Abstract
LIN-44/Wnt and LIN-17/Frizzled (Fz) function in a planar cell polarity (PCP)-like pathway to regulate the asymmetric B cell division in C. elegans. We observed asymmetric localization of LIN-17/Frizzled (Fz) and MIG-5/Dishevelled (Dsh) during the B cell division. LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized within the B cell prior to and after the B cell division and correlated with B cell polarity. Asymmetric localization of LIN-17::GFP was dependent upon LIN-44/Wnt and MIG-5/Dsh function. The LIN-17 transmembrane domain and a portion of the cysteine rich domain (CRD) was required for LIN-17 function and asymmetric distribution to the B cell daughters, while the conserved KTXXXW motif was only required for function. MIG-5::GFP was also asymmetrically localized within the B cell prior to and after the B cell division in a LIN-17 and LIN-44 dependent manner. Functions of the MIG-5 DEP, PDZ and DIX domains were also conserved. Thus, a novel PCP-like pathway, in which LIN-17 and MIG-5 are asymmetrically localized, is involved in the regulation of B cell polarity.
Keywords: LIN-17, MIG-5, asymmetric localization, Frizzled, Dishevelled, C. elegans, PCP
Introduction
Conserved planar cell polarity (PCP) pathways regulate the orientation of body surface hairs and cell migrations in organisms ranging from Drosophila to vertebrates (Tree et al., 2002; Veeman et al., 2003; Klein and Mlodzik, 2005). PCP pathways include six conserved core proteins that are asymmetrically localized within individual cells. PCP signaling begins with the co-localization of the core proteins within the cortex. Subsequently, specific proteins are transported to the proximal or distal cortex of individual cells in response to PCP signals (Adler, 2002; Mlodzik, 2002; Strutt, 2003). Fz and Dsh accumulate at the distal cortex, and Strabismus and Prickle accumulate at the proximal cortex, while Flamingo and Diego accumulate at both ends of individual cells in a co-dependent manner. Fz and Dsh play major roles, while the other four proteins appear to be required for the asymmetric localization and activation of Fz and Dsh (Adler, 2002; Mlodzik, 2002; Strutt, 2003). In C. elegans, the male specific blast cell B divides asymmetrically to generate a large anterior and a small posterior daughter cell which take on different cell fates (Herman and Horvitz, 1994). A novel Wnt/PCP-like pathway appears to regulate this asymmetric cell division (Wu and Herman, 2006). Asymmetric localization of MOM-5/Fz and cortical localization of DSH-2 have also been reported during C. elegans embryogenesis (Park et al., 2004; Hawkins et al., 2005), suggesting that a PCP-like pathway with asymmetric localization of Fz, and possibly Dsh, similar to what has been seen in Drosophila, is conserved in C. elegans.
Wnt signaling pathways function in almost all animals in diverse developmental processes (Cadigan and Nusse, 1997; Veeman et al., 2003). At least three major conserved Wnt signaling pathways have been recognized: Wnt/β-catenin, Wnt/calcium and Wnt/PCP (Nelson and Nusse, 2004). All Wnt pathways contain Fz and Dsh, however the molecular mechanisms of Fz and Dsh function in either Wnt/β-catenin or Wnt/PCP pathways are not clear. Each Fz receptor family member has an extracellular cysteine-rich domain (CRD), a transmembrane domain with seven transmembrane segments separated by three extracellular and three intracellular loops and a carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic domain (Bhanot et al., 1996). Although the CRD can physically interact with Wnt ligand to initiate Wnt signaling in cell culture assays (Hsieh et al., 1999; Dann et al., 2001), dimerization of the CRD is sufficient to activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling (Carron et al., 2003). Wnt/β-catenin signal initiation also involves the interaction of Wnt ligands with the extracellular domains of Fz as well as the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5 and 6/LRP5 and LRP6 or Drosophila Arrow (Pinson and Brennan, et al, 2000; Tamai and Semenov, et al, 2000; Wehrli and Dougan, et al, 2000). However, there are no clear LRP5/LRP6/Arrow homologs in C. elegans that function in Wnt signaling (He, 2004).
The affinity between the Fz CRD and Wingless appears to determine Fz involvement in the Wnt/β-catenin or PCP pathway (Rulifson et al., 2000). However, the CRDs of DFz and DFz2 were recently shown not to be essential for Wingless transduction (Chen et al., 2004), suggesting that either the extracellular portion (EP) of the CRD-deleted Fz or Fz2 was still able to bind Wg and initiate signaling (Povelones and Nusse, 2005) or that the transmembrane domain might be sufficient for signal transduction. Mutational analysis indicated that several residues in the loops between the seven transmembrane segments also affected Wnt/β-catenin signal initiation (Cong et al., 2004). The length and similarity of the cytoplasmic domains among Fz members varies, but a conserved Lys-Thr-X-X-X-Trp (KTXXXW) motif is located two amino acids after the seventh transmembrane segment in most Fz receptors. The KTXXXW motif appears to be required for Wnt/β-catenin signal transduction as well as membrane localization and phosphorylation of Dsh (Umbhauer et al., 2000), suggesting that this motif also functions in PCP pathways.
Dsh proteins contain the conserved PDZ, DIX and DEP domains. Deletion experiments in Drosophila and mice showed that the DIX and PDZ domains are required for the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, while the DEP and PDZ domains are required for PCP (Axelrod et al., 1998; Boutros et al., 1998; Boutros and Mlodzik, 1999). The Dsh PDZ domain was shown to bind to the mFz KTXXXW motif in vitro (Wong et al., 2003). However, the DEP but not the PDZ domain has been shown to be required for Dsh membrane localization in Drosophila (Rothbacher et al., 2000). Current evidence suggests that the KTXXXW motif might interact with Dsh to regulate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (Boutros and Mlodzik, 1999; Li et al., 1999) and might function to recruit Dsh to the plasma membrane in the PCP pathway.
Here we examine the changes in localization of LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh during the asymmetric B cell division. We demonstrate that the asymmetric localizations of these proteins correlated with the asymmetric B cell division and have examined the functions of conserved domains within LIN-17 and MIG-5 for their roles in asymmetric protein localization and in promoting cell polarity.
Materials and Methods
General methods and strains
Nematodes were cultured and manipulated by standard techniques (Brenner, 1974). N2 was used as the wild-type strain. The following mutations and transgenic lines were used:
Linkage Group I (LGI): lin-17(n671) and lin-44(n1792); LGII: mig-5(ok280), mhIs009 (Wu and Herman, 2006); LGIII: unc-119(e2498); LGV: him-5(e1490).
Strains were obtained from the C. elegans Genetics Center (University of Minnesota), or from C. elegans Gene Knockout Consortium.
LIN-17 and MIG-5 expression constructs
The LIN-17 CRD spans residues 19 to 204. Four constructs that encoded different lengths of the LIN-17 CRD each fused to GFP were made: CRDΔ1 removed residues 19 to 204, CRDΔ2 removed residues 40 to 204, CRDΔ3 removed residues 19 to 174 and CRDΔ4 removed residues 40 to 174 (Table 1). mhIs9 contains the lin-17::gfp fusion (Wu and Herman, 2006).
Table 1.
Function and localization of LIN-17 variants.
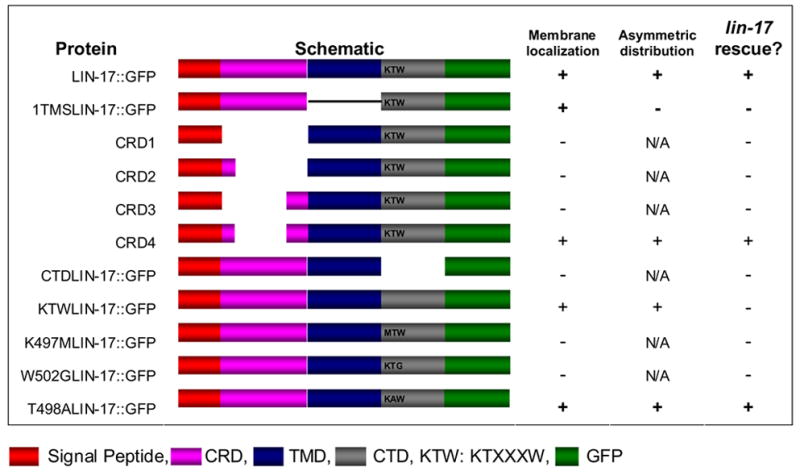
LIN-17 domains are illustrated by different colors as indicated below the table. Schematic structures of LIN-17 variants are shown. Membrane localization of each variants was recorded as +, if more than 50% worms displayed LIN-17::GFP membrane localization to the B cell (n>35, except CRDΔ1=19, CRDΔ3=14 and ΔCTD=16). Asymmetric distribution of LIN-17::GFP was recorded as +, if more than 50% worms displayed LIN-17::GFP asymmetric distribution to the B daughters. lin-17 rescue (B cell and T cell polarity) was recorded as +, if the percentage of normal B cell polarity worms that expressed the protein was significantly higher than lin-17 males as determined by T test (p < 0.05). Asymmetric distribution for variants that were not membrane localized is indicated as N/A (not applicable) as membrane localization is likely to be a prerequisite for asymmetric distribution.
We replaced the transmembrane domain of LIN-17 with the transmembrane segment of DAF-1 to generate 1TMSlin-17::gfp, using fragments of lin-17::gfp and synthetic fragment (Georgi et al., 1990; Inoue et al., 2004) (sequence available upon request).
Several constructs with different lengths of the LIN-17 CTD were made. ΔCTDlin-17::gfp encodes a LIN-17::GFP fusion protein in which the residues after the seventh transmembrane domain beginning at residue 496 were deleted. ΔKTWlin-17::gfp encodes a mutated LIN-17::GFP, in which the KTVHAW residues at positions 497 to 502 were deleted and the tripeptide SGR was inserted due to restriction sites included in the construction process. In order to investigate the function of the LIN-17 KTXXXW motif, we performed site-directed mutagenesis (Stratagene) to generate constructs K497Mlin-17::gfp, T498Alin-17::gfp and W502Glin-17::gfp.
In addition to the functional MIG-5::GFP constructs (Wu and Herman, 2006; Walston et al., 2006), another three MIG-5 deletion constructs were made. ΔDEPmig-5::gfp fused GFP to the carboxyl terminus of the first 357 amino acids of MIG-5, deleting the DEP domain. ΔPDZmig-5::gfp deleted amino acid residues 219 to 318 and fused GFP to the carboxyl terminus of the truncated MIG-5 protein. ΔDIXmig-5::gfp deleted amino acid residues 11 to 101.
All constructs were sequenced before transformation. The lin-17::gfp and mig-5::gfp constructs were microinjected at a concentration of 10 ng/μl and 5 ng/μl respectively, with the co-injection marker pPDMM0166 [unc-119 (+)] (Maduro and Pilgrim, 1995) at a concentration of 40 ng/μl, into unc-119 (e2498); him-5 (e1490) hermaphrodites, or with str-1::gfp at a concentration of 100 ng/μl, into him-5 (e1490) hermaphrodites. Since the lin-17(n671) mutation introduces a stop codon before the seventh LIN-17 transmembrane segment (Sawa et al., 1996) and causes B cell polarity defects in 89% of mutant males (Herman and Horvitz, 1994), we used it as the genetic background to examine the function and localization of all the lin-17::gfp constructs. The function of each protein was tested at least in two independent transgenic lines.
Microscopy and cell lineage analysis
Living transgenic animals were observed using a Zeiss Axioplan microscope equipped with Nomarski optics and epi-fluorescence or a Zeiss Laser Scanning Confocal microscope. Cell nomenclature and cell lineage analysis were as previously described (Sulston and Horvitz, 1977). N.x. refers to both daughters of cell N. Fates of the T and B cell descendants were determined by nuclear morphologies and size; orientation to the body axis (Herman and Horvitz, 1994) was used as an indicator of T and B cell polarities, as previously described (Herman et al., 1995). Phasmid dye-filling was also used as an indicator of T cell polarity (Herman and Horvitz, 1994).
Results
LIN-17/Fz is asymmetrically localized prior to and after the B cell division
During Drosophila eye development, asymmetric localization of Frizzled activity determines the R3 and R4 cell fates (Strutt, 2002). As B cell polarity in C. elegans males might be controlled by a PCP-like pathway and functional LIN-17::GFP protein was localized to the B cell membrane and rescued lin-17 mutants (Wu and Herman, 2006), we asked whether LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh were also asymmetrically localized within the B cell and its daughters. We examined the localization of LIN-17::GFP within the B cell and the distribution of LIN-17::GFP between the B.a and B.p daughter cells. Asymmetric localization occurs when the amount of protein, as detected by GFP intensity, varies within a cell, while asymmetric distribution occurs when the levels of protein as detected by relative GFP intensity differ between the two daughters. Prior to division, LIN-17::GFP accumulated asymmetrically to the anterior cortex and cytoplasm of the B cell in 81% of males (n=31) (Fig. 1A). After division, LIN-17::GFP was symmetrically localized within the B.a cell cortex, but was asymmetrically localized within the B.p cell in 76% (n=33) of males, with the anterior membrane and cytoplasm displaying a higher level of LIN-17::GFP than the posterior (Fig. 1B). The asymmetric localization of LIN-17::GFP to the anterior cortex and cytoplasm of the B and B.p cells was confirmed by 1μm Z sections through the B cell (Fig. 1D1–D6 and data not shown).
Figure 1. LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized within the B cell in lin-17 males prior to and after cell division.
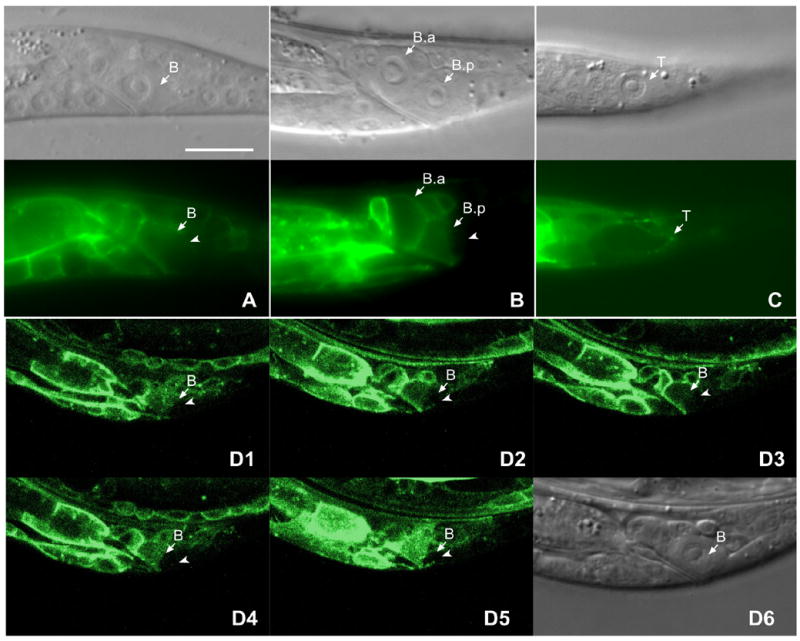
Panels (A–C) show the DIC image above and corresponding fluorescent image below. LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized within the B cell prior to (A) and after division (B). The posterior cortex and cytoplasm (arrow) of the B cell (A) or the B.p cell (B) displayed lower level of GFP intensity than the anterior of that cell. (C) LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized to the T cell and accumulated at the posterior cortex (arrowhead) of T cell. (D1–D5) show fluorescence confocal images of 1 μm Z sections through the B cell spatially sectioned from top to bottom. (D6) is the DIC image of B cell shown in D1–D5. Bar equals 10 μm in all panels.
The asymmetric T cell division is also controlled by LIN-44 and LIN-17, but is controlled differently than is the asymmetric B cell division (Wu and Herman, 2006). LIN-17::GFP was also asymmetrically localized within the T cell, however it accumulated to the posterior cortex of the T cell prior to division in 45% of animals (n=34) (Fig. 1C), while the rest were symmetrically localized, similar to the recent observations of Goldstein et al. 2006. The asymmetric localization of LIN-17 during B and T asymmetric cell divisions suggests that a mechanism involving asymmetric Fz localization, similar to Fz function during Drosophila PCP, also functions in C. elegans.
Asymmetric localization of LIN-17/Fz is dependent upon MIG-5/Dsh and LIN-44/Wnt
LIN-17::GFP was localized symmetrically in 81% of mig-5 males (n=19) before the B cell division (Fig. 2A) and in 80% (n=31) after division (Fig. 2B). The dependence of LIN-17::GFP asymmetric localization on MIG-5 is similar to the co-dependence of the asymmetric localization of the six Drosophila PCP core proteins (Strutt, 2003; Strutt, 2002). In contrast to the PCP pathways in the Drosophila wing and eye, but similar to Wnt involvement in PCP pathways that regulate cell migration during vertebrate gastrulation (Heisenberg et al., 2000; Tada et al., 2002; Weidinger and Moon, 2003), LIN-44/Wnt controls the asymmetric B cell division (Herman and Horvitz, 1994; Herman et al., 1995). LIN-17::GFP was localized symmetrically in 73% (n=30) of lin-44 males before the B cell division (Fig. 2C) and was symmetrically localized in 81% (n=52) after division of lin-44 males (Fig. 2D, E). However, while LIN-17::GFP was symmetrically localized within the B.a and B.p membranes, distribution of LIN-17::GFP to the B.a and B.p cells was reversed in 23% of lin-44 males, with the B.p cell membrane having a higher level than B.a (Fig. 2D), was equally distributed in 58% (Fig. 2E) and was normally distributed in 19% (n=52) of lin-44 males. The requirement of MIG-5 for LIN-17::GFP asymmetric localization is consistent with the asymmetric localization of Fz in Drosophila PCP, while the requirement of LIN-44/Wnt, together with Wnt signaling providing a positional cue for asymmetric localization of Fz in the T cell (Goldstein, 2006) and PLM neurons (Hilliard and Bargmann 2006), may indicate that a different mechanism that might be similar to that which functions in vertebrates regulates the asymmetric localization of LIN-17/Fz.
Figure 2. LIN-44 and MIG-5 were required for LIN-17::GFP asymmetric localization.
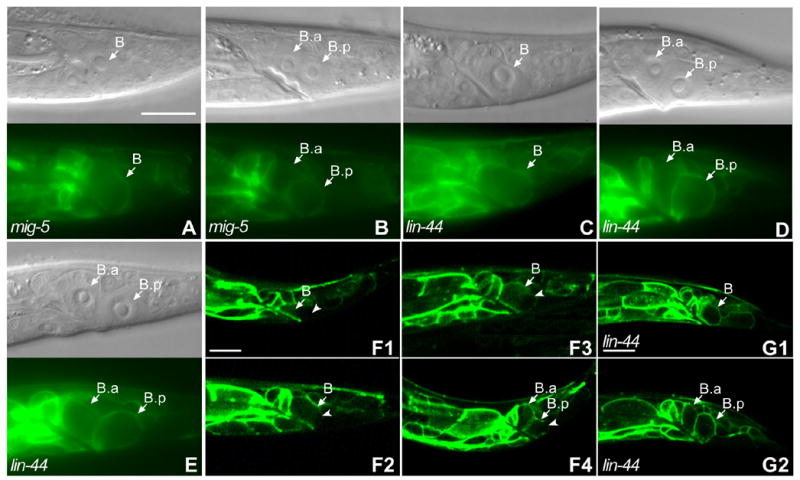
Panels (A–E) show the DIC image above and corresponding fluorescent image below. LIN-17::GFP was symmetrically localized within the B cell in mig-5 males (A) and lin-44 males (C), (compare to Fig. 1A). After the B cell division, the asymmetric localization of LIN-17::GFP was lost in mig-5 (B) and either reversed (D) or lost in lin-44 males (E) (compare to Fig. 1B). (F1-F4) localization of LIN-17::GFP at different time points during the B cell division: five hours after hatching (F1), before the B cell was about to divide (F2), during the B cell division (F3) and after the B cell division (F4). Arrowheads in F1-F4 point to the cell membrane or cortex that displayed lower GFP levels in the B or B.p cells. Bar in (A) equals 10 μm for (A–E) and bars in (F1) and (G1) equal 10 μm for (F1–F4) and (G1–G2).
Asymmetric localization of LIN-17::GFP during the B cell division resulted in its asymmetric distribution to the B daughters
To address whether asymmetric distribution of LIN-17 during the B cell division correlated with B daughter cell fates, we examined LIN-17::GFP localization during the B cell division in 16 live males. Five hours after hatching, LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized to the anterior B cell membrane and cytoplasm (Fig. 2F1). However, high levels of LIN-17::GFP in cells neighboring B sometimes made it difficult to determine whether LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized to the anterior membrane of the B cell itself or in the membrane of adjacent cells (Fig. 2F1). As the worms grew, LIN-17::GFP slowly extended from the anterior membrane of B toward the posterior in all males (Fig. 2F2) and eventually encircled the B cell by the time it was about to divide, although the level of LIN-17::GFP in the posterior membrane was still lower than the other parts of the B cell membrane (Fig. 2F3). After division, LIN-17::GFP was symmetrically localized within both the new B.a and B.p cell membranes (data not shown). However the B.a cell membrane had a higher level of LIN-17::GFP than the B.p membrane (data not shown). During the next twenty minutes, LIN-17::GFP was dynamically redistributed within the B.p cell resulting in its accumulation at the anterior membrane and its reduction at the posterior membrane (Fig. 2F4). LIN-17::GFP asymmetric localization in the B.p cell was maintained until B.a was about to divide. LIN-17::GFP remained uniform in the B.a cell membrane during this process.
We also observed LIN-17::GFP localization during the B cell division in six live lin-44 males. After five hours of post-embryonic development, two worms displayed normal asymmetric LIN-17::GFP localization, however in the other four lin-44 males LIN-17::GFP localized to the posterior B cell membrane (Fig 2G1). Since LIN-17::GFP was strongly expressed in the neighboring anterior cells, it was difficult to determine whether LIN-17::GFP localization was reversed within the B cell in these four lin-44 males. As the worms grew, levels of LIN-17::GFP increased in the posterior, but in contrast to the normal pattern, there was no obvious asymmetric localization within the B cell. Similar to the majority of lin-44 males we observed (above), there was no obvious asymmetric distribution to the B daughter cells during and after B cell division in these four lin-44 animals (Fig. 2G2), although they displayed reversed polarity. However, due to the strong expression of LIN-17::GFP in the anterior neighboring cells, reverse distribution of LIN-17::GFP in lin-44 males is likely to be underestimated.
In summary, prior to division, LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized, such that the anterior membrane of B cell had a higher level of LIN-17::GFP than the posterior membrane. During the division, LIN-17::GFP underwent a dynamic redistribution, resulting in its asymmetric localization within the B.p cell. Asymmetric localization of LIN-17::GFP prior to the B cell division might be required for LIN-17::GFP asymmetric distribution to the B daughters. The loss or reversal of LIN-17::GFP asymmetric distribution in lin-44 males may indicate that LIN-44 binding to LIN-17/Fz is required for the asymmetric distribution.
Domain requirements for LIN-17 asymmetric localization and function
LIN-17 has 13 cysteine residues in the conserved CRD, while most of Fz proteins have ten. Since LIN-44/Wnt was required for LIN-17::GFP asymmetric localization, we hypothesized that LIN-44 interaction with LIN-17 via the CRD caused LIN-17 asymmetric localization. We made four constructs with different extents of CRD deletions. CRDΔ1 did not contain any cysteine residues in the EP, whereas CRDΔ2 and CRDΔ3, each contained two different cysteine residues in the EP. CRDΔ1, CRDΔ2 and CRDΔ3 were not localized to B cell membrane (data not shown) and failed to rescue the T or B cell polarity defects of lin-17 mutants (Table 1). CRDΔ4, contained four cysteine residues in the EP, localized to B cell membrane, although not as well as full length LIN-17 (Fig. 3A), and 90% (n=58) of lin-17 males in which GFP was localized to the B cell membrane displayed normal B cell polarity. Thus CRDΔ4 can rescue lin-17 mutants. To test whether this rescue was dependent upon lin-44 function we examined CRDΔ4 in a lin-17; lin-44 double mutant background. We observed that 47% (n=17) of lin-17 lin-44 males that contained CRDΔ4 displayed reversed polarity while 35% displayed a loss of polarity and 18% displayed normal polarity (Fig. 3B). By contrast, only 12% (n=43) of lin-17 lin-44 males that did not contain CRDΔ4 displayed reversed polarity, while 71% displayed a loss of polarity and 17% displayed normal polarity. Therefore the ability of CRDΔ4 to rescue lin-17 is dependent upon LIN-44 function, suggesting that the EP of CRDΔ4 can recruit LIN-44/Wnt to trigger signaling. CRDΔ4 was asymmetrically distributed to the B.a and B.p cells and 89% (n=47) of males that displayed asymmetric distribution displayed normal polarity. In summary, much of the CRD is dispensable for LIN-17 asymmetric localization and function as a shortened CRD domain is sufficient.
Figure 3. Localization of truncated LIN-17 proteins.
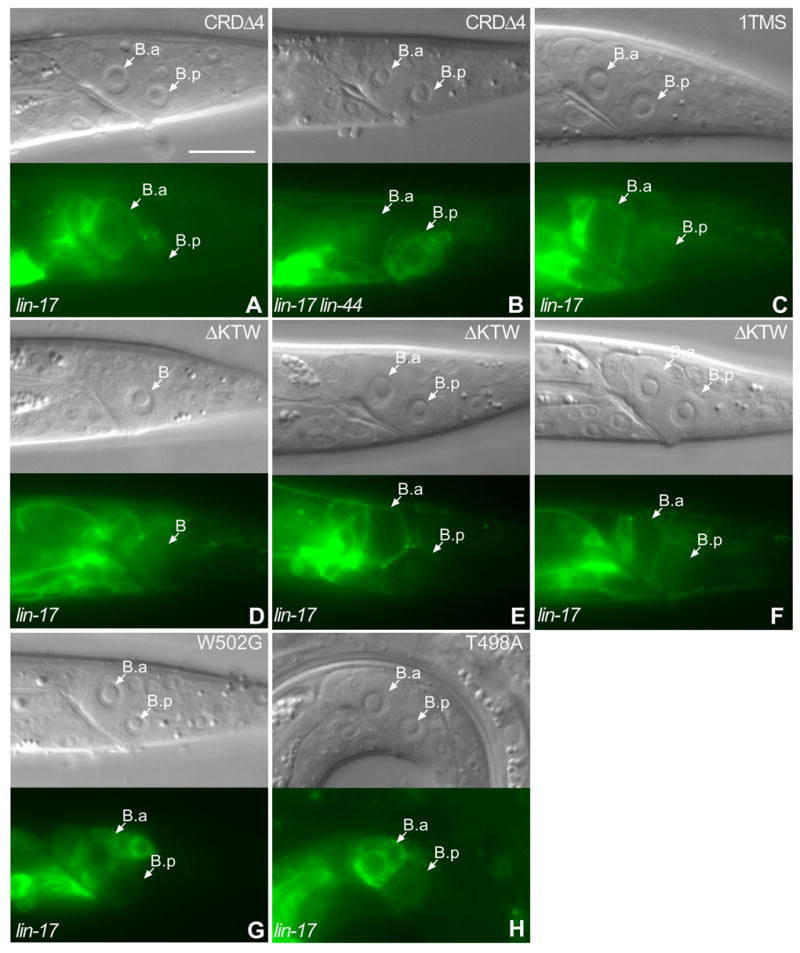
CRDΔ4 was localized to the B cell membrane, similar to LIN-17::GFP, but was also seen in the cytoplasm (A). CRDΔ4 asymmetric localization in the B daughters was reversed in lin-44 lin-17 males (B). 1TMSLIN-17::GFP was symmetrically localized in the membranes of the B daughters and failed to rescue lin-17 (C). ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized within the B cell (D) or the B.p cell (E and F) in lin-17 males, but failed to rescue B cell polarity (F). W502G LIN-17::GFP(G) and T498A LIN-17::GFP (H) were asymmetrically distributed to the B daughter cells in lin-17 males. Bar equals 10 μm in all panels.
Since LIN-44 is required for LIN-17 asymmetric localization and most of the CRD is not required, we hypothesized that LIN-44 might also interact with the extracellular loops between the LIN-17 transmembrane segments to regulate LIN-17 asymmetric localization and signal transduction, as is the case for rat Fz1 (Cong et al., 2004). The seven transmembrane segments of LIN-17 were replaced with the single transmembrane segment of DAF-1 to generate 1TMSLIN-17::GFP (Georgi et al., 1990; Inoue et al., 2004). 1TMSLIN-17::GFP localized to the B cell membrane, but failed to rescue the B cell polarity defect of lin-17 males as only 10% of the worms displayed normal polarity (n=77) (Fig. 3C and Table 1), similar to the 15% (n=68) of lin-17 males that displayed normal B cell polarity in the absence of the construct, which is consistent with the transmembrane domain fuction of rat Fz1 (Cong et al., 2004). Unexpectedly, 1TMSLIN-17::GFP was symmetrically localized to B daughter cells in 89% (n=71) of lin-17 males. These results indicate that the entire LIN-17 transmembrane domain is important for the asymmetric localization and function of LIN-17.
The conserved KTXXXW motif is located two residues after the transmembrane domain of many different Frizzled receptors, including LIN-17 (Umbhauer et al., 2000), and can physically interact with the Dsh PDZ domain in vitro (Wong et al., 2003). As MIG-5/Dsh is required for LIN-17 asymmetric localization, we asked whether the KTXXXW motif was also important for the asymmetric localization of LIN-17::GFP. A truncated protein that deleted the carboxyl terminal domain (CTD) including the KTXXXW motif, ΔCTDLIN-17::GFP, was not localized to the B cell membrane and failed to rescue lin-17 mutants, although it was localized to the membranes of other cells (Table 1 and data not shown). We deleted the KTXXXW motif to generate ΔKTXLIN-17::GFP, which was asymmetrically localized to the B cell membrane in a manner similar to LIN-17::GFP prior to and after division (Fig. 3D–F). However, asymmetric distribution of ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP did not strictly correlate with B cell polarity as only 45% (n=38) of animals that displayed asymmetric distribution to the B daughters had normal B cell polarity (Fig. 3E and F). Interestingly, ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP was localized in a manner similar to LIN-17::GFP in the T cell and rescued T cell polarity defects of lin-17 mutants as 71% (n=356) displayed normal polarity as determined by phasmid dye-filling. This indicates that KTXXXW motif is not absolutely required for LIN-17 asymmetric localization and that LIN-17 function differs in the B and T cells. Mutation of each of the three conserved residues in the KTXXXW motif affected membrane localization (Fig. 3G and H) and the function of LIN-17::GFP (Table 1). Specifically, the K497M and W502G mutant proteins rarely localized to the B cell membrane and failed to rescue the B cell polarity defect of lin-17 mutants (Table 1 and data not shown). The T498A mutant was localized to the B cell membrane in 81% of males (n=74) (Fig. 3H and data not shown) and 60% displayed normal polarity (n=60), which indicated that T498 played a lesser role than K497 and W502. It is curious that the K497M and W502G point mutants localized poorly to the membrane, while deletion of the entire KTXXXW motif did not affect membrane localization or asymmetric localization. One possible explanation for this difference could be that the KTXXXW motif is not involved in membrane localization and the mutations nonspecifically interfere with LIN-17 structure in such way that membrane localization is blocked. Despite the poor membrane localization of the K497M and W502G point mutants, when the mutant proteins were localized to the membrane, they were often asymmetrically localized, suggesting that the membrane localization defect may be non-specific. Another possibility is that the KTXXXW is involved in membrane localization and the ability of ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP to localize to the membrane could be due to the introduction of tripeptide SGR during the construction process. In summary, we conclude that the conserved residues of KTXXXW motif are required for LIN-17 function, but not for asymmetric localization.
MIG-5::GFP was asymmetrically localized to the B cell prior to and after cell division in a LIN-17 dependent manner
A functional mig-5::gfp fusion protein was expressed in the B cell and its daughters (Wu and Herman, 2006; Walston et al., 2006). Prior to the B cell division, MIG-5::GFP accumulated asymmetrically as puncta at the anterior cortex or membrane of the B cell in nine out of 13 males (Fig. 4A). This pattern was reminiscent of the unipolar membrane association of Dsh during PCP signal transduction (Axelrod, 2001). After the B cell division, MIG-5::GFP was also asymmetrically localized within the B daughters. 83% (n=46) of males displayed MIG-5::GFP accumulation or puncta at the posterior cortex of the B.a cell (Fig. 4B). 80% of males that displayed puncta at posterior cortex of the B.a cell also displayed MIG-5::GFP puncta at posterior cortex of B.p cell (Fig. 4B). MIG-5::GFP neither formed puncta nor associated with the plasma membrane in lin-17 males (n=13) (Fig. 4C). MIG-5::GFP was asymmetrically localized within the B cell and its daughters in lin-44 males, but the pattern was different than that observed in wild-type males. Prior to the B cell division, MIG-5::GFP accumulated in puncta at both anterior and posterior cortex of the B cell in 57% (n=28) of lin-44 males (Fig. 4D). After division, there were puncta at the anterior cortexes of both B.a and B.p cells in 63% (n=54) of lin-44 males (Fig. 4E), 29% (n=34) of which also displayed puncta at posterior ventral cortex of the B.p cell. Thus, in the absence of LIN-44/Wnt ligand, the asymmetric localization of MIG-5::GFP in the B cell or B daughters was often lost or reversed.
Figure 4. Formation of MIG-5::GFP puncta prior to and after the B cell division was dependent uponlin-17 but not lin-44.
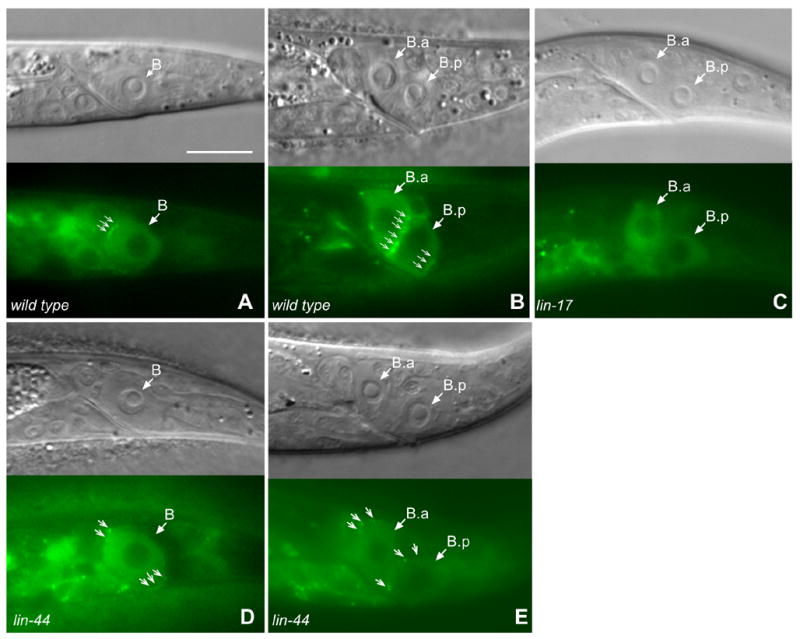
MIG-5::GFP accumulated at the anterior cortex of the B cell in wild-type males (A) and at the posterior cortex of B.a and B.p cells after division in wild type males (B) in a punctate pattern (small arrows). Posterior B.p puncta are slightly below the focal plane. MIG-5::GFP puncta were not observed in lin-17 males (C). In lin-44 males, prior to cell division, both anterior and posterior cortex of B cell displayed weak puncta (D) and after division, the anterior cortex of B.a and B.p cells displayed puncta (E). However, the MIG-5 puncta in lin-44 males were often mislocalized. Bar equals 10 μm in all panels.
The DIX, PDZ and DEP domains play different roles in MIG-5 asymmetric distribution and function
We have shown that MIG-5 was involved in the regulation of B cell polarity (Wu and Herman, 2006) and that the subcellular localization of MIG-5::GFP was regulated by LIN-17 and LIN-44 (Fig. 4). In order to examine whether a PCP-like pathway functions to regulate B cell polarity, we investigated the function of each MIG-5 domain in the regulation of B cell polarity. We made three constructs encoding truncated MIG-5::GFP proteins that deleted the conserved DEP, or DIX or PDZ domains. ΔDEPMIG-5::GFP was not localized to membrane and did not form puncta (n=13) (Fig. 5A, Table 2), suggesting that it did not bind to LIN-17/Fz receptor at the membrane. In other systems, Dsh puncta formation appears to be caused by Dsh localization to dynamic protein assemblies which requires the DIX domain (Capelluto et al., 2002; Schwarz-Romond et al., 2005). Thus it was surprising that ΔDEPMIG-5::GFP, which contains the DIX domain, failed to form puncta. ΔPDZMIG-5::GFP was associated with the membrane and formed puncta in 92% of males (Fig. 5B, Table 2) also accumulated in the nucleus in 4% (n=26) of males (data not shown), which indicates that PDZ domain might not be required for the interaction between LIN-17 and MIG-5. This is consistent with our observation that the LIN-17 KTXXXW motif, which in other systems binds to Dsh via the PDZ domain in vitro, is not required for asymmetric localization of LIN-17. ΔDIXMIG-5::GFP displayed membrane association but not puncta in 89% (n=18) of males (Fig. 5C, Table 2), which is consistent with the DIX function of Dvl2 in mammalian cultured cells (Schwarz-Romond et al., 2005). The function of each domain in the control of B cell polarity is different. MIG-5::GFP can rescue the mig-5 B cell polarity defect as 85% of mig-5 males that expressed MIG-5::GFP displayed normal B cell polarity (n=44), whereas 44% of mig-5 males displayed normal B cell polarity (n=58). ΔDEPMIG-5::GFP or ΔPDZMIG-5::GFP failed to rescue the mig-5 B cell polarity defect as only 42% (n=41) or 40% (n=31) displayed normal B cell polarity respectively. ΔDIXMIG-5::GFP partially rescued mig-5 B cell polarity defect as 60% (n=38) displayed normal B cell polarity (Table 2).
Figure 5. The DEP domain is required for MIG-5 membrane localization.
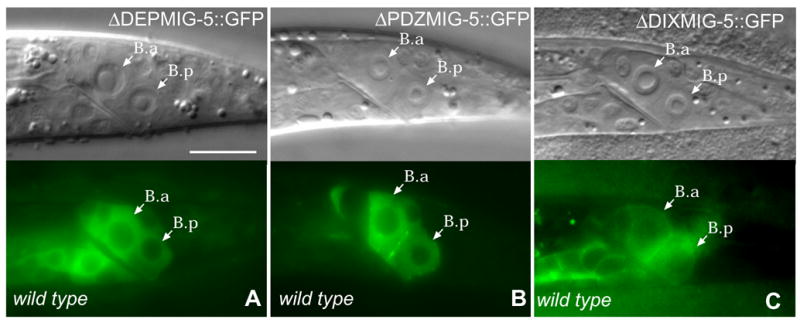
ΔDEPMIG-5::GFP was not associated with the membrane (A). ΔPDZMIG-5::GFP was expressed in punctate pattern in the B daughters (B). ΔDIXMIG-5::GFP can associate with plasma membrane (C). Bar equals 10 μm in all panels.
Table 2.
Function and localization of MIG-5 variants.
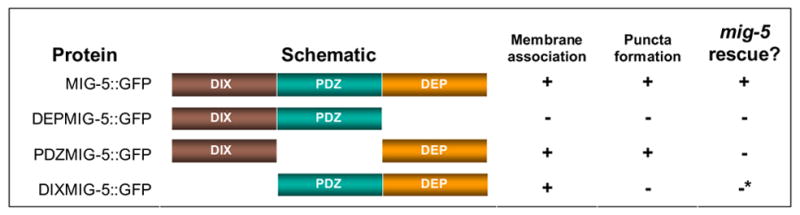
MIG-5 domains are illustrated by different colors as indicated. Schematic structures of MIG-5 variants are shown. Membrane association of each variant was recorded as +, if MIG-5::GFP was associated with the B cell membrane in more than 50% of worms (n>13), as described in the text. Puncta formation of MIG-5::GFP was recorded as +, if MIG-5::GFP puncta were observed in more than 50% of worms , as described in the text. mig-5 rescue was recorded as +, if the percentage of normal B cell polarity worms that expressed the protein was significantly higher than mig-5 males as determined by T test (p < 0.05).
ΔDIXMIG-5::GFP partially rescued mig-5, but the effect was not statistically significant.
Discussion
We have shown that LIN-17::GFP and MIG-5::GFP were asymmetrically localized during the B cell division and observed the correlation of asymmetric LIN-17::GFP distribution with B cell polarity. The LIN-17 transmembrane domain was required for LIN-17 function and asymmetric distribution to B daughters, while the KTXXXW motif was only required for function and much of the CRD was dispensable for localization and function. The MIG-5/Dsh DEP and PDZ domains played larger roles than did the DIX domain in rescuing B cell polarity. The DEP domain was required for MIG-5 membrane localization, while the PDZ and DIX domains were not.
A noncanonical Wnt pathway regulates B cell polarity
Wnt pathways in C. elegans are involved in the regulation of cell specification, cell migration and cell polarity during development (reviewed by Herman, 2002; Korswagen, 2002). In C. elegans, POP-1 is the only Tcf (Lin et al., 1995; Lo et al., 2004; reviewed by Herman and Wu, 2004), while there appear to be four β-catenin homologs: HMP-2 (Costa, et al., 1998), WRM-1, BAR-1 and SYS-1 (Natarajan et al., 2001; Kidd et al., 2005). HMP-2 is involved in cell adhesion, while WRM-1 functions with LIT-1/NLK to regulate POP-1 sub-cellular localization (Rocheleau et al., 1999). Both BAR-1 and SYS-1 interact with POP-1 directly to regulate POP-1 function (Kidd et al., 2005). BAR-1 can bind to POP-1, switching it from a repressor to an activator (Korswagen et al., 2000), so Wnt pathways that possess BAR-1 are Wnt/β-catenin or canonical Wnt pathways, while whether SYS-1 functions as a canonical component is not clear. The asymmetric localization of MOM-5 during C. elegans embryogenesis (Park et al., 2004) suggests that the PCP pathway is also conserved in C. elegans. We previously showed that BAR-1, SYS-1, WRM-1 and HMP-2 were not involved in the control of B cell polarity, while RHO-1 and ROCK are involved, which indicates a PCP-like pathway might regulate B cell polarity (Wu and Herman, 2006). This report provides further evidence that a PCP-like pathway is conserved in C. elegans and regulates the B cell polarity. First, the asymmetric localization of LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh were similar to Fz and Dsh in Drosophila. LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh accumulated to the anterior cortex of B cell, opposite to the LIN-44/Wnt source, which is similar to the asymmetric localization of Fz and Dsh to the distal cortex opposite to the signal source of individual cells during Drosophila wing hair formation (Strutt, 2001). Second, LIN-17 can recruit MIG-5 to the membrane prior to and after the B cell division, similar to the PCP pathway in Drosophila. DFz functions as the PCP signaling receptor in Drosophila and can recruit Dsh to the membrane (Axelrod et al., 1998). Third, the functions of the MIG-5 domains were conserved. The Dsh DEP domain was required for membrane association and the DEP and PDZ domains, that were required for Drosophila PCP (Boutros and Mlodzik, 1999), were also required to rescue B cell polarity, while the DIX domain was not that important. Fourth, the function of the LIN-17 KTXXXW was also conserved. The KTXXXW motif of XFz3 was required for the activation of β-catenin and for Dsh membrane association (Umbhauer et al., 2000), indicating that the KTXXXW motif functions in PCP signaling (Axelrod et al., 1998; Strutt, 2001). Interestingly, the ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP construct rescued B cell polarity but not T cell polarity. In addition, LIN-17 was asymmetrically localized to the posterior cortex of the T cell, but to the anterior cortex of the B cell. Furthermore, MIG-5/Dsh plays a large role in the control of B cell polarity but little or no role in the control of T cell polarity (Wu and Herman, 2006). This suggests that polarity is regulated differently in the T and B cells and that B cell polarity is regulated by a PCP like pathway, which might account for the requirement of the KTXXXW motif in the B cell but not in the T cell. However, we also observed that the effect of the K497M, T498A and W502G point mutants interfered with membrane localization in the B cell while removal of the entire KTXXXW motif did not. The reasons for this are not entirely clear. Either the motif is not actually required and the point mutants are causing non-specific effects or the motif is required and the SGR tripeptide that was inserted during the construction of the ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP fusion might confer some membrane association ability. In summary, a PCP-like pathway involving the asymmetric localization of LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh appears to regulate B cell polarity.
Asymmetric distribution of LIN-17 correlates with proper B cell polarity
Prior to the B cell division, LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically localized to the anterior B cell membrane and was dependent upon LIN-44 and MIG-5 function. During the B cell division, LIN-17::GFP was asymmetrically distributed to the B.a and B.p cells, with the B.a cell having a higher level than the B.p cell. It seems likely that the asymmetric distribution of LIN-17::GFP resulted from its asymmetric localization before division. Several lines of evidence suggest that asymmetric distribution of LIN-17 might be required for normal B daughter cell fates. First, asymmetric distribution of LIN-17::GFP correlated with B cell polarity in both rescued lin-17 males that displayed normal polarity and lin-44 males that displayed reversed polarity. Second, 1TMSLIN-17::GFP failed to rescue B cell polarity of lin-17 males and was symmetrically localized and distributed during B cell division. This suggests that the transmembrane domain is required for the function, asymmetric localization and asymmetric distribution of LIN-17. Third, ΔKTWLIN-17::GFP localized to the B cell membrane as well as the full length LIN-17::GFP (Fig. 3D–F), displayed asymmetric localization prior to cell division and asymmetric distribution after division, but failed to rescue lin-17. This result indicates that KTXXXW motif is not required for LIN-17 asymmetric localization but is essential for B cell polarity. Together, these results demonstrate that while asymmetric distribution of LIN-17 is highly correlated with proper B cell polarity, it is not always sufficient to rescue the B cell polarity defects of lin-17 males
Control of asymmetric B cell division by the asymmetric localization of LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh
Asymmetric cell division is essential for the generation of diverse cell fates during development (reviewed by (Horvitz and Herskowitz, 1992; Jan and Jan, 2000), which is often achieved through asymmetric distribution of factors during the division. For example, asymmetric localization of PAR proteins is required for the asymmetric division of the C. elegans zygote (reviewed by Cowan and Hyman, 2004; Nance, 2005) and Drosophila neuroblasts (reviewed by Knoblich, 2001; Pellettieri and Seydoux, 2002). In C. elegans, Wnt signaling components or targets MOM-5/Fz (Park et al., 2004), WRM-1/β-catenin, LIT-1/NLK-1 (Nakamura et al., 2005; Takeshita and Sawa, 2005), and POP-1/Tcf (reviewed by Herman and Wu, 2004) are asymmetrically localized during asymmetric cell divisions. Asymmetric localization of WRM-1 and LIT-1 at the anterior cortex of the EMS, V and T cells followed by their accumulation in the nuclei of the posterior daughter appears to lower the nuclear level of POP-1 in the posterior daughter (Lo et al., 2004; Nakamura et al., 2005; Takeshita and Sawa, 2005). However LIT-1 and WRM-1 do not play a major role in the control of B cell polarity, thus the asymmetric localizations of LIN-17 and MIG-5 are likely to control B cell polarity.
Our model for B cell polarity is shown in Figure 6. The LIN-44/Wnt polarity signal is secreted from the tail hypodermal cells (Herman et al., 1995) and is recruited by the LIN-17 CRD to bind to the LIN-17 transmemebrane domain on the B cell membrane. Activated LIN-17/Fz recruits MIG-5 to the membrane to form a LIN-17/MIG-5 complex via the MIG-5 DEP domain. This complex may be internalized, clearing it from the membrane, possibly through endocytosis. This would be similar to the β-arrestin-2 and Disheveled 2 dependant endocytosis of Fz4 in mammals (Chen et al., 2003) and Fz2/Arrow endocytosis in Drosophila (Marois et al., 2006). However disruption of the C. elegans β-arrestin-2 homolog, arr-1, which is primarily expressed in neurons (Fukuto et al., 2004), did not affect LIN-17::GFP localization (M.W. and M.H., unpublished data), suggesting that if endocytosis is involved, it must be ARR-1 independent. The asymmetric localization of the LIN-17 and MIG-5 may be achieved by transportation of the induced complex to the anterior B cell cortex or simply by clearing it from the posterior. MIG-5, through the DEP and DIX domains, forms puncta that might function to provide focal points for the cytoskeleton, via RHO-1 (Wu and Herman, 2006), to localize cell fate determinants to the anterior of the B cell. The asymmetric localization of LIN-17 and MIG-5 might be required for their asymmetric distribution to the B daughters, which might also play a role in the distribution of cell fate determinants.
Figure 6. Model for the correlation of B cell polarity with the asymmetric localization of LIN-17 and MIG-5.
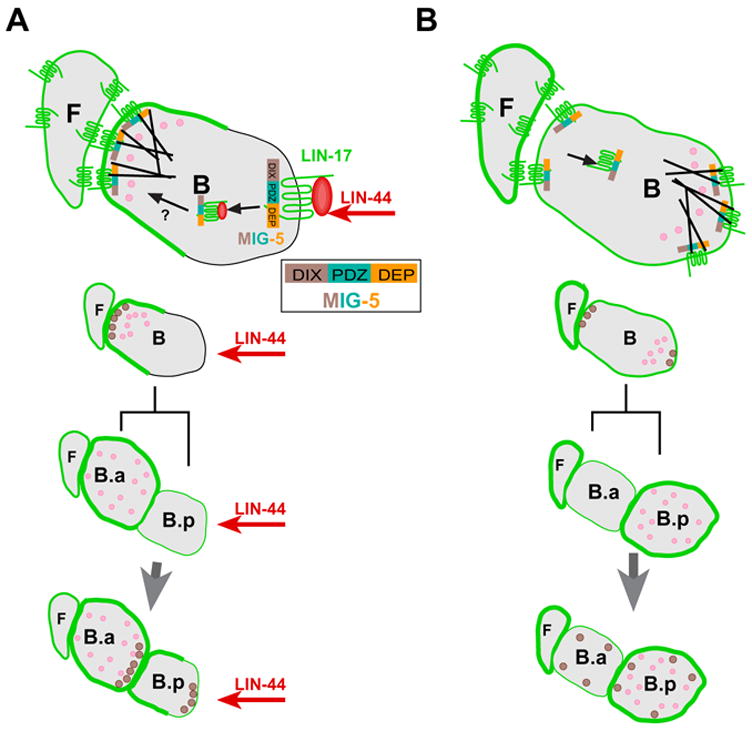
(A) When LIN-44/Wnt (red) is present, it is recruited by the LIN-17 (green) CRD and binds to the LIN-17 transmembrane domain, resulting in MIG-5 membrane association via the DEP domain (orange) and formation of a LIN-17-MIG-5 complex. See inset for MIG-5 domains. This complex is then internalized (arrow) removing it from the posterior membrane and it subsequently may be transported (? arrow) to the anterior cortex of B cell. Either mechanism could cause the asymmetric distribution of cell fate determinants (pink) and cytoskeletal components (black lines) prior to cell division, leading to displacement of the spindle cause the difference in B daughter cell sizes and the asymmetric distribution of LIN-17, MIG-5 as well as the cell fate determinants to the two daughters, resulting in the specification of different daughter cell fates. A similar mechanism leads to asymmetric localization of LIN-17 and MIG-5 in the B.p cell (below). The tail hypodermal cells are the source of LIN-44/Wnt signal are several cell diameters posterior of the B cell and are not shown. (B) When LIN-44 is absent, higher LIN-17 levels in the F cell and other neighbor cells might lead to dimeriztion with LIN-17 on the B cell membrane. This might initiate signaling independent of LIN-44 and cause LIN-17 to accumulate at both anterior and posterior cortex of B cell and in some cases the posterior cortex would have higher level than the anterior (not shown). Either the asymmetric localization of LIN-17 or simply the presence of LIN-17-MIG-5 complex in the posterior causes asymmetric localization of MIG-5 and cell fate determinants. The activation of signaling at the anterior of the B cell causes the reversed asymmetric distribution of cell fate determinants prior to B cell division and reversed B cell fates. MIG-5 is only shown in the cytoplasm due to space limitations, however MIG-5 could be shuttled between nucleus and the cytoplasm.
After the B division, LIN-17 is symmetrically localized in the B.a membrane and colocalizes with the MIG-5 punta in the posterior of B.a. However, LIN-17 is asymmetrically localized to the anterior of B.p membrane whereas the MIG-5 puncta also appear at the posterior. Although it appears that the posterior B.p MIG-5 puncta are present in the absence of LIN-17, MIG-5 puncta formation is dependant upon LIN-17 (Fig. 4C). Thus it is possible that a small amount of LIN-17::GFP, below the level of detection, remains in the posterior of B.p and complexes with MIG-5 or that the posterior B.p MIG-5 puncta require LIN-17 for formation, but not localization. The posterior localization of MIG-5 puncta in the B.a and B.p cells might then function to set the polarity of subsequent divisions.
Although LIN-44 functions as polarity signal and directs the asymmetric localization of LIN-17 and MIG-5 puncta, another anterior polarity signal might also exist. lin-44 males with reversed polarity often had a randomized or reversed LIN-17::GFP and MIG-5::GFP puncta distribution, leading to the reversal of B daughter fates. This might be caused by another signal, secreted from an anterior source. However, it is also possible that LIN-17 can auto-activate via dimerization. LIN-17::GFP is expressed strongly in the anterior neighbors of the B and B.a cells, such as the F cell. This might allow interaction of LIN-17 molecules on adjacent cells, leading to the initiation of signaling in the B cell, similar to the Fz auto-activation observed in Xenopus (Carron et al., 2003). This may cause the daughter cell that is closer to F cell or its neighbors to take the B.p cell fate and the other daughter to take the B.a cell fate in the absence of LIN-44. When LIN-44 is present, however, it overcomes the auto-activation signal, causing the anterior daughter to take the B.a cell fate and the posterior daughter to take the B.p cell fate.
Finally, the B cell exhibits interactions with its neighboring cells, F and U (Herman and Horvitz, 1994), reminiscent of the directional nonautonomous effect caused by fz mutant clones in Drosophila (Strutt and Strutt, 2002). Thus B cell polarity may be controlled by PCP-like interactions between neighboring cells, similar to those observed in Drosophila, as well as transduction of a secreted Wnt signal from more distant cells. This work has begun to provide insights in to how these two different signaling mechanisms are integrated.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of Herman lab for useful discussions. We thank Yuji Kohara for providing cDNA clones. Some strains used were obtained from the C. elegans Genetic Center, which is supported by NIH NCRR, or from the C. elegans Gene Knockout Consortium. This work was supported by NIH grants GM56339 to MH and P20 RR016475 from the NCRR INBRE Program.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Reference List
- Adler PN. Planar signaling and morphogenesis in Drosophila. Dev Cell. 2002;2:525–35. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod JD. Unipolar membrane association of Dishevelled mediates Frizzled planar cell polarity signaling. Genes Dev. 2001;15:1182–7. doi: 10.1101/gad.890501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod JD, Miller JR, Shulman JM, Moon RT, Perrimon N. Differential recruitment of Dishevelled provides signaling specificity in the planar cell polarity and Wingless signaling pathways. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2610–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.16.2610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhanot P, Brink M, Harryman Samos C, Hsieh JC, Wang Y, Macke JP, Andrew D, Nathans J, Nusse R. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature. 1996;382:225–230. doi: 10.1038/382225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutros M, Mlodzik M. Dishevelled: at the crossroads of divergent intracellular signaling pathways. Mech Dev. 1999;83:27–37. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutros M, Paricio N, Strutt DI, Mlodzik M. Dishevelled activates JNK and discriminates between JNK pathways in planar polarity and wingless signaling. Cell. 1998;94:109–18. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974;77:71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadigan KM, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 1997;11:3286–305. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capelluto DG, Kutateladze TG, Habas R, Finkielstein CV, He X, Overduin M. The DIX domain targets dishevelled to actin stress fibres and vesicular membranes. Nature. 2002;419:726–9. doi: 10.1038/nature01056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carron C, Pascal A, Djiane A, Boucaut JC, Shi DL, Umbhauer M. Frizzled receptor dimerization is sufficient to activate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:2541–50. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen CM, Strapps W, Tomlinson A, Struhl G. Evidence that the cysteine-rich domain of Drosophila Frizzled family receptors is dispensable for transducing Wingless. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:15961–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407103101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W, ten Berge D, Brown J, Ahn S, Hu LA, Miller WE, Caron MG, Barak LS, Nusse R, Lefkowitz RJ. Dishevelled 2 recruits beta-arrestin 2 to mediate Wnt5A-stimulated endocytosis of Frizzled 4. Science. 2003;301:1391–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1082808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cong F, Schweizer L, Varmus H. Wnt signals across the plasma membrane to activate the beta-catenin pathway by forming oligomers containing its receptors, Frizzled and LRP. Development. 2004;131:5103–15. doi: 10.1242/dev.01318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M, Raich W, Aqbunag C, Leung B, Hardin J, Priess JR. A putative catenin-cadherin system mediates morphogenesis of the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:297–08. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan CR, Hyman AA. Asymmetric cell division in C. elegans: cortical polarity and spindle positioning. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:427–53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111301.113823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dann CE, Hsieh JC, Rattner A, Sharma D, Nathans J, Leahy DJ. Insights into Wnt binding and signalling from the structures of two Frizzled cysteine-rich domains. Nature. 2001;412:86–90. doi: 10.1038/35083601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuto HS, Ferkey DM, Apicella AJ, Lans H, Sharmeen T, Chen W, Lefkowitz RJ, Jansen G, Schafer WR, Hart AC. G protein-coupled receptor kinase function is essential for chemosensation in C. elegans. Neuron. 2004;42:581–93. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgi LL, Albert PS, Riddle DL. daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase. Cell. 1990;61:635–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90475-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B, Takeshita H, Mizumoto K, Sawa H. Wnt signals can function as positional cues in establishing cell polarity. Dev Cell. 2006;10:391–6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.12.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins NC, Ellis GC, Bowerman B, Garriga G. MOM-5 frizzled regulates the distribution of DSH-2 to control C. elegans asymmetric neuroblast divisions. Dev Biol. 2005;284:246–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X, Semenov M, Tamai K, Zeng X. LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: arrows point the way. Development. 2004;8:1663–1677. doi: 10.1242/dev.01117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg CP, Tada M, Rauch GJ, Saude L, Concha ML, Geisler R, Stemple DL, Smith JC, Wilson SW. Silberblick/Wnt11 mediates convergent extension movements during zebrafish gastrulation. Nature. 2000;405:76–81. doi: 10.1038/35011068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman MA. Control of cell polarity by noncanonical Wnt signaling in C. elegans. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:233–41. doi: 10.1016/s1084-9521(02)00051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman MA, Horvitz HR. The Caenorhabditis elegans gene lin-44 controls the polarity of asymmetric cell divisions. Development. 1994;120:1035–47. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.5.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman MA, Vassilieva LL, Horvitz HR, Shaw JE, Herman RK. The C. elegans gene lin-44, which controls the polarity of certain asymmetric cell divisions, encodes a Wnt protein and acts cell nonautonomously. Cell. 1995;83:101–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman MA, Wu M. Noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways in C. elegans converge on POP-1/TCF and control cell polarity. Front Biosci. 2004;9:1530–9. doi: 10.2741/1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard MA, Bargmann CI. Wnt signals and frizzled activity orient anterior-posterior axon outgrowth in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2006;10:379–390. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz HR, Herskowitz I. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: two Bs or not two Bs, that is the question. Cell. 1992;68:237–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90468-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh JC, Rattner A, Smallwood PM, Nathans J. Biochemical characterization of Wnt-frizzled interactions using a soluble, biologically active vertebrate Wnt protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:3546–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T, Oz HS, Wiland D, Gharib S, Deshpande R, Hill RJ, Katz WS, Sternberg PW. C. elegans LIN-18 is a Ryk ortholog and functions in parallel to LIN-17/Frizzled in Wnt signaling. Cell. 2004;118:795–806. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan YN, Jan LY. Polarity in cell division: what frames thy fearful asymmetry? Cell. 2000;100:599–602. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80695-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd AR, 3rd, Miskowski JA, Siegfried KR, Sawa H, Kimble J. A beta-catenin identified by functional rather than sequence criteria and its role in Wnt/MAPK signaling. Cell. 2005;121:761–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein TJ, Mlodzik M. Planar cell polarization: an emerging model points in the right direction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:155–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.132806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoblich JA. Asymmetric cell division during animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:11–20. doi: 10.1038/35048085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korswagen HC. Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans: variations on a common signaling theme. Bioessays. 2002;24:801–10. doi: 10.1002/bies.10145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korswagen HC, Herman MA, Clevers HC. Distinct beta-catenins mediate adhesion and signalling functions in C. elegans. Nature. 2000;406:527–32. doi: 10.1038/35020099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Yuan H, Xie W, Mao J, Caruso AM, McMahon A, Sussman DJ, Wu D. Dishevelled proteins lead to two signaling pathways. Regulation of LEF-1 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:129–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R, Thompson S, Priess JR. pop-1 encodes an HMG box protein required for the specification of a mesoderm precursor in early C. elegans embryos. Cell. 1995;83:599–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo MC, Gay F, Odom R, Shi Y, Lin R. Phosphorylation by the beta-catenin/MAPK complex promotes 14-3-3-mediated nuclear export of TCF/POP-1 in signal-responsive cells in C. elegans. Cell. 2004;117:95–106. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maduro M, Pilgrim D. Identification and cloning of unc-119, a gene expressed in the Caenorhabditis elegans nervous system. Genetics. 1995;141:977–88. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.3.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marois E, Mahmoud A, Eaton S. The endocytic pathway and formation of the Wingless morphogen gradient. Development. 2006;133:307–17. doi: 10.1242/dev.02197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M. Planar cell polarization: do the same mechanisms regulate Drosophila tissue polarity and vertebrate gastrulation? Trends Genet. 2002;18:564–71. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(02)02770-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K, Kim S, Ishidate T, Bei Y, Pang K, Shirayama M, Trzepacz C, Brownell DR, Mello CC. Wnt signaling drives WRM-1/beta-catenin asymmetries in early C. elegans embryos. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1749–54. doi: 10.1101/gad.1323705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance J. PAR proteins and the establishment of cell polarity during C. elegans development. Bioessays. 2005;27:126–35. doi: 10.1002/bies.20175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan L, Witwer NE, Eisenmann DM. The divergent Caenorhabditis elegans beta-catenin proteins BAR-1, WRM-1 and HMP-2 make distinct protein interactions but retain functional redundancy in vivo. Genetics. 2001;159:159–72. doi: 10.1093/genetics/159.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 2004;303:1483–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1094291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park FD, Tenlen JR, Priess JR. C. elegans MOM-5/frizzled functions in MOM-2/Wnt-independent cell polarity and is localized asymmetrically prior to cell division. Curr Biol. 2004;14:2252–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellettieri J, Seydoux G. Anterior-posterior polarity in C. elegans and Drosophila--PARallels and differences. Science. 2002;298:1946–50. doi: 10.1126/science.1072162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinson KI, Brennan J, Monkley S, Avery BJ, Skarnes WC. An LDL-receptor-related protein mediates Wnt signalling in mice. Nature. 2000;6803:535–8. doi: 10.1038/35035124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povelones M, Nusse R. The role of the cysteine-rich domain of Frizzled in Wingless-Armadillo signaling. Embo J. 2005;24:3493–503. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocheleau CE, Yasuda J, Shin TH, Lin R, Sawa H, Okano H, Priess JR, Davis RJ, Mello CC. WRM-1 activates the LIT-1 protein kinase to transduce anterior/posterior polarity signals in C. elegans. Cell. 1999;97:717–26. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80784-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbacher U, Laurent MN, Deardorff MA, Klein PS, Cho KW, Fraser SE. Dishevelled phosphorylation, subcellular localization and multimerization regulate its role in early embryogenesis. Embo J. 2000;19:1010–22. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.5.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rulifson EJ, Wu CH, Nusse R. Pathway specificity by the bifunctional receptor frizzled is determined by affinity for wingless. Mol Cell. 2000;6:117–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H, Lobel L, Horvitz HR. The Caenorhabditis elegans gene lin-17, which is required for certain asymmetric cell divisions, encodes a putative seven-transmembrane protein similar to the Drosophila frizzled protein. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2189–97. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.17.2189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Romond T, Merrifield C, Nichols BJ, Bienz M. The Wnt signalling effector Dishevelled forms dynamic protein assemblies rather than stable associations with cytoplasmic vesicles. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:5269–77. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strutt D. Frizzled signalling and cell polarisation in Drosophila and vertebrates. Development. 2003;130:4501–13. doi: 10.1242/dev.00695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strutt DI. Asymmetric localization of frizzled and the establishment of cell polarity in the Drosophila wing. Mol Cell. 2001;7:367–75. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strutt DI. The asymmetric subcellular localisation of components of the planar polarity pathway. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:225–31. doi: 10.1016/s1084-9521(02)00041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strutt H, Strutt D. Nonautonomous planar polarity patterning in Drosophila: dishevelled-independent functions of frizzled. Dev Cell. 2002;3:851–63. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston JE, Horvitz HR. Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1977;56:110–56. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M, Concha ML, Heisenberg CP. Non-canonical Wnt signaling and regulation of gastrulation movements. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:251–260. doi: 10.1016/s1084-9521(02)00052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita H, Sawa H. Asymmetric cortical and nuclear localizations of WRM-1/beta-catenin during asymmetric cell division in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1743–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1322805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, Spokony R, Liu C, Katsuyama Y, Hess F, Saint-Jeannet JP, He X. LDL-receptor-related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature. 2000;6803:530–5. doi: 10.1038/35035117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tree DR, Ma D, Axelrod JD. A three-tiered mechanism for regulation of planar cell polarity. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:217–24. doi: 10.1016/s1084-9521(02)00042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbhauer M, Djiane A, Goisset C, Penzo-Mendez A, Riou JF, Boucaut JC, Shi DL. The C-terminal cytoplasmic Lys-thr-X-X-X-Trp motif in frizzled receptors mediates Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Embo J. 2000;19:4944–54. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.18.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veeman MT, Axelrod JD, Moon RT. A second canon. Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent Wnt signaling. Dev Cell. 2003;5:367–77. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walston T, Guo C, Proenca R, Wu M, Herman M, Hardin J, Hedgecock E. mig-5/Dsh controls cell fate determination and cell migration in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2006;298:485–97. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli M, Dougan ST, Caldwell K, O’Keefe L, Schwartz S, Vaizel-Ohayon D, Schejter E, Tomlinson A, DiNardo S. arrow encodes an LDL-receptor-related protein essential for Wingless signalling. Nature. 2000;6803:527–30. doi: 10.1038/35035110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidinger G, Moon RT. When Wnts antagonize Wnts. J Cell Biol. 2003;162:753–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200307181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong HC, Bourdelas A, Krauss A, Lee HJ, Shao Y, Wu D, Mlodzik M, Shi DL, Zheng J. Direct binding of the PDZ domain of Dishevelled to a conserved internal sequence in the C-terminal region of Frizzled. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1251–60. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00427-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M, Herman MA. A novel noncanonical Wnt pathway is involved in the regulation of the asymmetric B cell division in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2006;293:316–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


