Abstract
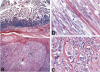
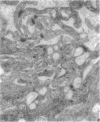
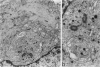
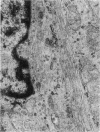
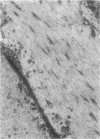
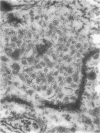
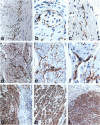
The interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) form a complex cell network within the gastrointestinal tract wall where they function as a pacemaker system. Expression of the kit proto-oncogene is essential for the development of this system. The aim of our study was to examine the hypothesis that gastrointestinal stromal tumors differentiate toward cells with an ICC phenotype. Ultrastructurally, 58 stromal tumors were characterized and found to share many features with ICC. Seventy-eight stromal tumors were immunophenotyped, particularly with regard to the kit receptor. All 78 tumors revealed strong, homogeneous immunoreactivity for the kit receptor as did ICC of adjacent and control gastrointestinal walls. Focal hyperplasia and hypertrophy of kit receptor positive cells were also observed in the gastrointestinal wall adjacent to the tumors. CD34 immunoreactivity observed in interstitial cells surrounding Auerbach's ganglia suggests that a subpopulation of ICC is CD34 positive and may explain why 56 of 78 stromal tumors were CD34 positive. Thirty control tumors, including gastrointestinal leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas, were all negative for the kit receptor. We conclude that gastrointestinal stromal tumors show striking morphological and immunophenotypic similarities with ICC and that they may originate from stem cells that differentiate toward a pacemaker cell phenotype. We propose that the noncommittal name "gastrointestinal stromal tumor" be replaced by gastrointestinal pacemaker cell tumor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelman H. D. Smooth muscle tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. What we know now that Stout didn't know. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986;10 (Suppl 1):83–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas-López C., Berezin I., Daniel E. E., Huizinga J. D. Pacemaker activity recorded in interstitial cells of Cajal of the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):C830–C835. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.4.C830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brainard J. A., Goldblum J. R. Stromal tumors of the jejunum and ileum: a clinicopathologic study of 39 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997 Apr;21(4):407–416. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199704000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson R. A., Klimstra D. S., Woodruff J. M. Subclassification of gastrointestinal stromal tumors based on evaluation by electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1996 Jul-Aug;20(4):373–393. doi: 10.3109/01913129609016340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. L. Smooth muscle tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. A study of 56 cases followed for a minimum of 10 years. Cancer. 1985 Nov 1;56(9):2242–2250. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19851101)56:9<2242::aid-cncr2820560918>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faussone-Pellegrini M. S., Pantalone D., Cortesini C. Smooth muscle cells, interstitial cells of Cajal and myenteric plexus interrelationships in the human colon. Acta Anat (Basel) 1990;139(1):31–44. doi: 10.1159/000146975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furitsu T., Tsujimura T., Tono T., Ikeda H., Kitayama H., Koshimizu U., Sugahara H., Butterfield J. H., Ashman L. K., Kanayama Y. Identification of mutations in the coding sequence of the proto-oncogene c-kit in a human mast cell leukemia cell line causing ligand-independent activation of c-kit product. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1736–1744. doi: 10.1172/JCI116761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera G. A., Cerezo L., Jones J. E., Sack J., Grizzle W. E., Pollack W. J., Lott R. L. Gastrointestinal autonomic nerve tumors. 'Plexosarcomas'. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989 Aug;113(8):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera G. A., Pinto de Moraes H., Grizzle W. E., Han S. G. Malignant small bowel neoplasm of enteric plexus derivation (plexosarcoma). Light and electron microscopic study confirming the origin of the neoplasm. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Mar;29(3):275–284. doi: 10.1007/BF01296263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga J. D., Thuneberg L., Klüppel M., Malysz J., Mikkelsen H. B., Bernstein A. W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):347–349. doi: 10.1038/373347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langton P., Ward S. M., Carl A., Norell M. A., Sanders K. M. Spontaneous electrical activity of interstitial cells of Cajal isolated from canine proximal colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7280–7284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers G. Y., Erlandson R. A., Casper E. S., Brennan M. F., Woodruff J. M. Gastrointestinal autonomic nerve tumors. A clinicopathological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of 12 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993 Sep;17(9):887–897. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199309000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecoin L., Gabella G., Le Douarin N. Origin of the c-kit-positive interstitial cells in the avian bowel. Development. 1996 Mar;122(3):725–733. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.3.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley B. J., Tyrrell L., Lu S. Z., Ma Y. S., Langley K., Ding T. G., Duffy T., Jacobs P., Tang L. H., Modlin I. Somatic c-KIT activating mutation in urticaria pigmentosa and aggressive mastocytosis: establishment of clonality in a human mast cell neoplasm. Nat Genet. 1996 Mar;12(3):312–314. doi: 10.1038/ng0396-312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod C. B., Tsokos M. Gastrointestinal autonomic nerve tumor. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1991 Jan-Feb;15(1):49–55. doi: 10.3109/01913129109021303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Yamagata A., Nishikawa S., Yoshinaga K., Kobayashi S., Nishi K., Nishikawa S. Requirement of c-kit for development of intestinal pacemaker system. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):369–375. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda R., Takahashi T., Nakamura S., Sekido Y., Nishida K., Seto M., Seito T., Sugiura T., Ariyoshi Y., Takahashi T. Expression of the c-kit protein in human solid tumors and in corresponding fetal and adult normal tissues. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):339–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur M. T., Clark H. B. Gastric stromal tumors. Reappraisal of histogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1983 Sep;7(6):507–519. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198309000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. An immunohistochemical study of cellular differentiation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988 May;89(5):601–610. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/89.5.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Virolainen M., Maarit-Sarlomo-Rikala Gastrointestinal stromal tumors--value of CD34 antigen in their identification and separation from true leiomyomas and schwannomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Feb;19(2):207–216. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199502000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monihan J. M., Carr N. J., Sobin L. H. CD34 immunoexpression in stromal tumours of the gastrointestinal tract and in mesenteric fibromatoses. Histopathology. 1994 Nov;25(5):469–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb00009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. L., Wadden C., Fletcher C. D. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: correlation of immunophenotype with clinicopathological features. J Pathol. 1991 Jun;164(2):107–117. doi: 10.1002/path.1711640204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Urtreger A., Avivi A., Zimmer Y., Givol D., Yarden Y., Lonai P. Developmental expression of c-kit, a proto-oncogene encoded by the W locus. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):911–923. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson S., Kindblom L. G., Angervall L., Tisell L. E. Metastasizing gastric epithelioid leiomyosarcomas (leiomyoblastomas) in young individuals with long-term survival. Cancer. 1992 Aug 15;70(4):721–732. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920815)70:4<721::aid-cncr2820700402>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu F. H., Ray P., Brown K., Barker P. E., Jhanwar S., Ruddle F. H., Besmer P. Primary structure of c-kit: relationship with the CSF-1/PDGF receptor kinase family--oncogenic activation of v-kit involves deletion of extracellular domain and C terminus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge S. A., Worwood M., Oscier D., Jacobs A., Padua R. A. FMS mutations in myelodysplastic, leukemic, and normal subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1377–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode J., Dhillon A. P., Doran J. F., Jackson P., Thompson R. J. PGP 9.5, a new marker for human neuroendocrine tumours. Histopathology. 1985 Feb;9(2):147–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumessen J. J., Mikkelsen H. B., Qvortrup K., Thuneberg L. Ultrastructure of interstitial cells of Cajal in circular muscle of human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumessen J. J., Mikkelsen H. B., Thuneberg L. Ultrastructure of interstitial cells of Cajal associated with deep muscular plexus of human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91784-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumessen J. J., Peters S., Thuneberg L. Light- and electron microscopical studies of interstitial cells of Cajal and muscle cells at the submucosal border of human colon. Lab Invest. 1993 Apr;68(4):481–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanks J. H., Harris M., Banerjee S. S., Eyden B. P. Gastrointestinal autonomic nerve tumours: a report of nine cases. Histopathology. 1996 Aug;29(2):111–121. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.d01-502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K. M., Lee S. T., Lu-Kuo J. M., Ward D. C., Le Paslier D., Altherr M. R., Dorman T. E., Moir D. T. A YAC contig spanning a cluster of human type III receptor protein tyrosine kinase genes (PDGFRA-KIT-KDR) in chromosome segment 4q12. Genomics. 1994 Jul 15;22(2):431–436. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. M., Evans D. J. The significance of PGP 9.5 in tumours--an immunohistochemical study of gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Histopathology. 1990 Aug;17(2):175–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1990.tb00693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torihashi S., Ward S. M., Nishikawa S., Nishi K., Kobayashi S., Sanders K. M. c-kit-dependent development of interstitial cells and electrical activity in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 1995 Apr;280(1):97–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00304515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinden J. M., Rumessen J. J., Liu H., Descamps D., De Laet M. H., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Interstitial cells of Cajal in human colon and in Hirschsprung's disease. Gastroenterology. 1996 Oct;111(4):901–910. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(96)70057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Dvorak A. M. Gastrointestinal autonomic nerve (GAN) tumor. Ultrastructural evidence for a newly recognized entity. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Apr;110(4):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. M., Burns A. J., Torihashi S., Sanders K. M. Mutation of the proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 1;480(Pt 1):91–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N. Steel locus defines new multipotent growth factor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90280-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamataka A., Kato Y., Tibboel D., Murata Y., Sueyoshi N., Fujimoto T., Nishiye H., Miyano T. A lack of intestinal pacemaker (c-kit) in aganglionic bowel of patients with Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg. 1995 Mar;30(3):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(95)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]