Abstract
Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism is a dominantly inherited form of hypertension believed to be caused by the presence of a hybrid CYP11B1/CYP11B2 gene which has arisen from an unequal crossing over between the two CYP11B genes in a previous meiosis. We have studied a French pedigree with seven affected individuals in which two affected individuals also have adrenal tumors and two others have micronodular adrenal hyperplasia. One of the adrenal tumors and the surrounding adrenal tissue has been removed, giving a rare opportunity to study the regulation and action of the hybrid gene causing the disease. The hybrid CYP11B gene was demonstrated to be expressed at higher levels than either CYP11B1 or CYP11B2 in the cortex of the adrenal by RT-PCR and Northern blot analysis. In situ hybridization showed that both CYP11B1 and the hybrid gene were expressed in all three zones of the cortex. In cell culture experiments hybrid gene expression was stimulated by ACTH leading to increased production of aldosterone and the hybrid steroids characteristic of glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism. The genetic basis of the adrenal pathologies in this family is not known but may be related to the duplication causing the hyperaldosteronism.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnow K. M., Slutsker L., Vitek J., Cole T., Speiser P. W., New M. I., White P. C., Pascoe L. Mutations in the CYP11B1 gene causing congenital adrenal hyperplasia and hypertension cluster in exons 6, 7, and 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4552–4556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnow K. M., Tusie-Luna M. T., Pascoe L., Natarajan R., Gu J. L., Nadler J. L., White P. C. The product of the CYP11B2 gene is required for aldosterone biosynthesis in the human adrenal cortex. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1513–1522. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domalik L. J., Chaplin D. D., Kirkman M. S., Wu R. C., Liu W. W., Howard T. A., Seldin M. F., Parker K. L. Different isozymes of mouse 11 beta-hydroxylase produce mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1853–1861. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Sanchez C. E., Foecking M. F., Ferris M. W., Chavarri M. R., Uribe L., Gomez-Sanchez E. P. The production of monoclonal antibodies against aldosterone. Steroids. 1987 Jun;49(6):581–587. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(87)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Sanchez C. E., Montgomery M., Ganguly A., Holland O. B., Gomez-Sanchez E. P., Grim C. E., Weinberger M. H. Elevated urinary excretion of 18-oxocortisol in glucocorticoid-suppressible aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):1022–1024. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Sánchez C. E., León L. M., Gómez-Sánchez E. P. Biotin-hydrazide derivatives for the development of steroid enzyme-linked immunoassays. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Nov;43(6):523–527. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90239-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilvesmäki V., Voutilainen R. Interaction of phorbol ester and adrenocorticotropin in the regulation of steroidogenic P450 genes in human fetal and adult adrenal cell cultures. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1450–1458. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Haji M., Yanase T., Nawata H., Kato K., Ibayashi H. A case of glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism with aldosterone producing adenoma. Endocrinol Jpn. 1988 Apr;35(2):311–320. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.35.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Mitsuuchi Y., Toda K., Yokoyama Y., Miyahara K., Miura S., Ohnishi T., Ichikawa Y., Nakao K., Imura H. Role of steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase and steroid 18-hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1458–1462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrethon M. C., Jaillard C., Defayes G., Begeot M., Saez J. M. Human cultured adrenal fasciculata-reticularis cells are targets for angiotensin-II: effects on cytochrome P450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage, cytochrome P450 17 alpha-hydroxylase, and 3 beta-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid and proteins and on steroidogenic responsiveness to corticotropin and angiotensin-II. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 May;78(5):1212–1219. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.5.8175981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrethon M. C., Naville D., Begeot M., Saez J. M. Regulation of corticotropin receptor number and messenger RNA in cultured human adrenocortical cells by corticotropin and angiotensin II. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1828–1833. doi: 10.1172/JCI117168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G., Powers M., Rich G. M., Cook S., Ulick S., Lalouel J. M. A chimaeric 11 beta-hydroxylase/aldosterone synthase gene causes glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism and human hypertension. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):262–265. doi: 10.1038/355262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Dluhy R. G., Powers M., Rich G. M., Gutkin M., Fallo F., Gill J. R., Jr, Feld L., Ganguly A., Laidlaw J. C. Hereditary hypertension caused by chimaeric gene duplications and ectopic expression of aldosterone synthase. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):66–74. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukawa N., Nonaka Y., Ying Z., Higaki J., Ogihara T., Okamoto M. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAS encoding rat aldosterone synthase: variants of cytochrome P-450(11 beta). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 31;169(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91460-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo K., Kawai K., Tsuchiyama H., Ueki Y. Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism. Ultrastructural observation of a case. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1985 Nov;35(6):1511–1519. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1985.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K., Yoshinaga K., Goto K., Katsushima I., Maebashi M., Demura H., Iino M., Demura R., Torikai T. A case of glucocorticoid-responsive hyperaldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Dec;28(12):1807–1815. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-12-1807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara K., Kawamoto T., Mitsuuchi Y., Toda K., Imura H., Gordon R. D., Shizuta Y. The chimeric gene linked to glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism encodes a fused P-450 protein possessing aldosterone synthase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):885–891. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet E., Dupont J., Vitek A., White P. C. Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta). J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20961–20967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I., Peterson R. E. A new form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):300–305. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka Y., Okamoto M., Morohashi K., Kirita S., Hashimoto T., Omura T. Functional expression of cDNAs for bovine 11 beta-hydroxylase-aldosterone synthases, P450(11 beta)-2 and -3 and their chimeras. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):779–780. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90423-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberfield S. E., Levine L. S., Stoner E., Chow D., Rauh W., Greig F., Lee S. M., Lightner E., Witte M., New M. I. Adrenal glomerulosa function in patients with dexamethasone-suppressible hyperaldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):158–164. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogishima T., Mitani F., Ishimura Y. Isolation of two distinct cytochromes P-45011 beta with aldosterone synthase activity from bovine adrenocortical mitochondria. J Biochem. 1989 Apr;105(4):497–499. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogishima T., Suzuki H., Hata J., Mitani F., Ishimura Y. Zone-specific expression of aldosterone synthase cytochrome P-450 and cytochrome P-45011 beta in rat adrenal cortex: histochemical basis for the functional zonation. Endocrinology. 1992 May;130(5):2971–2977. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.5.1572304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Wada A., Lauber M., Yamano T., Okamoto M. Aldosterone biosynthesis in mitochondria of isolated zones of adrenal cortex. J Steroid Biochem. 1988 Jul;31(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascoe L., Curnow K. M. Genetic recombination as a cause of inherited disorders of aldosterone and cortisol biosynthesis and a contributor to genetic variation in blood pressure. Steroids. 1995 Jan;60(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(94)00003-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
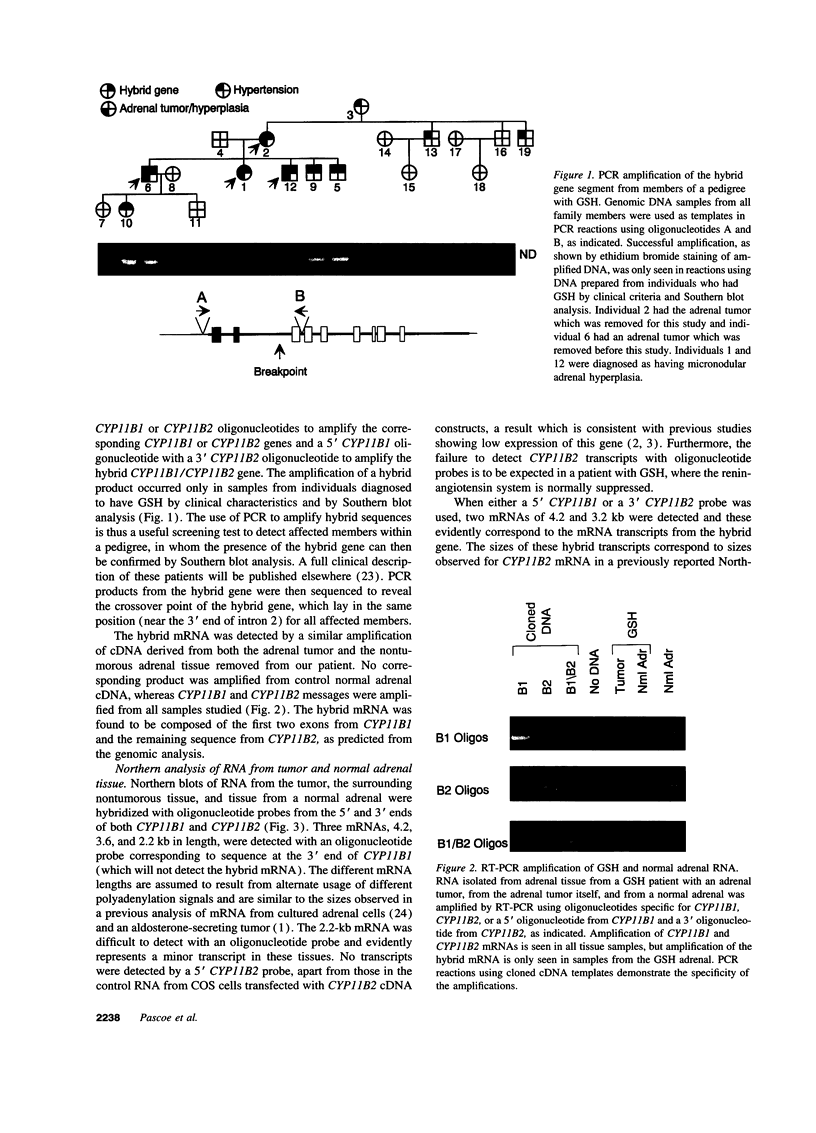
- Pascoe L., Curnow K. M., Slutsker L., Connell J. M., Speiser P. W., New M. I., White P. C. Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism results from hybrid genes created by unequal crossovers between CYP11B1 and CYP11B2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8327–8331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascoe L., Curnow K. M., Slutsker L., Rösler A., White P. C. Mutations in the human CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) gene causing corticosterone methyloxidase II deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4996–5000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasano H., Okamoto M., Sasano N. Immunohistochemical study of cytochrome P-450 11 beta-hydroxylase in human adrenal cortex with mineralo- and glucocorticoid excess. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;413(4):313–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00783023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibony M., Gasc J. M., Soubrier F., Alhenc-Gelas F., Corvol P. Gene expression and tissue localization of the two isoforms of angiotensin I converting enzyme. Hypertension. 1993 Jun;21(6 Pt 1):827–835. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.21.6.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Regulation of the synthesis of steroidogenic enzymes in adrenal cortical cells by ACTH. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:427–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. J., Ruse J. L., Laidlaw J. C. Hypertension, increased aldosterone secretion and low plasma renin activity relieved by dexamethasone. Can Med Assoc J. 1966 Nov 26;95(22):1109–1119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulick S., Chan C. K., Gill J. R., Jr, Gutkin M., Letcher L., Mantero F., New M. I. Defective fasciculata zone function as the mechanism of glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Nov;71(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-5-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulick S., Chu M. D., Land M. Biosynthesis of 18-oxocortisol by aldosterone-producing adrenal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5498–5502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Haniu M., Shively J. E., Shen W. H., Hall P. The synthesis of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex. Two zones (fasciculata and glomerulosa) possess one enzyme for 11 beta-, 18-hydroxylation, and aldehyde synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3556–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]