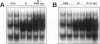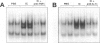Abstract
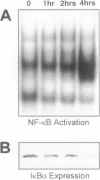
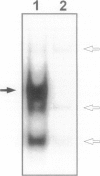
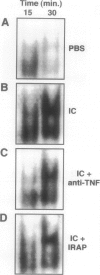
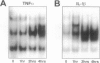
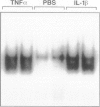
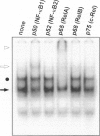
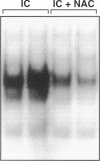
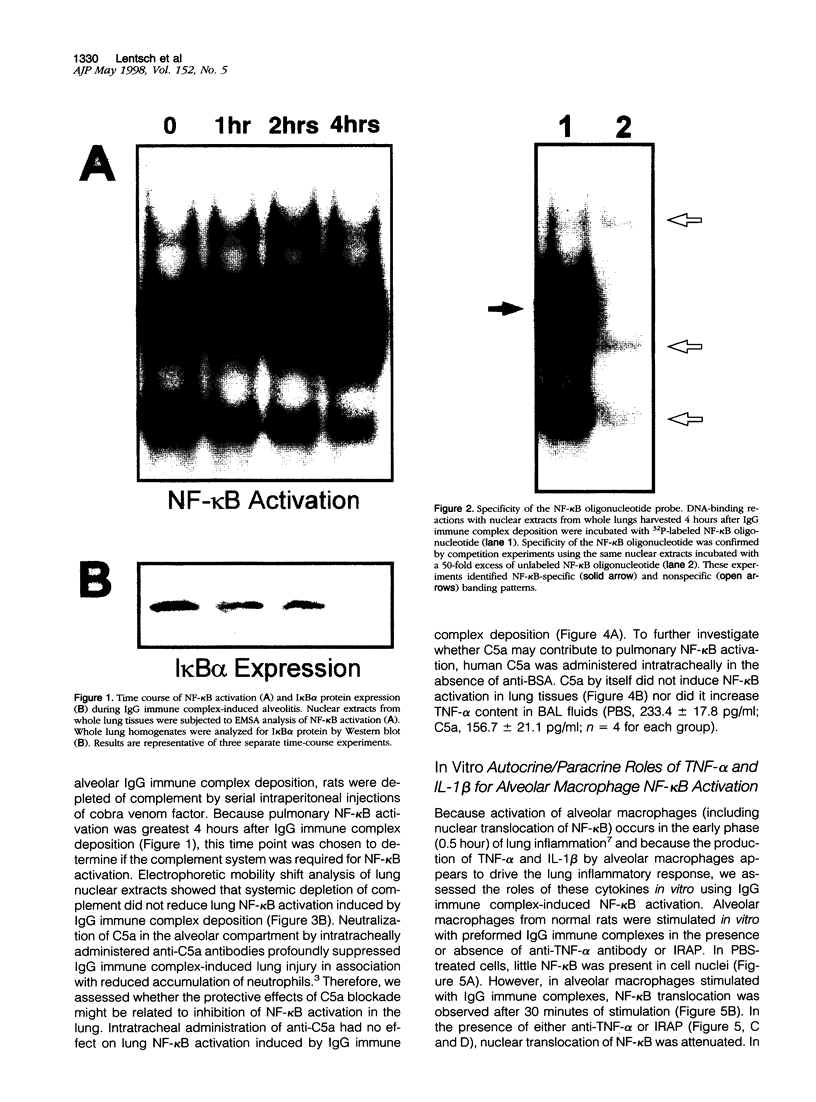
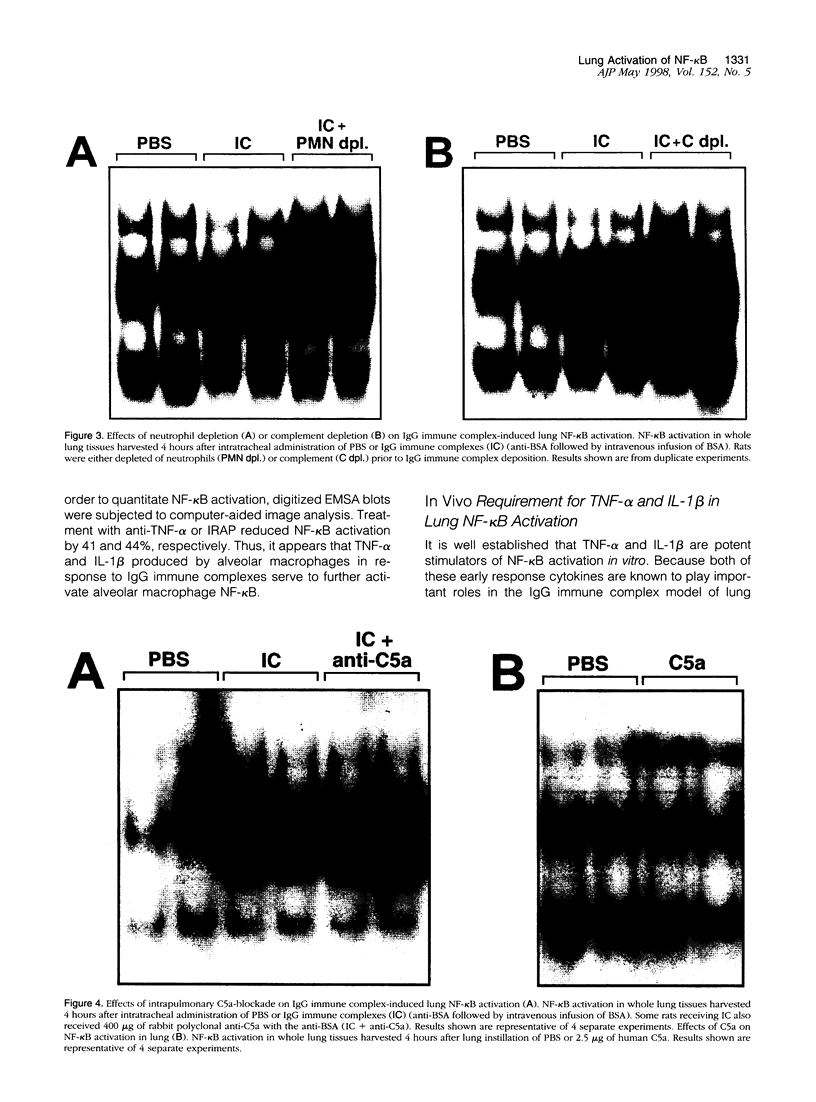
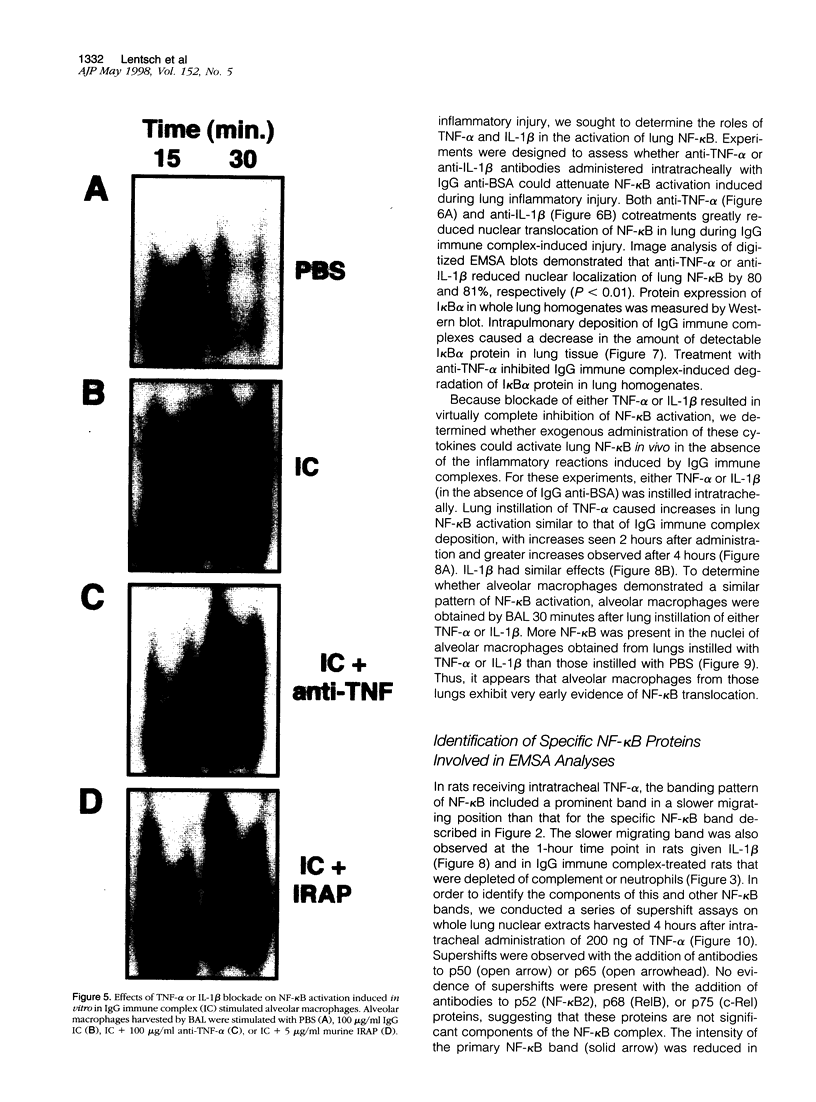
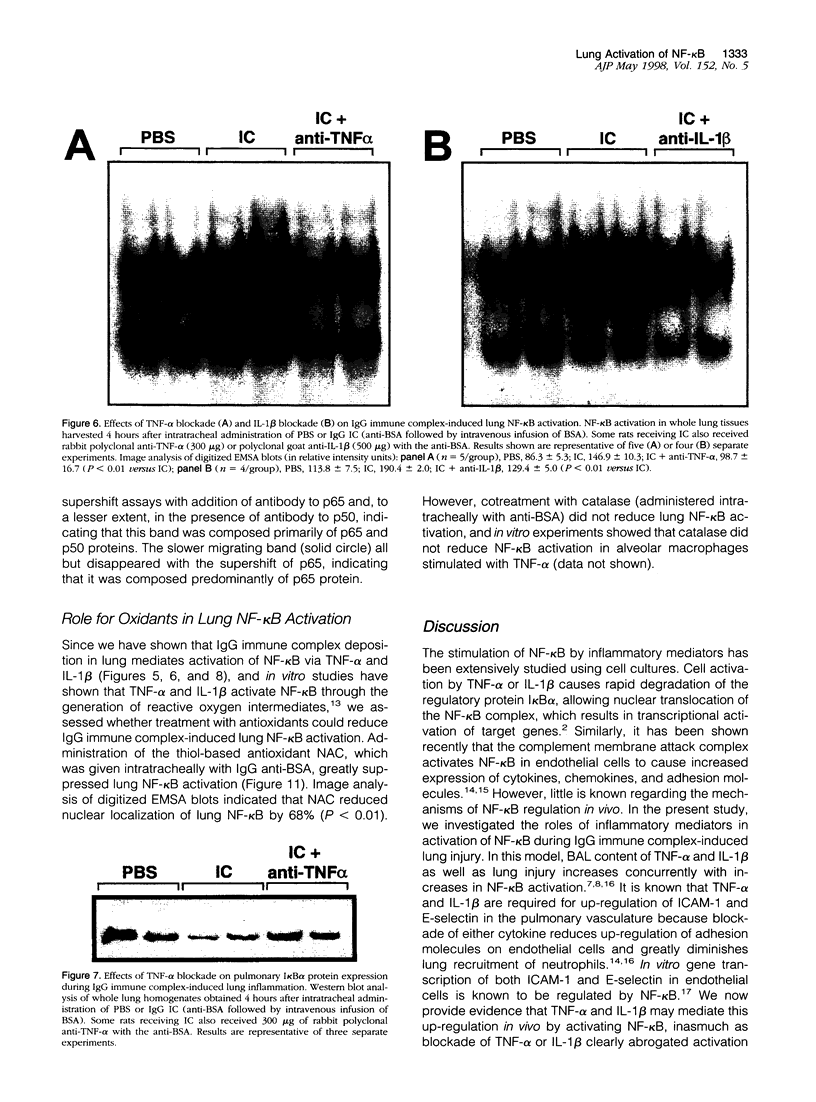
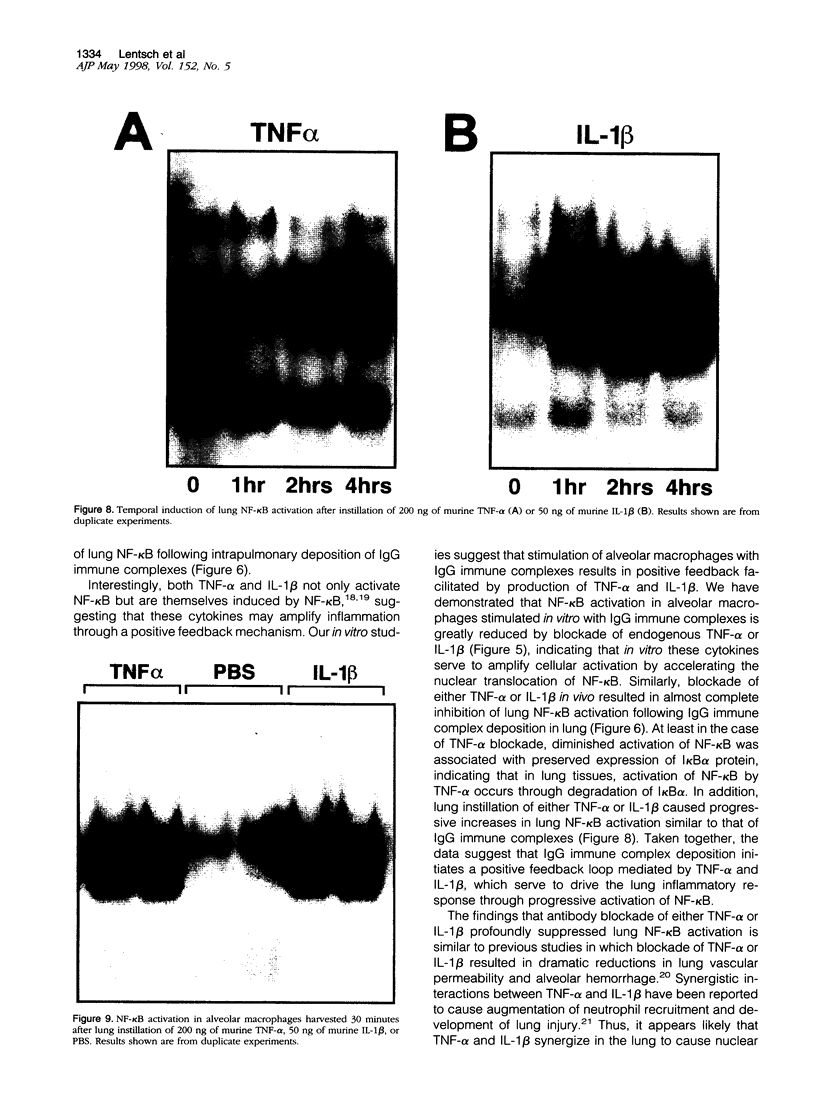
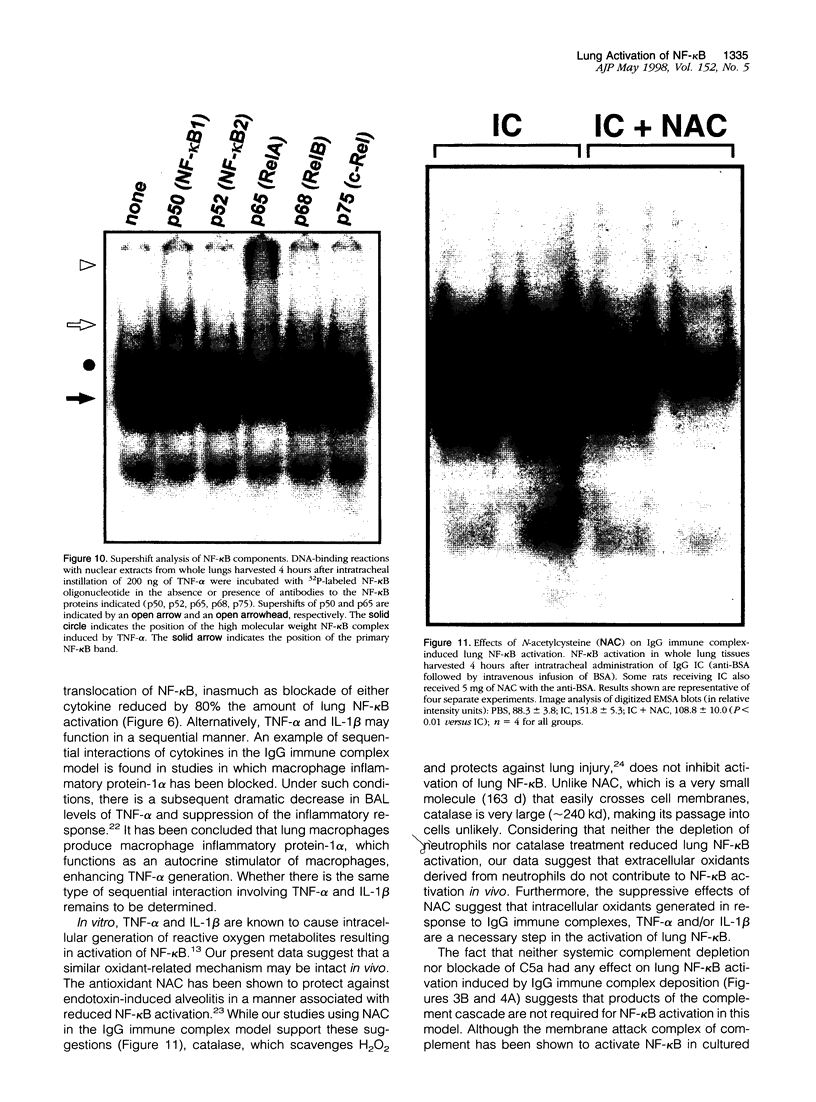
The development of acute lung inflammatory injury induced by alveolar deposition of IgG immune complexes in rats requires increased production of the proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) as well as the complement activation product, C5a. Transcription of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta genes are known to be regulated by the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB). During IgG immune complex-induced lung inflammation, NF-kappaB has been shown to be activated in both alveolar macrophages and whole lung tissues. In the current studies we sought to determine whether TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, the complement system and oxidants contribute to the activation of NF-kappaB in the lung. Electrophoretic mobility shift analysis of nuclear extracts from whole lung tissues demonstrated that NF-kappaB activation induced by the presence of IgG immune complexes occurred independently of the complement system and neutrophils. Intrapulmonary instillation of TNF-alpha or IL-1beta into normal lung induced NF-kappaB, whereas C5a was incapable of causing NF-kappaB activation. In alveolar macrophages stimulated in vitro with IgG immune complexes, NF-kappaB activation was greatly attenuated in the presence of antibodies to TNF-alpha or IL-1beta. Similarly, in vivo blockade of TNF-alpha or IL-1beta suppressed lung NF-kappaB activation during IgG immune complex-induced lung injury. N-acetylcysteine, but not catalase, suppressed activation of lung NF-kappaB. These data suggest that TNF-alpha and IL-1beta function in an autocrine or paracrine manner to amplify the lung inflammatory response through activation of NF-kappaB. Oxidants not derived from neutrophils also appear to play a role in this process, whereas complement activation products are not involved in this phenomenon.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin A. S., Jr The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. S., Blackwell T. R., Holden E. P., Christman B. W., Christman J. W. In vivo antioxidant treatment suppresses nuclear factor-kappa B activation and neutrophilic lung inflammation. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 15;157(4):1630–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Read M. A., Neish A. S., Whitley M. Z., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J. 1995 Jul;9(10):899–909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deryckere F., Gannon F. A one-hour minipreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from animal tissues. Biotechniques. 1994 Mar;16(3):405–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. H., Ward P. A. The phlogistic role of C3 leukotactic fragments in myocardial infarcts of rats. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):885–900. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Marois J., Garoufalis J., D'Addario M., Roulston A., Kwan I., Pepin N., Lacoste J., Nguyen H., Bensi G. Characterization of a functional NF-kappa B site in the human interleukin 1 beta promoter: evidence for a positive autoregulatory loop. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6231–6240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Role of oxygen metabolites in immune complex injury of lung. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2365–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgore K. S., Schmid E., Shanley T. P., Flory C. M., Maheswari V., Tramontini N. L., Cohen H., Ward P. A., Friedl H. P., Warren J. S. Sublytic concentrations of the membrane attack complex of complement induce endothelial interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 through nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Am J Pathol. 1997 Jun;150(6):2019–2031. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgore K. S., Shen J. P., Miller B. F., Ward P. A., Warren J. S. Enhancement by the complement membrane attack complex of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced endothelial cell expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 1;155(3):1434–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentsch A. B., Shanley T. P., Sarma V., Ward P. A. In vivo suppression of NF-kappa B and preservation of I kappa B alpha by interleukin-10 and interleukin-13. J Clin Invest. 1997 Nov 15;100(10):2443–2448. doi: 10.1172/JCI119786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Schmid E., Beck-Schimmer B., Till G. O., Friedl H. P., Brauer R. B., Hugli T. E., Miyasaka M., Warner R. L., Johnson K. J. Requirement and role of C5a in acute lung inflammatory injury in rats. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jul 15;98(2):503–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI118818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Vaporciyan A. A., Miyasaka M., Tamatani T., Ward P. A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha regulates in vivo intrapulmonary expression of ICAM-1. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1739–1749. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Varani J., Dame M. K., Lane C. L., Smith C. W., Anderson D. C., Ward P. A. Role of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) in neutrophil-mediated lung injury in rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1396–1406. doi: 10.1172/JCI115446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Ward P. A. Immune complex-induced lung and dermal vascular injury. Differing requirements for tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):331–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Ernst M. K. In vivo control of NF-kappa B activation by I kappa B alpha. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4685–4695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Albermann K., Baeuerle P. A. Nuclear factor kappa B: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun. 1992;17(4):221–237. doi: 10.3109/10715769209079515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanley T. P., Schmal H., Friedl H. P., Jones M. L., Ward P. A. Role of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1 alpha) in acute lung injury in rats. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4793–4802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S. Intrapulmonary interleukin 1 mediates acute immune complex alveolitis in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):604–610. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91608-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S., Yabroff K. R., Remick D. G., Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Kunkel R. G., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Tumor necrosis factor participates in the pathogenesis of acute immune complex alveolitis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1873–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI114374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselius L. J., Smirnov I. M., O'Brien-Ladner A. R., Nelson M. E. Synergism of intratracheally administered tumor necrosis factor with interleukin-1 in the induction of lung edema in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1995 May;125(5):618–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]