The genetics of colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(13):1946–1956. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(94)00385-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. T. Membrane proteases: roles in tissue remodeling and tumour invasion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):802–809. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90103-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corasanti J. G., Celik C., Camiolo S. M., Mittelman A., Evers J. L., Barbasch A., Hobika G. H., Markus G. Plasminogen activator content of human colon tumors and normal mucosae: separation of enzymes and partial purification. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Aug;65(2):345–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbaldo C., Cunningham M., Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P. Plasmin-catalyzed proteolysis in colorectal neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 15;55(20):4688–4695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbaldo C., Masouye I., Saurat J. H., Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P. Plasminogen activation in melanocytic neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4547–4552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh S., Sier C. F., Griffioen G., Vloedgraven H. J., de Boer A., Welvaart K., van de Velde C. J., van Krieken J. H., Verheijen J. H., Lamers C. B. Prognostic relevance of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 1;54(15):4065–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh S., Sier C. F., Heerding M. M., Griffioen G., Lamers C. B., Verspaget H. W. Urokinase receptor and colorectal cancer survival. Lancet. 1994 Aug 6;344(8919):401–402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelister J. S., Lewin M. R., Driver H. E., Savage F., Mahmoud M., Gaffney P. J., Boulos P. B. Plasminogen activators in experimental colorectal neoplasia: a role in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence? Gut. 1987 Jul;28(7):816–821. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.7.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelister J. S., Mahmoud M., Lewin M. R., Gaffney P. J., Boulos P. B. Plasminogen activators in human colorectal neoplasia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Sep 20;293(6549):728–731. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6549.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Kirkeby L. T., Kristensen P., Lund L. R., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in stromal cells in adenocarcinomas of the colon in humans. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollas W., Blasi F., Boyd D. Role of the urokinase receptor in facilitating extracellular matrix invasion by cultured colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3690–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemitsu T., Koike A., Yamamoto S. Study of the cell proliferation kinetics in ulcerative colitis, adenomatous polyps, and cancer. Cancer. 1985 Sep 1;56(5):1094–1098. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850901)56:5<1094::aid-cncr2820560523>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komminoth P. Digoxigenin as an alternative probe labeling for in situ hybridization. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1992 Jun;1(2):142–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretz K., Möller P., Schwartz-Albiez R. Plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in human colorectal carcinoma tissues are not expressed by the tumour cells. Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A(8):1184–1189. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightdale C., Lipkin M., Deschner E. In vivo measurements in familial polyposis: kinetics and location of proliferating cells in colonic adenomas. Cancer Res. 1982 Oct;42(10):4280–4283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning A. M., Williams A. C., Game S. M., Paraskeva C. Differential sensitivity of human colonic adenoma and carcinoma cells to transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta): conversion of an adenoma cell line to a tumorigenic phenotype is accompanied by a reduced response to the inhibitory effects of TGF-beta. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1471–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):161–195. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto T., Bussey H. J., Morson B. C. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975 Dec;36(6):2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naitoh H., Eguchi Y., Ueyama H., Kodama M., Hattori T. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, 2 and plasminogen in colon cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1995 Jan;86(1):48–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1995.tb02987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien M. J., Winawer S. J., Zauber A. G., Gottlieb L. S., Sternberg S. S., Diaz B., Dickersin G. R., Ewing S., Geller S., Kasimian D. The National Polyp Study. Patient and polyp characteristics associated with high-grade dysplasia in colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):371–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani H., Pyke C., Danø K., Nagura H. Expression of urokinase receptor in various stromal-cell populations in human colon cancer: immunoelectron microscopical analysis. Int J Cancer. 1995 Sep 15;62(6):691–696. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910620608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Sappino A. P., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is induced in migrating endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Oct;153(1):129–139. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041530117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Eriksen J., Danø K. The plasminogen activation system in human colon cancer: messenger RNA for the inhibitor PAI-1 is located in endothelial cells in the tumor stroma. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4067–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Ralfkiaer E., Rønne E., Høyer-Hansen G., Kirkeby L., Danø K. Immunohistochemical detection of the receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator in human colon cancer. Histopathology. 1994 Feb;24(2):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb01291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter L. S., Kruithof E. K., Cajot J. F., Sordat B. The role of the urokinase receptor in extracellular matrix degradation by HT29 human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1993 Feb 1;53(3):444–450. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. H., Goldman H., Ransohoff D. F., Appelman H. D., Fenoglio C. M., Haggitt R. C., Ahren C., Correa P., Hamilton S. R., Morson B. C. Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol. 1983 Nov;14(11):931–968. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønnov-Jessen L., Petersen O. W., Koteliansky V. E., Bissell M. J. The origin of the myofibroblasts in breast cancer. Recapitulation of tumor environment in culture unravels diversity and implicates converted fibroblasts and recruited smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):859–873. doi: 10.1172/JCI117736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Belin D., Huarte J., Hirschel-Scholz S., Saurat J. H., Vassalli J. D. Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1073–1079. doi: 10.1172/JCI115406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Dietrich P. Y., Skalli O., Widgren S., Gabbiani G. Colonic pericryptal fibroblasts. Differentiation pattern in embryogenesis and phenotypic modulation in epithelial proliferative lesions. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;415(6):551–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00718649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sier C. F., Fellbaum C., Verspaget H. W., Schmitt M., Griffioen G., Graeff H., Hôfler H., Lamers C. B. Immunolocalization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in adenomas and carcinomas of the colorectum. Histopathology. 1991 Sep;19(3):231–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sier C. F., Quax P. H., Vloedgraven H. J., Verheijen J. H., Griffioen G., Ganesh S., Lamers C. B., Verspaget H. W. Increased urokinase receptor levels in human gastrointestinal neoplasia and related liver metastases. Invasion Metastasis. 1993;13(6):277–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sier C. F., Verspaget H. W., Griffioen G., Verheijen J. H., Quax P. H., Dooijewaard G., De Bruin P. A., Lamers C. B. Imbalance of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in human colorectal neoplasia. Implications of urokinase in colorectal carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Dec;101(6):1522–1528. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90387-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim P. S., Stephens R. W., Fayle D. R., Doe W. F. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps: quantitative expression of active and proenzyme. Int J Cancer. 1988 Oct 15;42(4):483–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Aznavoorian S., Liotta L. A. Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:541–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzumiya J., Hasui Y., Kohga S., Sumiyoshi A., Hashida S., Ishikawa E. Comparative study of plasminogen activator antigens in colonic carcinomas and adenomas. Int J Cancer. 1988 Oct 15;42(4):627–632. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K., Powe D. G., Gray T., Turner D. R., Hewitt R. E. Regional variations of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human colorectal cancer: a quantitative study by image analysis. Int J Cancer. 1995 Jan 27;60(3):308–314. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910600305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissot J. D., Hauert J., Bachmann F. Characterization of plasminogen activators from normal human breast and colon and from breast and colon carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1984 Sep 15;34(3):295–302. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Sawaya R., Mohanam S., Loskutoff D. J., Bruner J. M., Rao V. H., Oka K., Tomonaga M., Nicolson G. L., Rao J. S. Expression and cellular localization of messenger RNA for plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in human astrocytomas in vivo. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3329–3332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Crama-Bohbouth G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Dooijewaard G., Weterman I. T., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activators in the intestine of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Griffioen G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Dooijewaard G., van den Ingh H. F., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activator profiles in neoplastic tissues of the human colon. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4520–4524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]