Abstract
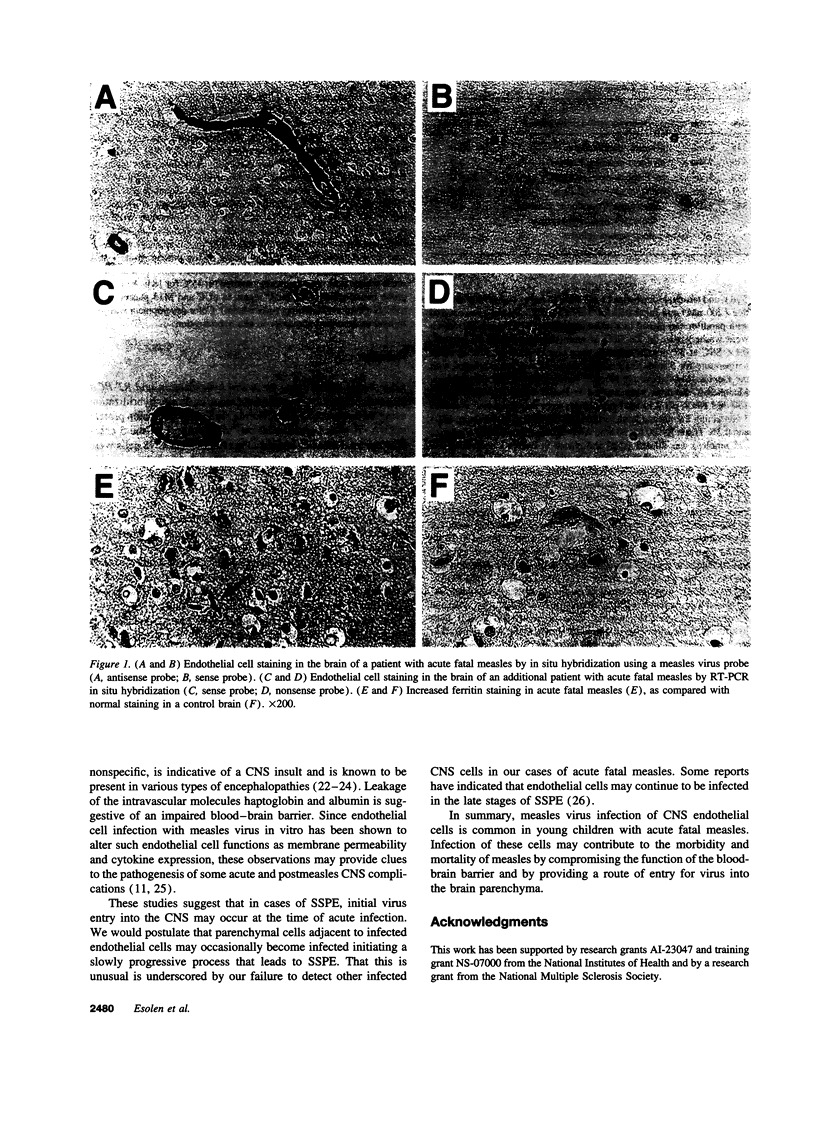
Neurologic diseases are important complications of measles. The role of virus infection of the central nervous system as well as the route of virus entry has been unclear. Five autopsied cases of individuals who died with severe acute measles 3-10 d after the onset of the rash were studied for evidence of viral involvement of the central nervous system. In all cases, in situ hybridization and RT-PCR in situ hybridization techniques showed endothelial cell infection. Immunoperoxidase staining with an anti-ferritin antibody revealed a reactive microgliosis. These data suggest that endothelial cells in the brain are frequently infected during acute fatal measles. This site of infection may provide a portal of entry for virus in individuals who subsequently develop subacute sclerosing panencephalitis or measles inclusion body encephalitis and a target for immunologic reactions in post-measles encephalomyelitis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chakrabarti R., Hofman F. M., Pandey R., Mathes L. E., Roy-Burman P. Recombination between feline exogenous and endogenous retroviral sequences generates tropism for cerebral endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1994 Feb;144(2):348–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. H., Allen I. V., Hurwitz L. J., Millar J. H. Measles-virus antibody and antigen in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Lancet. 1967 Mar 11;1(7489):542–544. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. R., Menzies S. L., St Martin S. M., Mufson E. J. Cellular distribution of transferrin, ferritin, and iron in normal and aged human brains. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):595–611. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka E., Bayer P. I., Büki K., Várady G. Influence of the measles virus on the proliferation and protein synthesis of aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1990;37(2):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edington N., Smyth B., Griffiths L. The role of endothelial cell infection in the endometrium, placenta and foetus of equid herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) abortions. J Comp Pathol. 1991 May;104(4):379–387. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9975(08)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. L., Ransohoff R. M., McMahon J. T., Jacobs B. S., Barna B. P. Characterization of adult human astrocytes derived from explant culture. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Dec;27(4):697–705. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman B. B. Diffuse microgliosis associated with cerebral atrophy in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1993 Jul;34(1):65–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson S. L., Friedman H. M., Cines D. B. Viral infection of vascular endothelial cells alters production of colony-stimulating activity. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1382–1390. doi: 10.1172/JCI112114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes I., Jenney M. E., Newton R. W., Morris D. J., Klapper P. E. Measles encephalitis during immunosuppressive treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Jun;68(6):775–778. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.6.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtrel B., Chakrabarti L., Hurtrel M., Montagnier L. Target cells during early SIV encephalopathy. Res Virol. 1993 Jan-Feb;144(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2516(06)80010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Griffin D. E., Hirsch R. L., Wolinsky J. S., Roedenbeck S., Lindo de Soriano I., Vaisberg A. Measles encephalomyelitis--clinical and immunologic studies. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):137–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J., Zhou A. L., McQuaid S., Cosby S. L., Allen I. V. Cerebral endothelial cell infection by measles virus in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: ultrastructural and in situ hybridization evidence. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1991 Aug;17(4):289–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1991.tb00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laegreid W. W., Burrage T. G., Stone-Marschat M., Skowronek A. Electron microscopic evidence for endothelial infection by African horsesickness virus. Vet Pathol. 1992 Nov;29(6):554–556. doi: 10.1177/030098589202900615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D. L. FREQUENCY OF COMPLICATIONS OF MEASLES, 1963. REPORT ON A NATIONAL INQUIRY BY THE PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY SERVICE IN COLLABORATION WITH THE SOCIETY OF MEDICAL OFFICERS OF HEALTH. Br Med J. 1964 Jul 11;2(5401):75–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5401.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean D. M., Best J. M., Smith P. A., Larke R. P., McNaughton G. A. Viral infections of Toronto children during 1965: II. Measles encephalitis and other complications. Can Med Assoc J. 1966 Apr 23;94(17):905–910. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. R., Griffin D. E., Obriecht C. R., Vaisberg A. J., Johnson R. T. Acute measles in patients with and without neurological involvement: distribution of measles virus antigen and RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):433–442. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyanagi S., Rorke L. B., Katz M., Koprowski H. Histopathology and electron microscopy of three cases of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE). Acta Neuropathol. 1971;18(1):58–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00684475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Lavi E., Blank K. J., Gaulton G. N. Intracerebral hemorrhages and syncytium formation induced by endothelial cell infection with a murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6015–6024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6015-6024.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Lavi E., Stieber A., Gaulton G. N. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarction and hemorrhage induced by a murine leukemia virus. Lab Invest. 1994 Jan;70(1):78–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressetar H. G., Webster H. D., Stoner G. L. Brain vascular endothelial cells express JC virus large tumor antigen in immunocompetent and cyclophosphamide-treated hamsters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8170–8174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lanier M., Davis L. E., Blisard K. S., Woodfin B. M., Wallace J. M., Caskey L. S. Influenza A virus in the mouse: hepatic and cerebral lesions in a Reye's syndrome-like illness. Int J Exp Pathol. 1991 Oct;72(5):489–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluga E., Budka H., Jellinger K., Pichler E. SSPE-like inclusion body disorder in treated childhood leukemia. Acta Neuropathol Suppl. 1975;Suppl 6:267–272. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-08456-4_47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soilu-Hänninen M., Erälinna J. P., Hukkanen V., Röyttä M., Salmi A. A., Salonen R. Semliki Forest virus infects mouse brain endothelial cells and causes blood-brain barrier damage. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6291–6298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6291-6298.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Nelson J. A. Role of human immunodeficiency virus and cytomegalovirus in AIDS encephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):73–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Umemura T., Goryo M., Itakura C. Chronic lesions of thrombo-embolic meningo-encephalomyelitis in calves. J Comp Pathol. 1991 Oct;105(3):303–312. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9975(08)80198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]