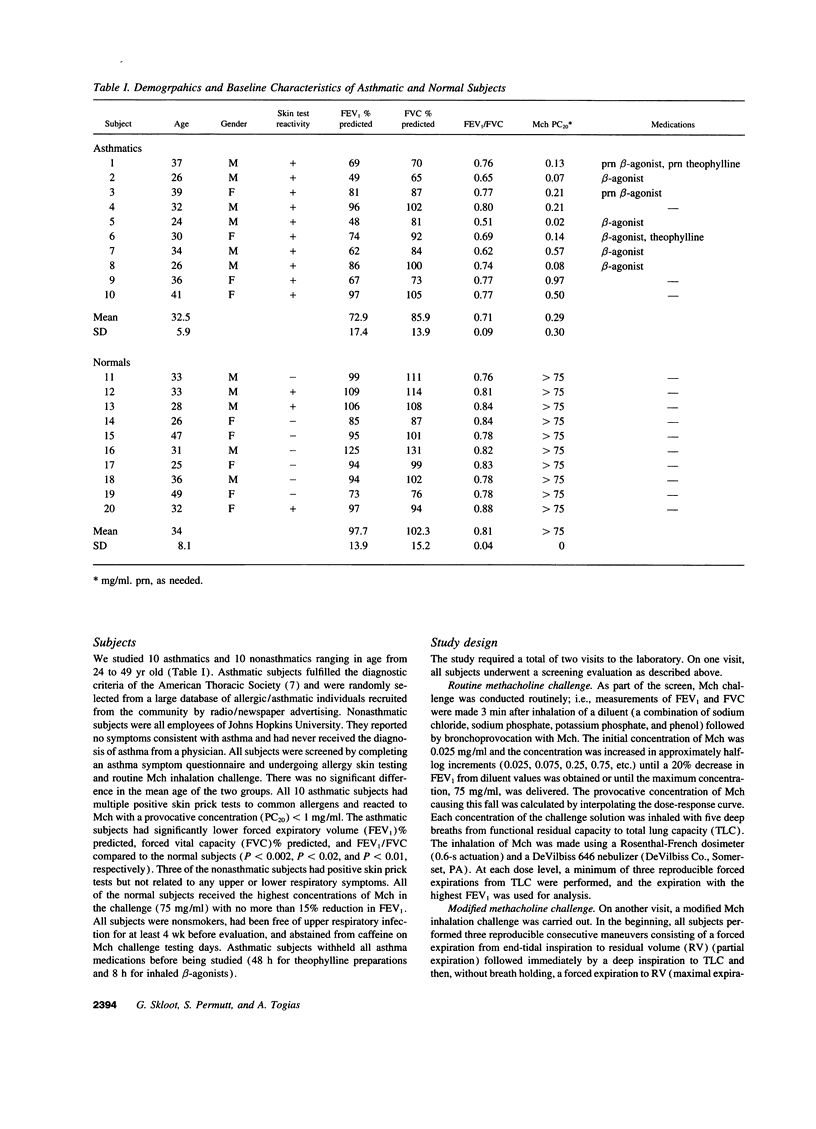
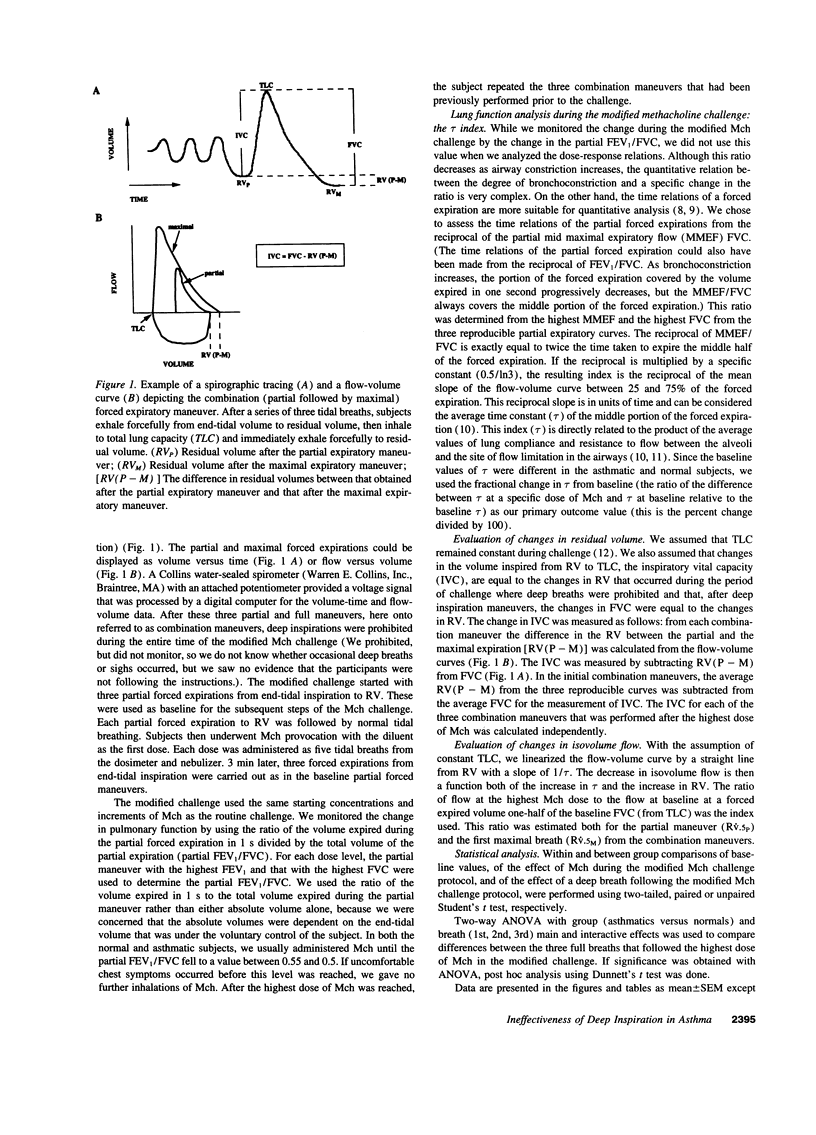
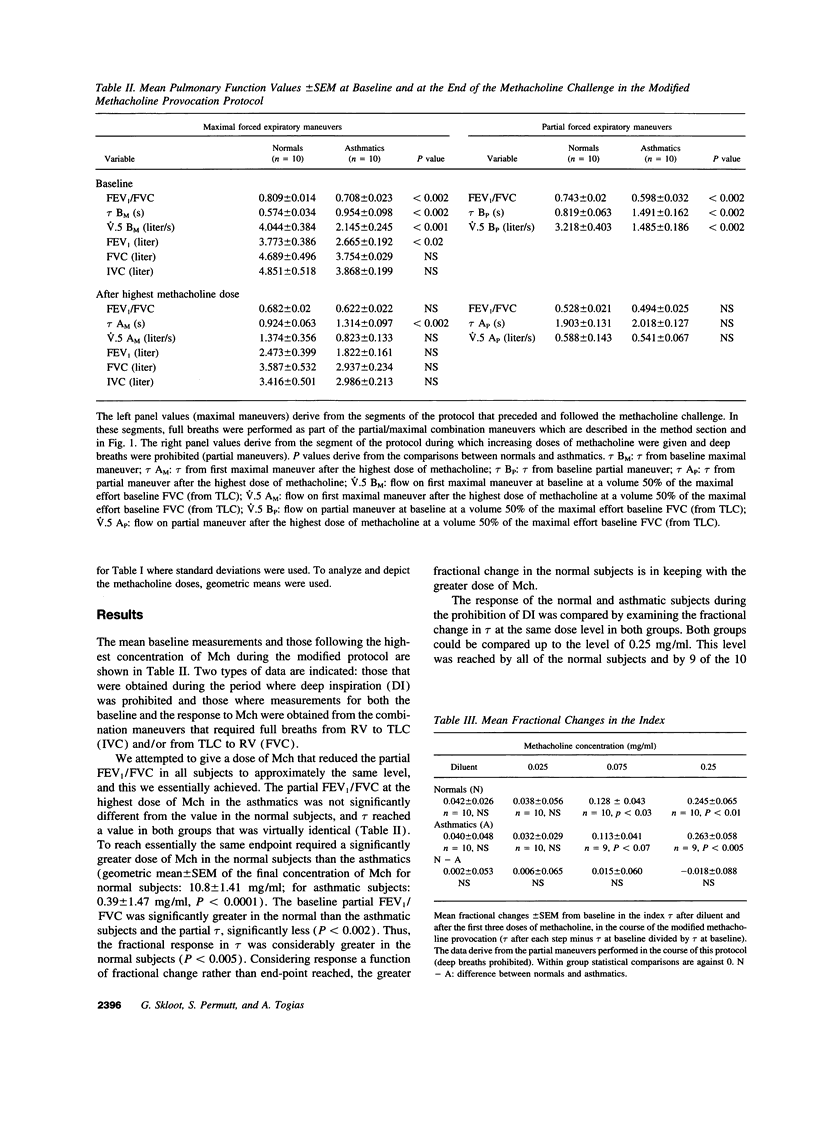
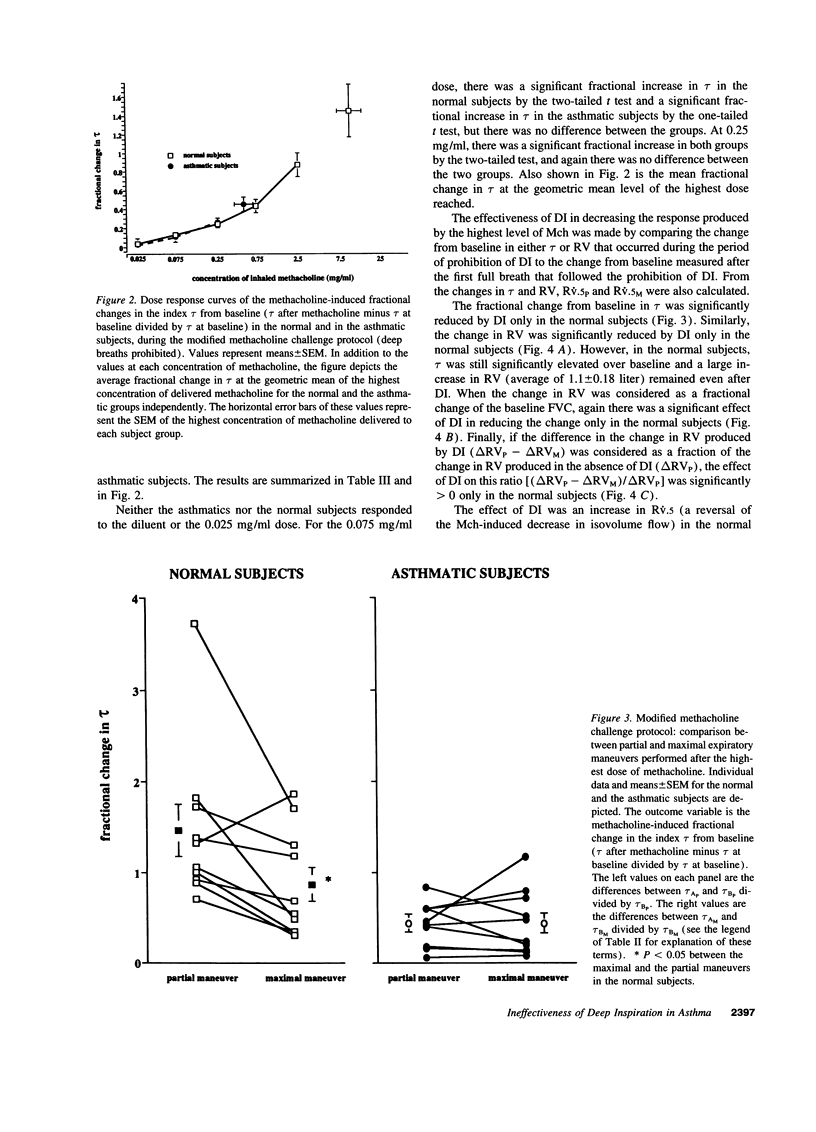
Abstract
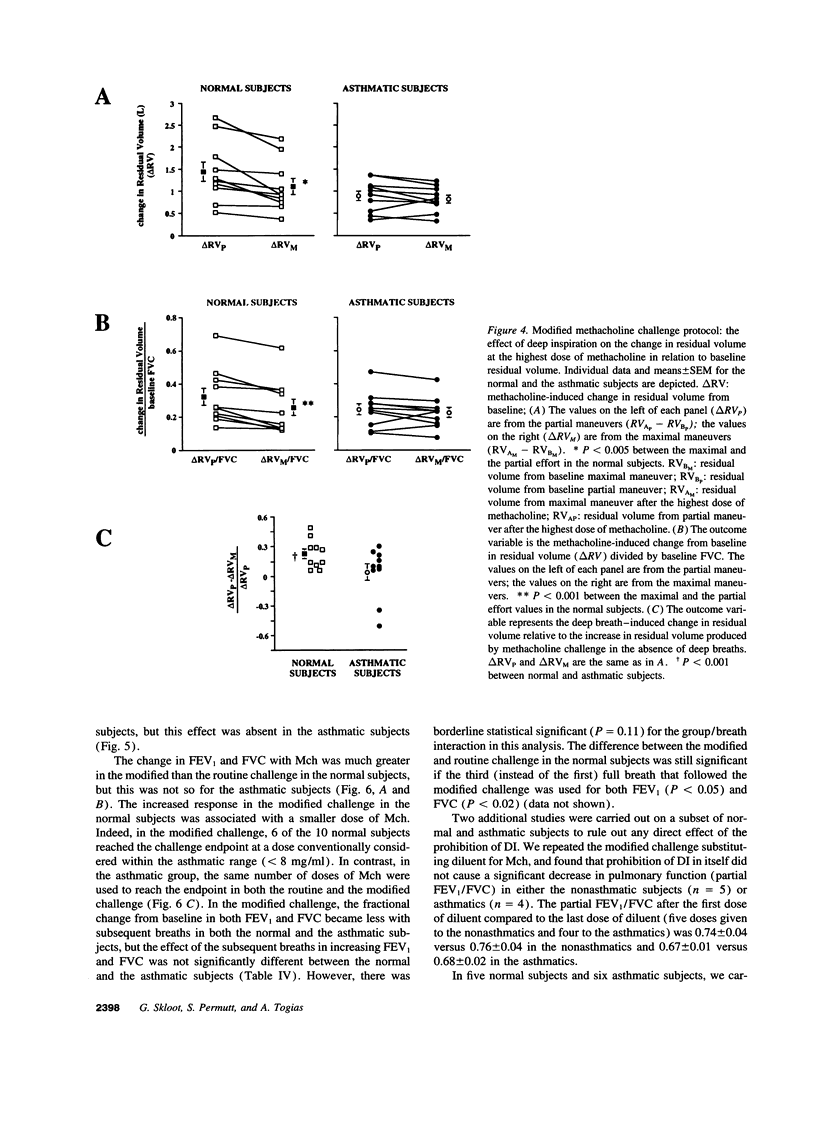
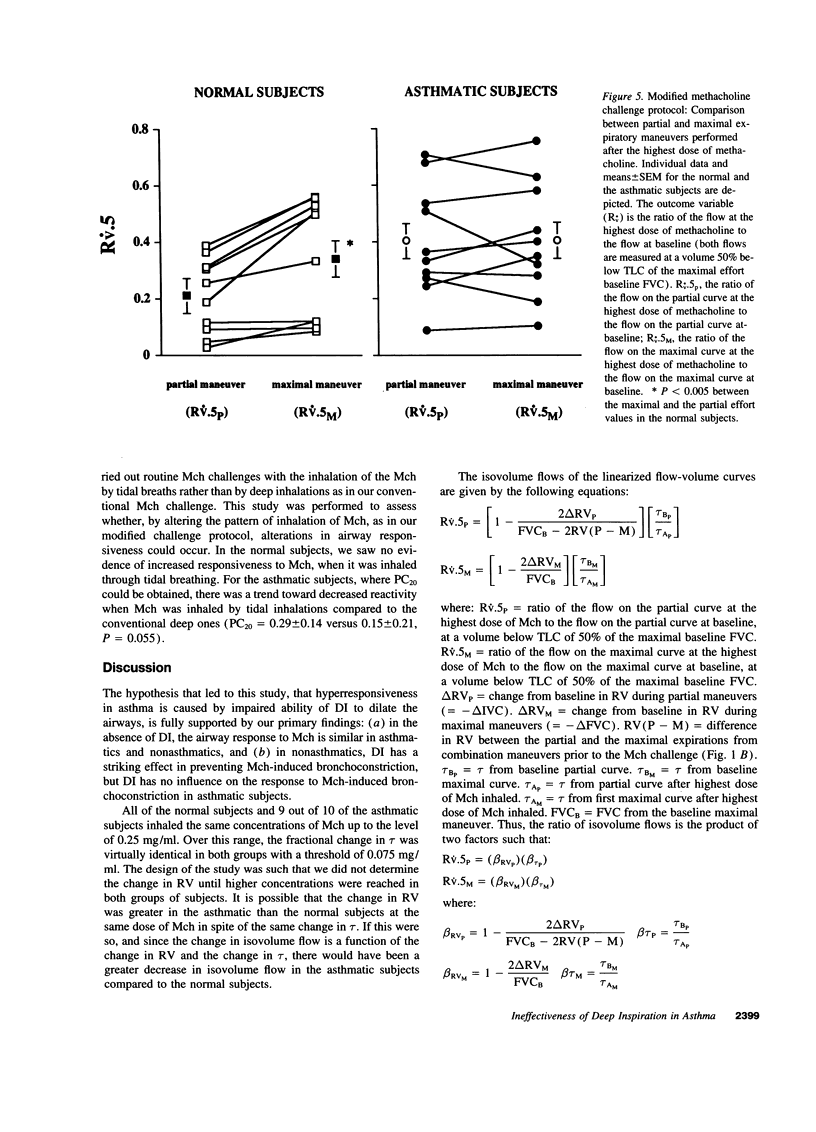
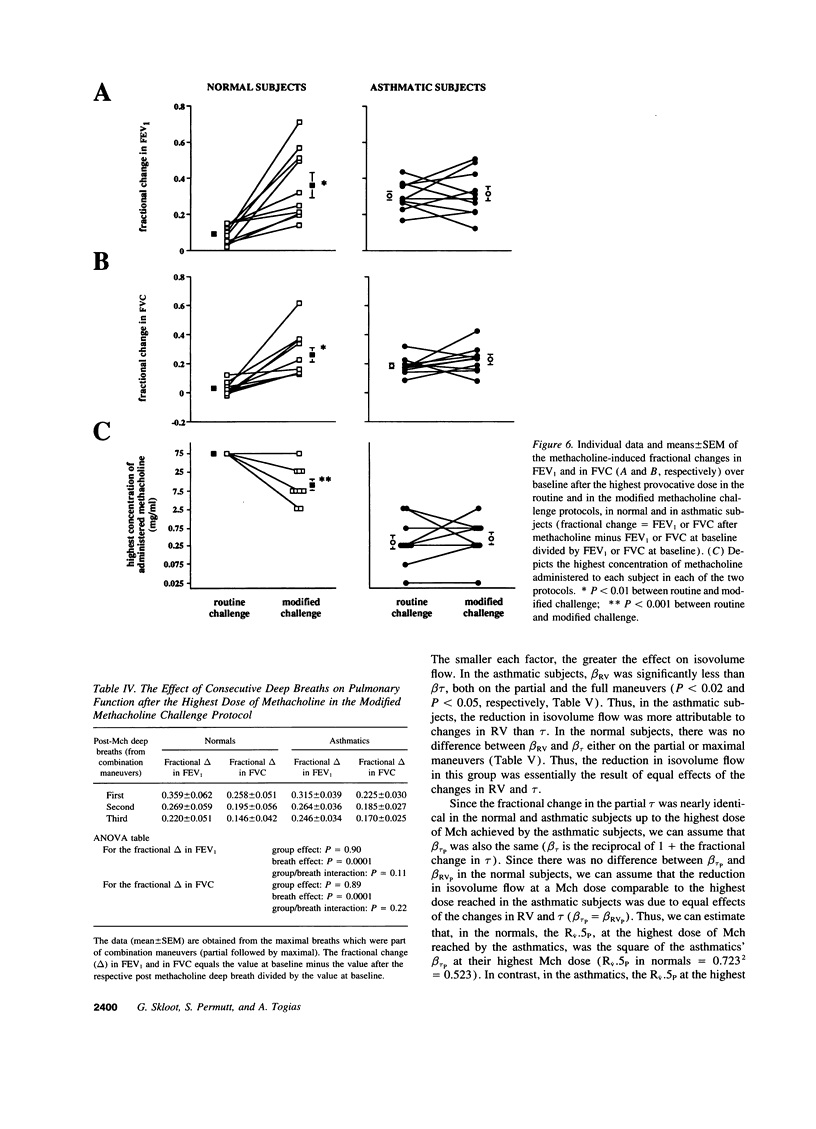
We hypothesized that hyperresponsiveness in asthma is caused by an impairment in the ability of inspiration to stretch airway smooth muscle. If the hypothesis was correct, we reasoned that the sensitivity to inhaled methacholine in normal and asthmatic subjects should be the same if the challenge was carried out under conditions where deep inspirations were prohibited. 10 asthmatic and 10 normal subjects received increasing concentrations of inhaled methacholine under conditions where forced expirations from a normal end-tidal inspiration were performed. When no deep inspirations were allowed, the response to methacholine was similar in the normal and asthmatic subjects, compatible with the hypothesis we propose. Completely contrary to our expectations, however, was the marked responsivity to methacholine that remained in the normal subjects after deep breaths were initiated. 6 of the 10 normal subjects had > 20% reduction in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV 1) at doses of methacholine < 8 mg/ml, whereas there was < 15% reduction with 75 mg/ml during routine challenge. The ability of normal subjects to develop asthmatic responses when the modulating effects of increases in lung volume was voluntarily suppressed suggests that an intrinsic impairment of the ability of inspiration to stretch airway smooth muscle is a major feature of asthma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burns C. B., Taylor W. R., Ingram R. H., Jr Effects of deep inhalation in asthma: relative airway and parenchymal hysteresis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Nov;59(5):1590–1596. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.5.1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebatch H. J., Finucane K. E., Smith M. M. Pulmonary conductance and elastic recoil relationships in asthma and emphysema. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Feb;34(2):143–153. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicpinigaitis P. V., Spungen A. M., Bauman W. A., Absgarten A., Almenoff P. L. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness after cervical spinal cord injury. Chest. 1994 Apr;105(4):1073–1076. doi: 10.1378/chest.105.4.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding D. J., Martin J. G., Macklem P. T. Effects of lung volume on maximal methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction in normal humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1324–1330. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish J. E., Ankin M. G., Kelly J. F., Peterman V. I. Regulation of bronchomotor tone by lung inflation in asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 May;50(5):1079–1086. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.5.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Mead J. Time dependence of flow-volume curves. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Dec;37(6):793–797. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunst S. J. Contractile force of canine airway smooth muscle during cyclical length changes. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):759–769. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunst S. J., Stropp J. Q. Pressure-volume and length-stress relationships in canine bronchi in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jun;64(6):2522–2531. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.6.2522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunst S. J., Stropp J. Q., Service J. Mechanical modulation of pressure-volume characteristics of contracted canine airways in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 May;68(5):2223–2229. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.5.2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunst S. J., Warner D. O., Wilson T. A., Hyatt R. E. Parenchymal interdependence and airway response to methacholine in excised dog lobes. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Dec;65(6):2490–2497. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.6.2490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby J. G., Juniper E. F., Hargreave F. E., Zamel N. Total lung capacity does not change during methacholine-stimulated airway narrowing. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Dec;61(6):2144–2147. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.6.2144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai-Fook S. J., Beck K. C., Sutcliffe A. M., Donaldson J. T. Effect of edema and height on bronchial diameter and shape in excised dog lung. Respir Physiol. 1984 Feb;55(2):223–237. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai-Fook S. J., Hyatt R. E., Rodarte J. R. Effect of parenchymal shear modulus and lung volume on bronchial pressure-diameter behavior. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Jun;44(6):859–868. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.44.6.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapp N. L., Hyatt R. E. Some factors affecting the relationship of maximal expiratory flow to lung volume in health and disease. Dis Chest. 1967 May;51(5):475–481. doi: 10.1378/chest.51.5.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklem P. T. Mechanical factors determining maximum bronchoconstriction. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1989 Jun;6:516s–519s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg P., Larsson K., Sundblad B. M., Zhiping W. Importance of the time interval between FEV1 measurements in a methacholine provocation test. Eur Respir J. 1993 May;6(5):680–686. doi: 10.1016/s0012-3692(16)47463-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marthan R., Woolcock A. J. Is a myogenic response involved in deep inspiration-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatics? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Nov;140(5):1354–1358. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.5.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J., Takishima T., Leith D. Stress distribution in lungs: a model of pulmonary elasticity. J Appl Physiol. 1970 May;28(5):596–608. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.5.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michoud M. C., Lelorier J., Amyot R. Factors modulating the interindividual variability of airway responsiveness to histamine. The influence of H1 and H2 receptors. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1981;17(5):807–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh P. S., Proctor D. F., Permutt S., Kelly B., Evering S. Bronchial closure with Mecholyl in excised dog lobes. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Sep;31(3):409–415. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NADEL J. A., TIERNEY D. F. Effect of a previous deep inspiration on airway resistance in man. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Jul;16:717–719. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.4.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham W. M., Shepard R. H., Norman P. S., Fish J. E. Analysis of time course and magnitude of lung inflation effects on airway tone: relation to airway reactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2):240–245. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino R., Violante B., Crimi E., Brusasco V. Time course and calcium dependence of sustained bronchoconstriction induced by deep inhalation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Dec;144(6):1262–1266. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.6.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino R., Violante B., Selleri R., Brusasco V. Changes in residual volume during induced bronchoconstriction in healthy and asthmatic subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Aug;150(2):363–368. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.2.8049816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliss L. B., Ingenito E. P., Ingram R. H., Jr Responsiveness, inflammation, and effects of deep breaths on obstruction in mild asthma. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 May;66(5):2298–2304. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.5.2298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pride N. B., Permutt S., Riley R. L., Bromberger-Barnea B. Determinants of maximal expiratory flow from the lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Nov;23(5):646–662. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.5.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hoppin F. G., Jr Hysteresis of contracted airway smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Dec;47(6):1251–1262. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.6.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterk P. J., Daniel E. E., Zamel N., Hargreave F. E. Limited bronchoconstriction to methacholine using partial flow-volume curves in nonasthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):272–277. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley J. R., Paré P. D., Engel L. A. Reversibility of induced bronchoconstriction by deep inspiration in asthmatic and normal subjects. Eur Respir J. 1989 Apr;2(4):331–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock A. J., Salome C. M., Yan K. The shape of the dose-response curve to histamine in asthmatic and normal subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jul;130(1):71–75. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



