Abstract
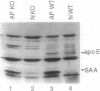
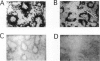
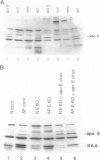
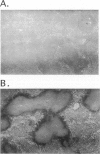
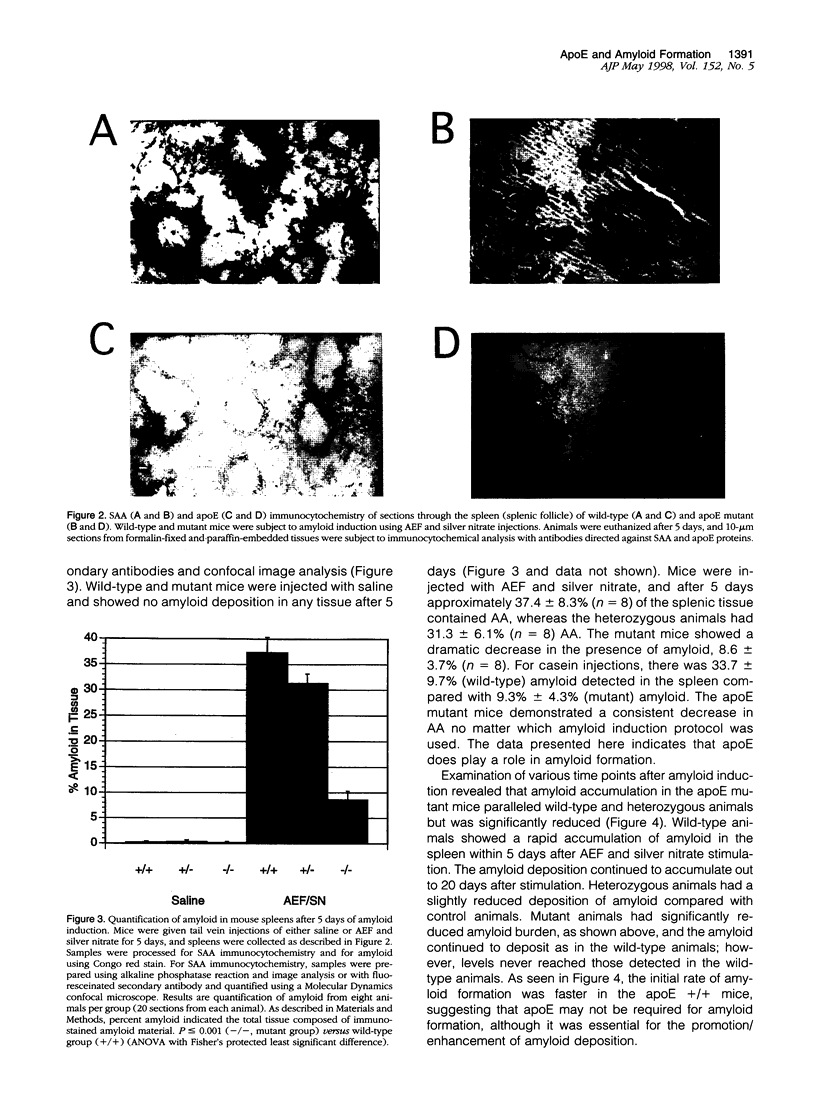
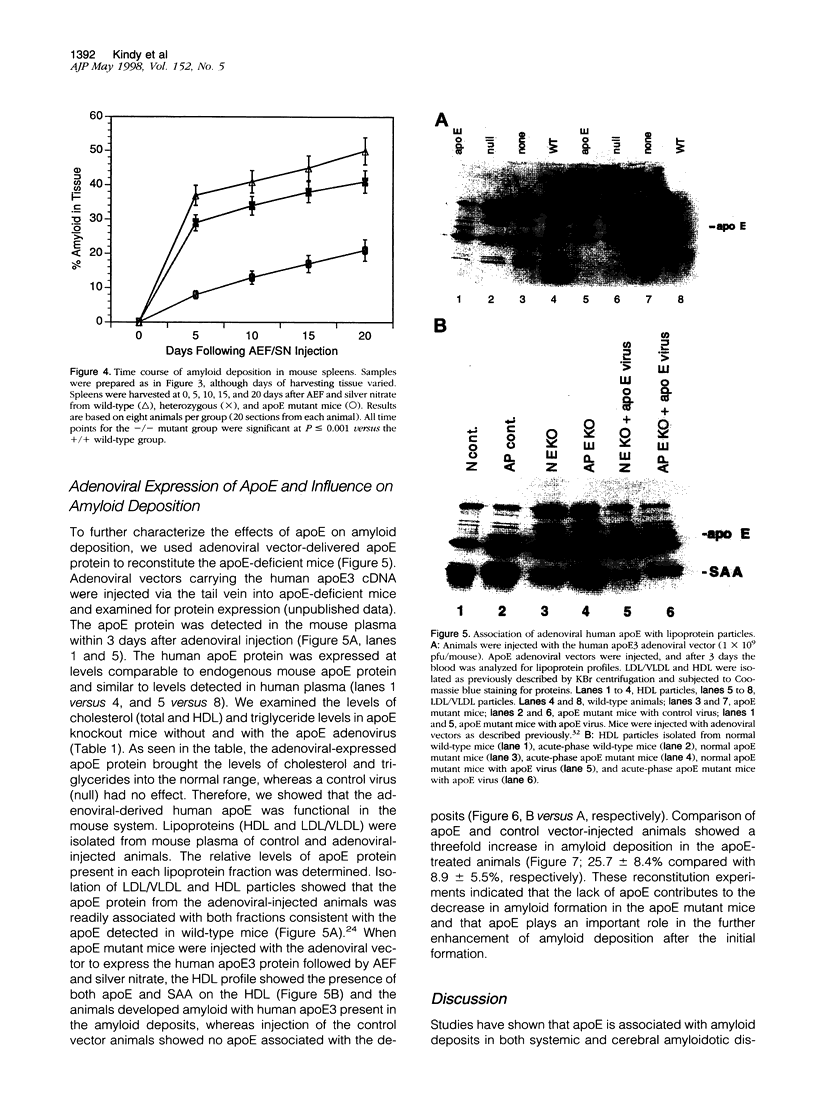
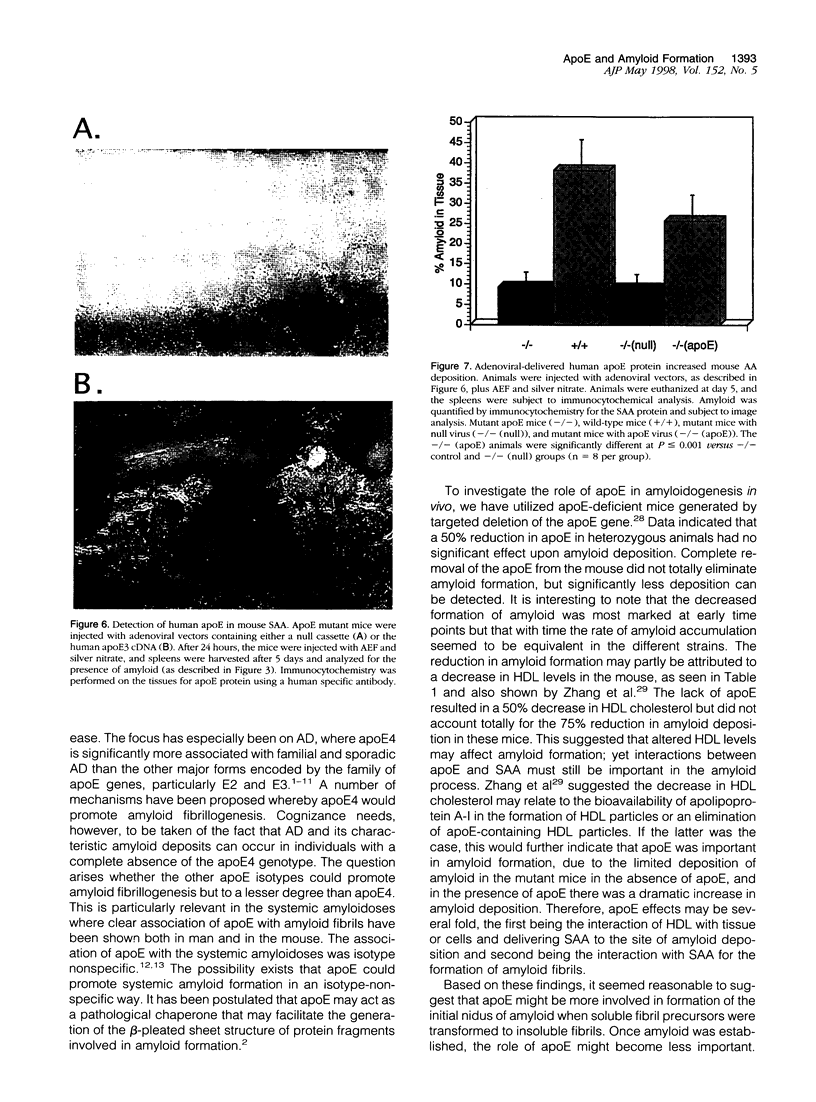
Apolipoproteins have been implicated in the formation of amyloid fibrils. Recent studies have demonstrated that apolipoprotein E (apoE), alone or in combination with apolipoprotein J (apoJ), and other lipoproteins appear to enhance deposition of amyloid fibrils both in systemic and cerebral amyloids, especially Alzheimer's disease (AD). ApoE enhanced the ability of the amyloid beta-protein (1-40) fragment (A beta) to form fibrils in vitro, with apoE4 promoting the greatest fibril formation. ApoE was found associated with both human and mouse amyloid A (AA) deposits. To define the role of apoE in vivo, we utilized mice lacking the apoE gene by gene targeting. We used the AA model in mice to characterize the function of the apoE protein in amyloid fibrillogenesis. ApoE-deficient mice exhibited a decrease in deposition of AA when compared with heterozygous mutant or wild-type animals. In addition, apoE-deficient mice that were injected with an adenovirus that expressed the human apoE3 gene had restored AA deposition and the apoE was associated with the AA fibrils. These results are agreement with the in vitro studies using the beta-peptide and suggest that apoE is not essential for amyloid fibrillogenesis but can promote the development of amyloid deposition.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ailles L., Kisilevsky R., Young I. D. Induction of perlecan gene expression precedes amyloid formation during experimental murine AA amyloidogenesis. Lab Invest. 1993 Oct;69(4):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrad M. A., Kisilevsky R., Willmer J., Chen S. J., Skinner M. Further characterization of amyloid-enhancing factor. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botto M., Hawkins P. N., Bickerstaff M. C., Herbert J., Bygrave A. E., McBride A., Hutchinson W. L., Tennent G. A., Walport M. J., Pepys M. B. Amyloid deposition is delayed in mice with targeted deletion of the serum amyloid P component gene. Nat Med. 1997 Aug;3(8):855–859. doi: 10.1038/nm0897-855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissette L., Young I., Narindrasorasak S., Kisilevsky R., Deeley R. Differential induction of the serum amyloid A gene family in response to an inflammatory agent and to amyloid-enhancing factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19327–19332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Prelli F., Pras M., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E carboxyl-terminal fragments are complexed to amyloids A and L. Implications for amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17610–17615. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W., Fornwald J., Brawner M., Wetzel R. Native complex formation between apolipoprotein E isoforms and the Alzheimer's disease peptide A beta. Biochemistry. 1996 Jun 4;35(22):7123–7130. doi: 10.1021/bi952852v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans K. C., Berger E. P., Cho C. G., Weisgraber K. H., Lansbury P. T., Jr Apolipoprotein E is a kinetic but not a thermodynamic inhibitor of amyloid formation: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):763–767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Isla T., West H. L., Rebeck G. W., Harr S. D., Growdon J. H., Locascio J. J., Perls T. T., Lipsitz L. A., Hyman B. T. Clinical and pathological correlates of apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1996 Jan;39(1):62–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshii Y., Kawano H., Cui D., Takeda T., Gondo T., Takahashi M., Kogishi K., Higuchi K., Ishihara T. Amyloid A protein amyloidosis induced in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice. Am J Pathol. 1997 Oct;151(4):911–917. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Kisilevsky R. A high resolution ultrastructural study of experimental murine AA amyloid. Lab Invest. 1996 Mar;74(3):670–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindy M. S., King A. R., Perry G., de Beer M. C., de Beer F. C. Association of apolipoprotein E with murine amyloid A protein amyloid. Lab Invest. 1995 Oct;73(4):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R., Lemieux L. J., Fraser P. E., Kong X., Hultin P. G., Szarek W. A. Arresting amyloidosis in vivo using small-molecule anionic sulphonates or sulphates: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med. 1995 Feb;1(2):143–148. doi: 10.1038/nm0295-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koudinov A., Matsubara E., Frangione B., Ghiso J. The soluble form of Alzheimer's amyloid beta protein is complexed to high density lipoprotein 3 and very high density lipoprotein in normal human plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 15;205(2):1164–1171. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozarsky K. F., McKinley D. R., Austin L. L., Raper S. E., Stratford-Perricaudet L. D., Wilson J. M. In vivo correction of low density lipoprotein receptor deficiency in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit with recombinant adenoviruses. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13695–13702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Yee A., Brewer H. B., Jr, Das S., Potter H. Amyloid-associated proteins alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and apolipoprotein E promote assembly of Alzheimer beta-protein into filaments. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):92–94. doi: 10.1038/372092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara E., Frangione B., Ghiso J. Characterization of apolipoprotein J-Alzheimer's A beta interaction. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7563–7567. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara E., Soto C., Governale S., Frangione B., Ghiso J. Apolipoprotein J and Alzheimer's amyloid beta solubility. Biochem J. 1996 Jun 1;316(Pt 2):671–679. doi: 10.1042/bj3160671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Ottman R., Tatemichi T. K., Tang M. X., Maestre G., Ngai C., Tycko B., Ginsberg H. The apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):752–754. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Sipe J. D. Murine model for human secondary amyloidosis: genetic variability of the acute-phase serum protein SAA response to endotoxins and casein. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1121–1127. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Narindrasorasak S., Kisilevsky R. Circular-dichroism studies on two murine serum amyloid A proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):775–783. doi: 10.1042/bj2560775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohm T. G., Kirca M., Bohl J., Scharnagl H., Gross W., März W. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism influences not only cerebral senile plaque load but also Alzheimer-type neurofibrillary tangle formation. Neuroscience. 1995 Jun;66(3):583–587. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00596-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedrahita J. A., Zhang S. H., Hagaman J. R., Oliver P. M., Maeda N. Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Schmader K., Breitner J. C., Benson M. D., Brown W. T., Goldfarb L., Goldgaber D., Manwaring M. G., Szymanski M. H., McCown N. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distributions in late-onset Alzheimer's disease and in other amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):710–711. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91709-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahama T., Miura K., Ju S. T., Kisilevsky R., Gruys E., Cohen A. S. Amyloid enhancing factor-loaded macrophages in amyloid fibril formation. Lab Invest. 1990 Jan;62(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroo M., Kawahara E., Nakanishi I., Migita S. Specific deposition of serum amyloid A protein 2 in the mouse. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):709–716. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Carreras I., Gonnerman W. A., Cathcart E. S., de Beer M. C., de Beer F. C. Characterization of the inbred CE/J mouse strain as amyloid resistant. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1480–1485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Bramson R., Mar H., Wight T. N., Kisilevsky R. A temporal and ultrastructural relationship between heparan sulfate proteoglycans and AA amyloid in experimental amyloidosis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Oct;39(10):1321–1330. doi: 10.1177/39.10.1940305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan A. F., de Beer F. C., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A. Identification of three isoform patterns of human serum amyloid A protein. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):203–207. doi: 10.1042/bj2500203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Huang D. Y., Dong L. M., Salvesen G. S., Pericak-Vance M., Schmechel D., Saunders A. M., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Binding of human apolipoprotein E to synthetic amyloid beta peptide: isoform-specific effects and implications for late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8098–8102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tape C., Tan R., Nesheim M., Kisilevsky R. Direct evidence for circulating apoSAA as the precursor of tissue AA amyloid deposits. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Sep;28(3):317–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki A., Kawano M., Namba Y., Kawakami M., Ikeda K. A high frequency of apolipoprotein E4 isoprotein in Japanese patients with late-onset nonfamilial Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Dec 12;163(2):166–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90373-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb N. R., de Beer M. C., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Kindy M. S., Banka C. L., Tsukamoto K., Rader D. L., de Beer F. C. Adenoviral vector-mediated overexpression of serum amyloid A in apoA-I-deficient mice. J Lipid Res. 1997 Aug;38(8):1583–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Castaño E. M., Golabek A., Vogel T., Frangione B. Acceleration of Alzheimer's fibril formation by apolipoprotein E in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1030–1035. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. J., Chan W., Wetzel R. Seeding of A beta fibril formation is inhibited by all three isotypes of apolipoprotein E. Biochemistry. 1996 Sep 24;35(38):12623–12628. doi: 10.1021/bi961074j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. H., Reddick R. L., Piedrahita J. A., Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):468–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1411543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer M. C., de Beer F. C., Beach C. M., Carreras I., Sipe J. D. Mouse serum amyloid A protein. Complete amino acid sequence and mRNA analysis of a new isoform. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2830673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]