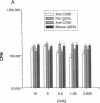
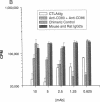
Abstract
The activation and differentiation of T cells require both antigen/MHC recognition and costimulatory signals. The present studies examined the role of B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) costimulation in the prototypic autoimmune disorder, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). In adoptively transferred EAE, in vitro activation of myelin basic protein (MBP)-specific lymph node cells was inhibited by the combination of anti-CD80 plus anti-CD86, but not individually. However, in actively induced disease, one injection of anti-CD80 significantly reduced disease, while anti-CD86 exacerbated disease. Interestingly, one injection of CTLA-4Ig suppressed disease, while multiple injections resulted in enhanced disease. Thus, the costimulation provided by B7-1 molecules appears to be important for the development of encephalitogenic T cells. The enhanced disease caused by multiple injections of CTLA-4Ig or a single injection of anti-CD86 suggests an inhibitory function for CD86 interaction with its counterreceptors CD28 and CTLA-4 in EAE. Alternatively, these results are consistent with an essential timing requirement for the coordinated interaction of B7 and CD28 family receptors, and that disruption of this critical timing can have opposing results on the outcome of an immune response.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando D. G., Clayton J., Kono D., Urban J. L., Sercarz E. E. Encephalitogenic T cells in the B10.PL model of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) are of the Th-1 lymphokine subtype. Cell Immunol. 1989 Nov;124(1):132–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma M., Ito D., Yagita H., Okumura K., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L., Somoza C. B70 antigen is a second ligand for CTLA-4 and CD28. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):76–79. doi: 10.1038/366076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J. L., Madri J. A., Ruddle N. H., Hashim G., Janeway C. A., Jr Surface expression of alpha 4 integrin by CD4 T cells is required for their entry into brain parenchyma. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):57–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussiotis V. A., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Daley J., Gray G., Nadler L. M. Activated human B lymphocytes express three CTLA-4 counterreceptors that costimulate T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11059–11063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher P. The two-signal model of lymphocyte activation twenty-one years later. Immunol Today. 1992 Feb;13(2):74–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90138-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caux C., Vanbervliet B., Massacrier C., Azuma M., Okumura K., Lanier L. L., Banchereau J. B70/B7-2 is identical to CD86 and is the major functional ligand for CD28 expressed on human dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1841–1847. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry D. B., Reiner S. L., Linsley P. S., Locksley R. M. Differential effects of blockade of CD28-B7 on the development of Th1 or Th2 effector cells in experimental leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1994 Nov 1;153(9):4142–4148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft M., Bradley L. M., Swain S. L. Naive versus memory CD4 T cell response to antigen. Memory cells are less dependent on accessory cell costimulation and can respond to many antigen-presenting cell types including resting B cells. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):2675–2685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Klussman K., Linsley P. S., Aruffo A. Differential costimulatory effects of adhesion molecules B7, ICAM-1, LFA-3, and VCAM-1 on resting and antigen-primed CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):1985–1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):139–165. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Freeman G. J., Rhynhart K., Nadler L. M. Selective induction of B7/BB-1 on interferon-gamma stimulated monocytes: a potential mechanism for amplification of T cell activation through the CD28 pathway. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;137(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90091-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Borriello F., Hodes R. J., Reiser H., Gribben J. G., Ng J. W., Kim J., Goldberg J. M., Hathcock K., Laszlo G. Murine B7-2, an alternative CTLA4 counter-receptor that costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2185–2192. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Borriello F., Hodes R. J., Reiser H., Hathcock K. S., Laszlo G., McKnight A. J., Kim J., Du L., Lombard D. B. Uncovering of functional alternative CTLA-4 counter-receptor in B7-deficient mice. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):907–909. doi: 10.1126/science.7694362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Freedman A. S., Segil J. M., Lee G., Whitman J. F., Nadler L. M. B7, a new member of the Ig superfamily with unique expression on activated and neoplastic B cells. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2714–2722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Boussiotis V. A., Ng J. W., Restivo V. A., Jr, Lombard L. A., Gray G. S., Nadler L. M. Cloning of B7-2: a CTLA-4 counter-receptor that costimulates human T cell proliferation. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):909–911. doi: 10.1126/science.7694363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Gray G., Nadler L. M. Human T-cell clonal anergy is induced by antigen presentation in the absence of B7 costimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6586–6590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. M., Noel P. J., Sperling A. I., Walunas T. L., Gray G. S., Bluestone J. A., Thompson C. B. Absence of B7-dependent responses in CD28-deficient mice. Immunity. 1994 Sep;1(6):501–508. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribben J. G., Freeman G. J., Boussiotis V. A., Rennert P., Jellis C. L., Greenfield E., Barber M., Restivo V. A., Jr, Ke X., Gray G. S. CTLA4 mediates antigen-specific apoptosis of human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):811–815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathcock K. S., Laszlo G., Dickler H. B., Bradshaw J., Linsley P., Hodes R. J. Identification of an alternative CTLA-4 ligand costimulatory for T cell activation. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):905–907. doi: 10.1126/science.7694361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathcock K. S., Laszlo G., Pucillo C., Linsley P., Hodes R. J. Comparative analysis of B7-1 and B7-2 costimulatory ligands: expression and function. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):631–640. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Witmer-Pack M., Inaba M., Hathcock K. S., Sakuta H., Azuma M., Yagita H., Okumura K., Linsley P. S., Ikehara S. The tissue distribution of the B7-2 costimulator in mice: abundant expression on dendritic cells in situ and during maturation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1849–1860. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inobe M., Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A., Nagai Y., Tamakoshi M., Uede T. Identification of an alternatively spliced form of the murine homologue of B7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):443–449. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K., Johnson J. G. Molecules involved in T-cell costimulation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90054-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. K. The ups and downs of T cell costimulation. Immunity. 1994 Sep;1(6):443–446. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Bluestone J. A., Nadler L. M., Thompson C. B. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol Today. 1994 Jul;15(7):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamradt T., Soloway P. D., Perkins D. L., Gefter M. L. Pertussis toxin prevents the induction of peripheral T cell anergy and enhances the T cell response to an encephalitogenic peptide of myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3296–3302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchroo V. K., Das M. P., Brown J. A., Ranger A. M., Zamvil S. S., Sobel R. A., Weiner H. L., Nabavi N., Glimcher L. H. B7-1 and B7-2 costimulatory molecules activate differentially the Th1/Th2 developmental pathways: application to autoimmune disease therapy. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):707–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. P., Ritchie S. C., Hendrix R., Linsley P. S., Hathcock K. S., Hodes R. J., Lowry R. P., Pearson T. C. Regulation of immunostimulatory function and costimulatory molecule (B7-1 and B7-2) expression on murine dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5208–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenschow D. J., Ho S. C., Sattar H., Rhee L., Gray G., Nabavi N., Herold K. C., Bluestone J. A. Differential effects of anti-B7-1 and anti-B7-2 monoclonal antibody treatment on the development of diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1145–1155. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenschow D. J., Su G. H., Zuckerman L. A., Nabavi N., Jellis C. L., Gray G. S., Miller J., Bluestone J. A. Expression and functional significance of an additional ligand for CTLA-4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11054–11058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Bolling S. F., Linsley P. S., Wei R. Q., Gordon D., Thompson C. B., Turka L. A. Long-term acceptance of major histocompatibility complex mismatched cardiac allografts induced by CTLA4Ig plus donor-specific transfusion. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1801–1806. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Greene J. L., Brady W., Bajorath J., Ledbetter J. A., Peach R. Human B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) bind with similar avidities but distinct kinetics to CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors. Immunity. 1994 Dec;1(9):793–801. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(94)80021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Greene J. L., Tan P., Bradshaw J., Ledbetter J. A., Anasetti C., Damle N. K. Coexpression and functional cooperation of CTLA-4 and CD28 on activated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A. The role of the CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:191–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu P., Zhou X., Chen S. J., Moorman M., Morris S. C., Finkelman F. D., Linsley P., Urban J. F., Gause W. C. CTLA-4 ligands are required to induce an in vivo interleukin 4 response to a gastrointestinal nematode parasite. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):693–698. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannie M. D., Morrison-Plummer J., McConnell T. J. Differentiation of encephalitogenic T cells confers resistance to an inhibitory anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):7293–7306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:153–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron R. M., Racke M., Spatz M., McFarlin D. E. Cerebral vascular endothelial cells are effective targets for in vitro lysis by encephalitogenic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. J., Perez V. L., Shea C. M., Gray G. S., Abbas A. K. Costimulator dependence of lymphokine secretion by naive and activated CD4+ T lymphocytes from TCR transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5220–5225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. L., Jenkins M. K., Schwartz R. H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: a costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:445–480. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa Y., Wachi E., Tominaga K., Abe M., Wakasa H. A novel monoclonal antibody (FUN-1) identifies an activation antigen in cells of the B-cell lineage and Reed-Sternberg cells. J Pathol. 1993 Mar;169(3):309–315. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin P. J., Scott D., Quigley L., Albert P. S., Feder O., Gray G. S., Abe R., June C. H., Racke M. K. Role of B7:CD28/CTLA-4 in the induction of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):1481–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Bonomo A., Scott D. E., Cannella B., Levine A., Raine C. S., Shevach E. M., Röcken M. Cytokine-induced immune deviation as a therapy for inflammatory autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1961–1966. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Burnett D., Pak S. H., Albert P. S., Cannella B., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E., Scott D. E. Retinoid treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. IL-4 production correlates with improved disease course. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):450–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razi-Wolf Z., Galvin F., Gray G., Reiser H. Evidence for an additional ligand, distinct from B7, for the CTLA-4 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11182–11186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchese F., Hausmann B., Hubele S., Lane P. Mice transgenic for a soluble form of murine CTLA-4 show enhanced expansion of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells and defective antibody production in vivo. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):809–817. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagerström C. G., Kerr E. M., Allison J. P., Davis M. M. Activation and differentiation requirements of primary T cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8987–8991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Germain R. N., Linsley P. S., Paul W. E. CD28-mediated costimulation of interleukin 2 (IL-2) production plays a critical role in T cell priming for IL-4 and interferon gamma production. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):299–304. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna M. P., van Parijs L., Sharpe A. H., Abbas A. K., Freeman G. J. A negative regulatory function of B7 revealed in B7-1 transgenic mice. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):415–421. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walunas T. L., Lenschow D. J., Bakker C. Y., Linsley P. S., Freeman G. J., Green J. M., Thompson C. B., Bluestone J. A. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):405–413. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. R., Unanue E. R. Costimulatory requirements of murine Th1 clones. The role of accessory cell-derived signals in responses to anti-CD3 antibody. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Holly R. D., Clark E. A. B lymphoblast antigen (BB-1) expressed on Epstein-Barr virus-activated B cell blasts, B lymphoblastoid cell lines, and Burkitt's lymphomas. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):823–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yong T., Meininger G. A., Linthicum D. S. Enhancement of histamine-induced vascular leakage by pertussis toxin in SJL/J mice but not BALB/c mice. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jun;45(1-2):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Paul W. E. CD4pos, NK1.1pos T cells promptly produce interleukin 4 in response to in vivo challenge with anti-CD3. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1285–1295. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Steinman L. The T lymphocyte in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:579–621. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Seventer G. A., Shimizu Y., Shaw S. Roles of multiple accessory molecules in T-cell activation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Jun;3(3):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]