Abstract
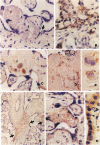
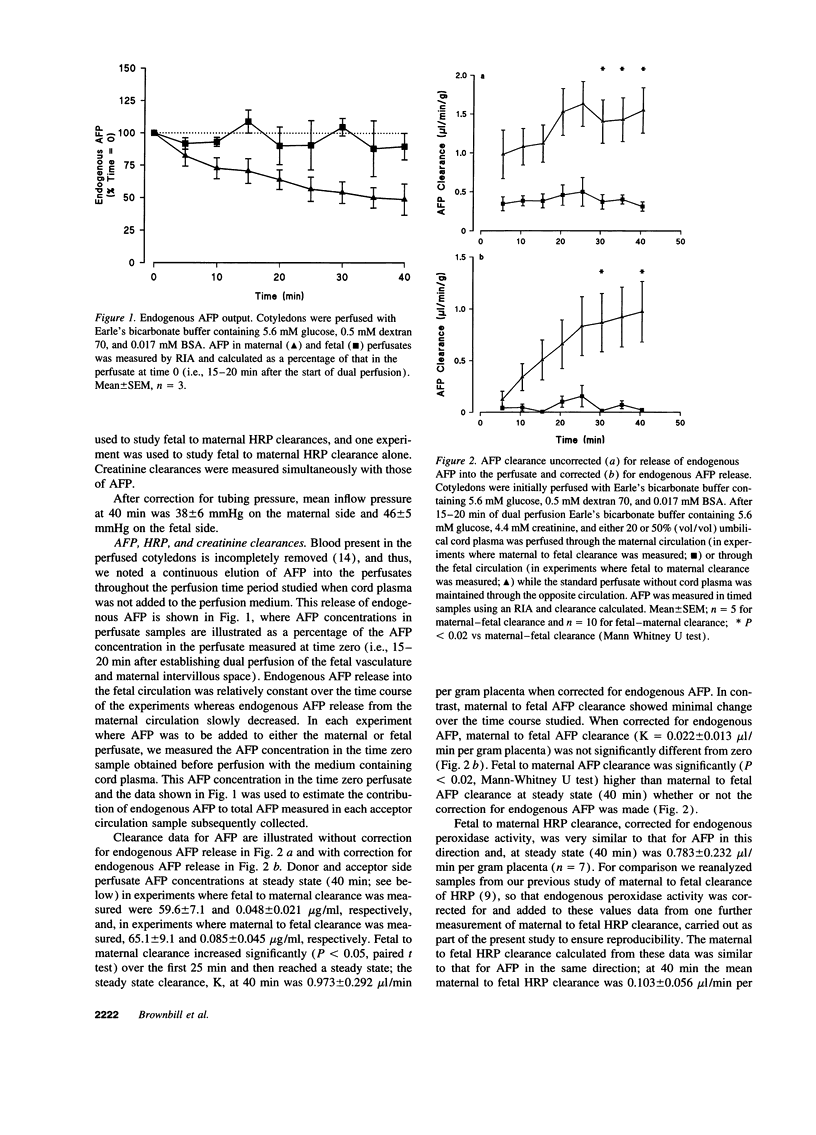
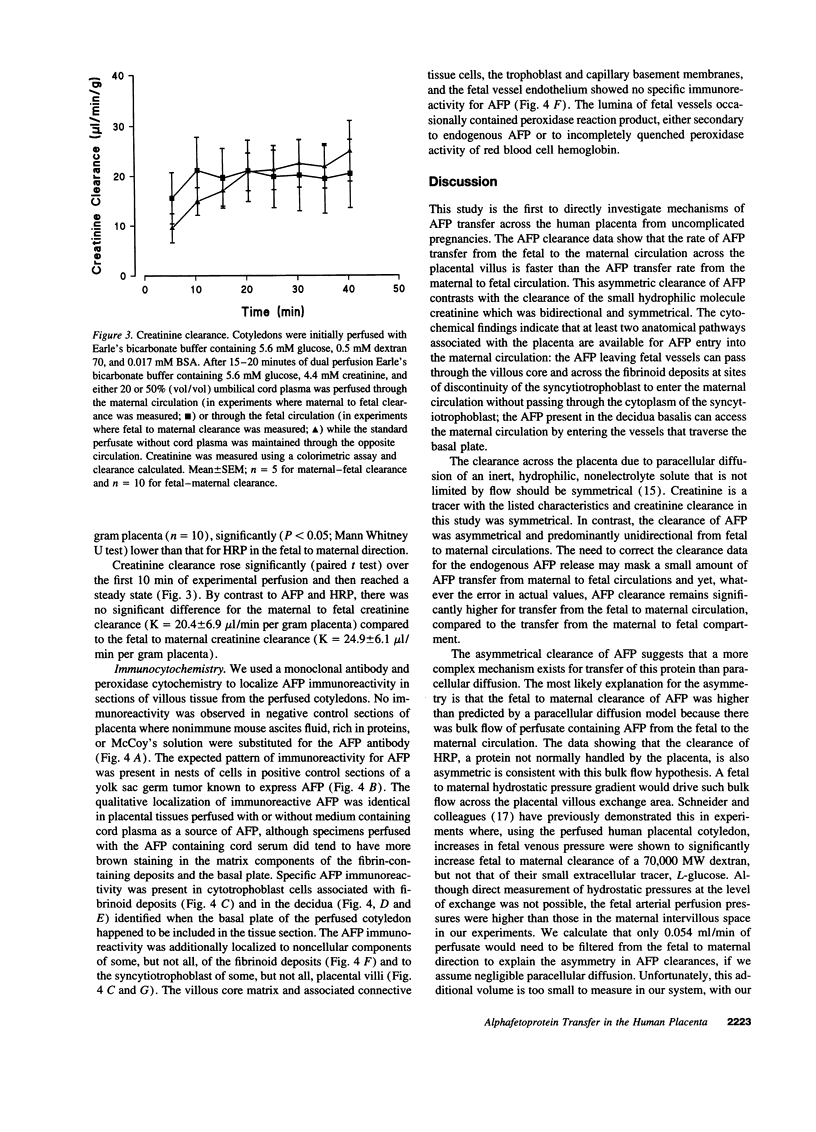
We investigated the mechanisms of alphafetoprotein (AFP) transfer across the human placenta by correlating measurements of AFP transfer with cytochemical localization of AFP. Placental cotyledons were dually perfused in vitro with either the fetal or maternal perfusate containing umbilical cord plasma as a source of AFP. Steady state AFP clearance, corrected for release of endogenous AFP, was 0.973 +/- 0.292 microliter/min per gram in the fetal to maternal direction (n = 10), significantly higher (P < 0.02) than that in the maternal to fetal direction (n = 5; 0.022 +/- 0.013 microliter/min per gram). Clearance of a similarly sized protein, horseradish peroxidase was also asymmetric but clearance of the small tracer creatinine was not. Using a monoclonal antibody, we localized AFP to fibrinoid deposits in regions of villi with discontinuities of the syncytiotrophoblast, to cytotrophoblast cells in these deposits, to syncytiotrophoblast on some villi, and to trophoblast cells in the decidua. We conclude that AFP transfer in the placenta is asymmetric and that there are two available pathways for AFP transfer: (a) from the fetal circulation into the villous core and across fibrinoid deposits at discontinuities in the villous syncytiotrophoblast to enter the maternal circulation; and (b) AFP present in the decidua could enter vessels that traverse the basal plate.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain M. D., Copas D. K., Landon M. J., Stacey T. E. In vivo permeability of the human placenta to inulin and mannitol. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:313–319. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain M. D., Copas D. K., Taylor A., Landon M. J., Stacey T. E. Permeability of the human placenta in vivo to four non-metabolized hydrophilic molecules. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:505–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berhe A., Bardsley W. G., Harkes A., Sibley C. P. Molecular charge effects on the protein permeability of the guinea-pig placenta. Placenta. 1987 Jul-Aug;8(4):365–380. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(87)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd P. A., Keeling J. W. Raised maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein in the absence of fetal abnormality--placental findings. A quantitative morphometric study. Prenat Diagn. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):369–373. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970060505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D., Jones C. J., Sibley C. P., Nelson D. M. Paracellular permeability pathways in the human placenta: a quantitative and morphological study of maternal-fetal transfer of horseradish peroxidase. Placenta. 1993 Jan-Feb;14(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. Fibrinoid necrosis of placental villi. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1968 Apr;75(4):448–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1968.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D. Normal biology of alpha-fetoprotein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Aug 22;259:7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb25397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Schmidt D., Darnule A. T., Weyland B. R., Rose E., Alpert E. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, and unconjugated estriol levels in midtrimester trisomy 18 pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992 May;166(5):1388–1392. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(92)91610-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illsley N. P., Hall S., Penfold P., Stacey T. E. Diffusional permeability of the human placenta. Contrib Gynecol Obstet. 1985;13:92–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khadempour M. H., Laing I., Gowenlock A. H. An optimised radioimmunoassay for maternal serum alpha1-fetoprotein using polyethylene glycol. Ann Clin Biochem. 1978 Jul;15(4):213–220. doi: 10.1177/000456327801500146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupferminc M. J., Tamura R. K., Wigton T. R., Glassenberg R., Socol M. L. Placenta accreta is associated with elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein. Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Aug;82(2):266–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. M., Crouch E. C., Curran E. M., Farmer D. R. Trophoblast interaction with fibrin matrix. Epithelialization of perivillous fibrin deposits as a mechanism for villous repair in the human placenta. Am J Pathol. 1990 Apr;136(4):855–865. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolini U., Fisk N. M., Talbert D. G., Rodeck C. H., Kochenour N. K., Greco P., Hubinont C., Santolaya J. Intrauterine manometry: technique and application to fetal pathology. Prenat Diagn. 1989 Apr;9(4):243–254. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970090404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salafia C. M., Silberman L., Herrera N. E., Mahoney M. J. Placental pathology at term associated with elevated midtrimester maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein concentration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 May;158(5):1064–1066. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Panigel M., Dancis J. Transfer across the perfused human placenta of antipyrine, sodium and leucine. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Nov 15;114(6):822–828. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90909-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Sodha R. J., Prögler M., Young M. P. Permeability of the human placenta for hydrophilic substances studied in the isolated dually in vitro perfused lobe. Contrib Gynecol Obstet. 1985;13:98–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. P., Boyd R. D. Control of transfer across the mature placenta. Oxf Rev Reprod Biol. 1988;10:382–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stulc J., Stulcová B. Asymmetrical transfer of inert hydrophilic solutes across rat placenta. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):R670–R675. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.265.3.R670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. L., Blakemore K. J. Evaluation of elevations in maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein: a review. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1990 May;45(5):269–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg K. L., Burry K. J., Adams A. K., Kirk E. P., Faber J. J. Permeability of placenta to inulin. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 May;158(5):1165–1169. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uriel J. The physiological role of alpha-fetoprotein in cell growth and differentiation. J Nucl Med Allied Sci. 1989 Jul-Sep;33(3 Suppl):12–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Furth R., Adinolfi M. In vitro synthesis of the foetal alpha 1-globulin in man. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1296–1299. doi: 10.1038/2221296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D. M., O'Grady J. P., Faber J. J., Thornburg K. L. Diffusion permeability of cyanocobalamin in human placenta. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):R459–R464. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.3.R459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]