Abstract
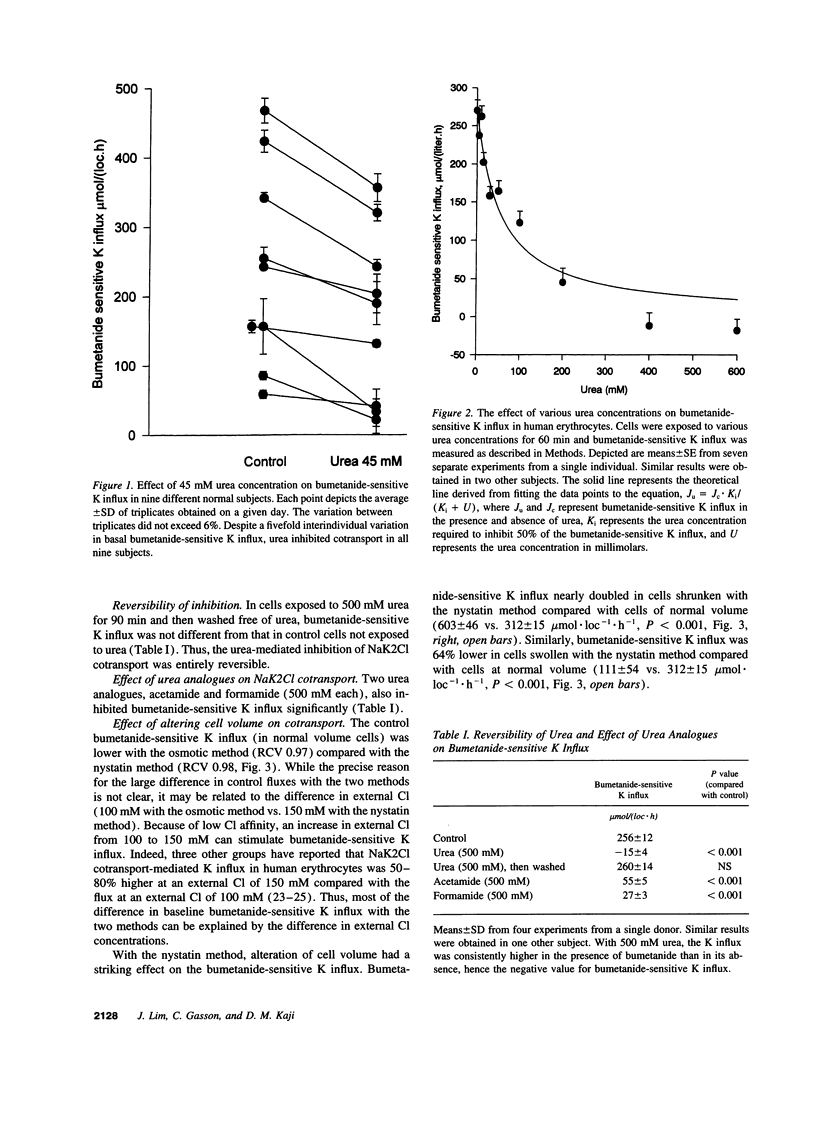
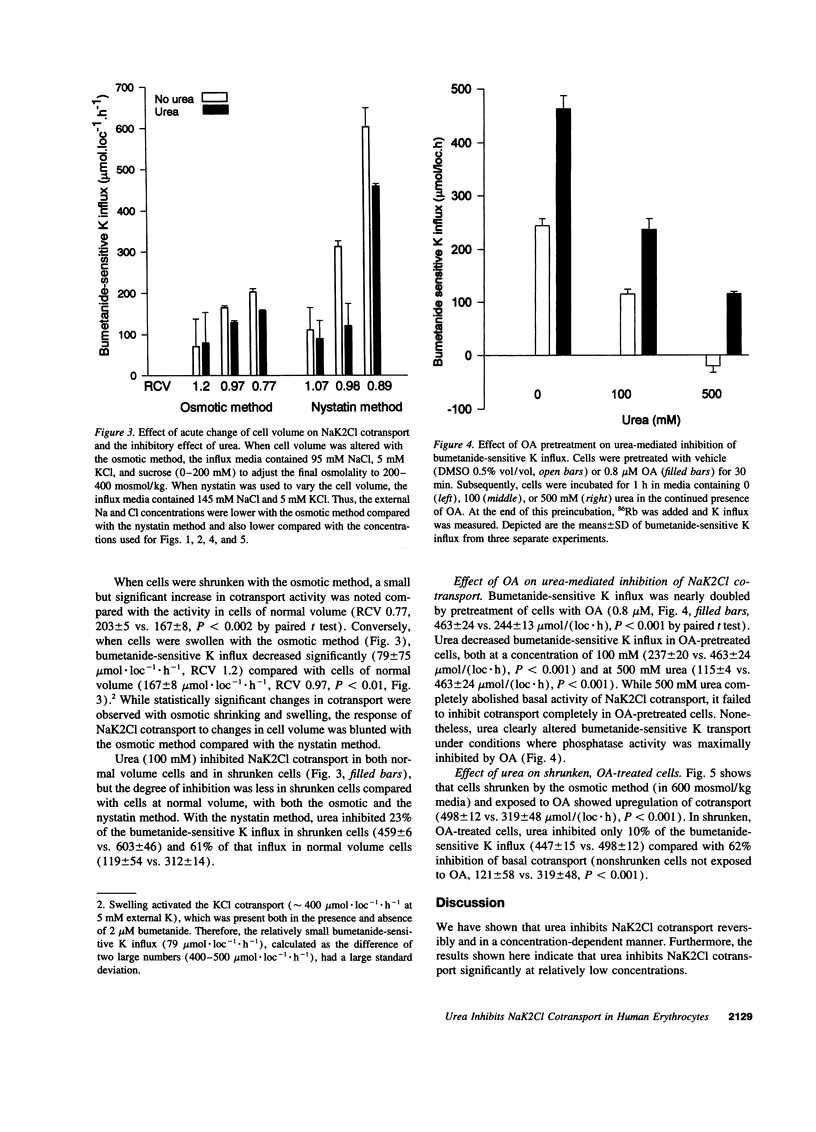
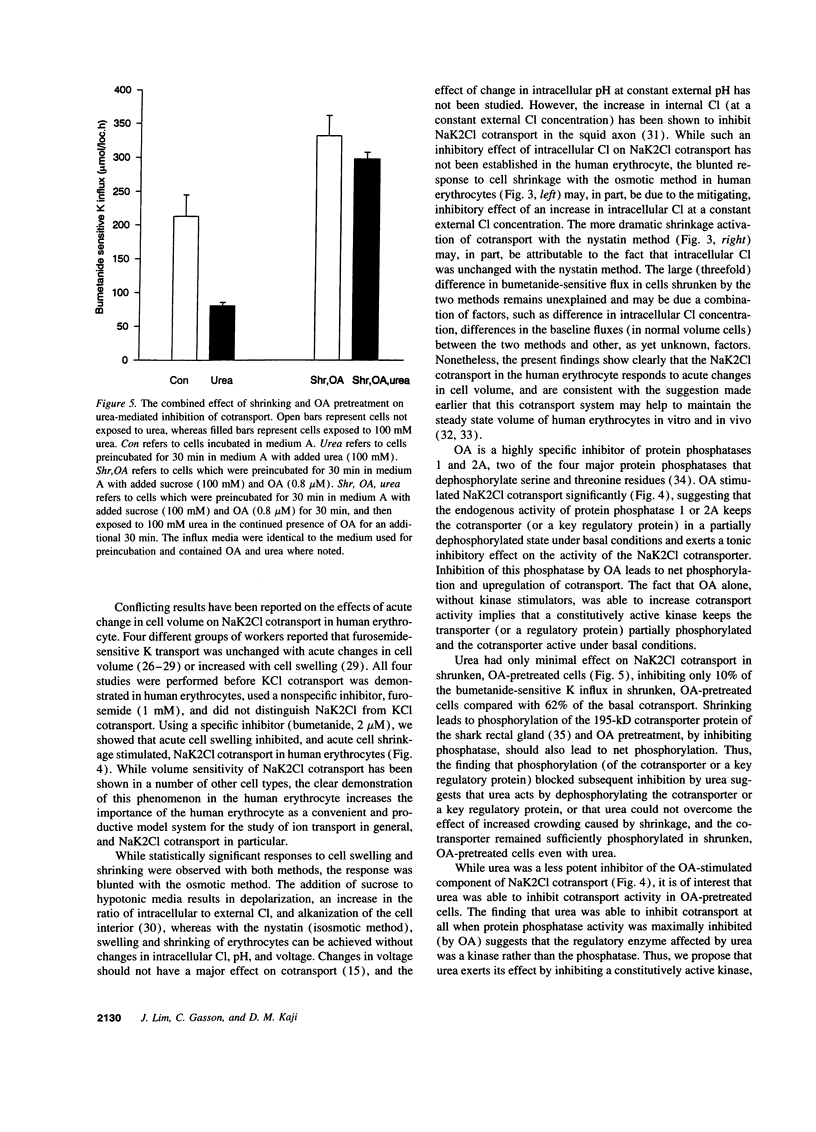
We examined the effect of urea on NaK2Cl cotransport in human erythrocytes. In erythrocytes from nine normal subjects, the addition of 45 mM urea, a concentration commonly encountered in uremic subjects, inhibited NaK2Cl cotransport by 33 +/- 7%. Urea inhibited NaK2Cl cotransport reversibly, and in a concentration-dependent fashion with half-maximal inhibition at 63 +/- 10 mM. Acute cell shrinkage increased, and acute cell swelling decreased NaK2Cl cotransport in human erythrocytes. Okadaic acid (OA), a specific inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A, increased NaK2Cl cotransport by nearly 80%, suggesting an important role for these phosphatases in the regulation of NaK2Cl cotransport. Urea inhibited bumetanide-sensitive K influx even when protein phosphatases were inhibited with OA, suggesting that urea acted by inhibiting a kinase. In cells subjected to shrinking and OA pretreatment, maneuvers expected to increase the net phosphorylation, urea inhibited cotransport only minimally, suggesting that urea acted by causing a net dephosphorylation of the cotransport protein, or some key regulatory protein. The finding that concentrations of urea found in uremic subjects inhibited NaK2Cl cotransport, a widespread transport pathway with important physiological functions, suggests that urea is not only a marker for accumulation of other uremic toxins, but may be a significant uremic toxin itself.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adragna N. C., Tosteson D. C. Effect of volume changes on ouabain-insensitive net outward cation movements in human red cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01872531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahm J. Urea permeability of human red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jul;82(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Altamirano A. A., Russell J. M. Osmotic stimulation of Na(+)-K(+)-Cl- cotransport in squid giant axon is [Cl-]i dependent. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):C749–C753. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.4.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. T., Kahn T., Kaji D. M. Mechanism of alteration of sodium potassium pump of erythrocytes from patients with chronic renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1811–1820. doi: 10.1172/JCI111600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R. Influence of loop diuretics and anions on passive potassium influx into human red cells. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:61–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry D. B., Tuck M. L., Brickman A. S., Yanagawa N., Lee D. B. Sodium transport in red blood cells from dialyzed uremic patients. Kidney Int. 1986 Jun;29(6):1197–1202. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhm J., Göbel B. O. Role of the furosemide-sensitive Na+/K+ transport system in determining the steady-state Na+ and K+ content and volume of human erythrocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF01870572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B. Effects of urea on K-Cl cotransport in sheep red blood cells: evidence for two signals of swelling. Am J Physiol. 1995 Apr;268(4 Pt 1):C1026–C1032. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.4.C1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Ellory J. C. Stimulation of the sodium-potassium pump by trypsin in low potassium type erythrocytes of goats. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:25–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Stewart G. W., Ellory J. C. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman J. C., Hoffman J. F. Ionic and osmotic equilibria of human red blood cells treated with nystatin. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Aug;74(2):157–185. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROLLMAN E. F., GROLLMAN A. Toxicity of urea and its role in the pathogenesis of uremia. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):749–754. doi: 10.1172/JCI103855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Schmidt W. F., 3rd, McManus T. J. Catecholamine-stimulated ion transport in duck red cells. Gradient effects in electrically neutral [Na + K + 2Cl] Co-transport. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jul;80(1):125–147. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. The Na-K-Cl cotransporters. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):C869–C885. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.4.C869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Hagge W. W., Wagoner R. D., Dinapoli R. P., Rosevear J. W. Effects of urea loading in patients with far-advanced renal failure. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Jan;47(1):21–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji D. M., Gasson C. Urea activation of K-Cl transport in human erythrocytes. Am J Physiol. 1995 Apr;268(4 Pt 1):C1018–C1025. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.4.C1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji D., Kahn T. Kinetics of Cl-dependent K influx in human erythrocytes with and without external Na: effect of NEM. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 1):C490–C496. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.5.C490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji D., Thomas K. Na+-K+ pump in chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 2):F785–F793. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.5.F785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji D. Volume-sensitive K transport in human erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Dec;88(6):719–738. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.6.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kracke G. R., Dunham P. B. Effect of membrane potential on furosemide-inhibitable sodium influxes in human red blood cells. J Membr Biol. 1987;98(2):117–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01872124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauf P. K., Perkins C. M., Adragna N. C. Cell volume and metabolic dependence of NEM-activated K+-Cl- flux in human red blood cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):C124–C128. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.1.C124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytle C., Forbush B., 3rd The Na-K-Cl cotransport protein of shark rectal gland. II. Regulation by direct phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25438–25443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macey R. I. Transport of water and urea in red blood cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C195–C203. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mairbäurl H., Hoffman J. F. Internal magnesium, 2,3-diphosphoglycerate, and the regulation of the steady-state volume of human red blood cells by the Na/K/2Cl cotransport system. J Gen Physiol. 1992 May;99(5):721–746. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.5.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton A. P., Colclasure G. C., Parker J. C. Model for the role of macromolecular crowding in regulation of cellular volume. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10504–10506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill W. C., Mikkelsen R. B. Furosemide-sensitive Na+ and K+ transport and human erythrocyte volume. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 26;896(2):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C. In defense of cell volume? Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):C1191–C1200. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.5.C1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C. Urea alters set point volume for K-Cl cotransport, Na-H exchange, and Ca-Na exchange in dog red blood cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):C447–C452. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.2.C447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAJAGOPALAN K. V., FRIDOVICH I., HANDLER P. Competitive inhibition of enzyme activity by urea. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey P. H., Clark M. E., Hand S. C., Bowlus R. D., Somero G. N. Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1214–1222. doi: 10.1126/science.7112124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Harrison B. Macromolecular crowding increases binding of DNA polymerase to DNA: an adaptive effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1871–1875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


