Abstract
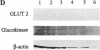
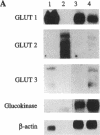
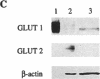
Glucose homeostasis is controlled by a glucose sensor in pancreatic beta-cells. Studies on rodent beta-cells have suggested a role for GLUT2 and glucokinase in this control function and in mechanisms leading to diabetes. Little direct evidence exists so far to implicate these two proteins in glucose recognition by human beta-cells. The present in vitro study investigates the role of glucose transport and phosphorylation in beta-cell preparations from nondiabetic human pancreata. Human beta-cells differ from rodent beta-cells in glucose transporter gene expression (predominantly GLUT1 instead of GLUT2), explaining their low Km (3 mmol/liter) and low VMAX (3 mmol/min per liter) for 3-O-methyl glucose transport. The 100-fold lower GLUT2 abundance in human versus rat beta-cells is associated with a 10-fold slower uptake of alloxan, explaining their resistance to this rodent diabetogenic agent. Human and rat beta-cells exhibit comparable glucokinase expression with similar flux-generating influence on total glucose utilization. These data underline the importance of glucokinase but not of GLUT2 in the glucose sensor of human beta-cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedoya F. J., Wilson J. M., Ghosh A. K., Finegold D., Matschinsky F. M. The glucokinase glucose sensor in human pancreatic islet tissue. Diabetes. 1986 Jan;35(1):61–67. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E. Mechanisms of glucose stimulated insulin secretion in health and in diabetes: some re-evaluations and proposals. Diabetologia. 1975 Feb;11(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00422811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu K. C., Province M. A., Permutt M. A. Glucokinase gene is genetic marker for NIDDM in American blacks. Diabetes. 1992 Jul;41(7):843–849. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.7.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Leiser M., Wu Y. J., Fusco-DeMane D., Emran O. A., Surana M., Jetton T. L., Magnuson M. A., Weir G., Fleischer N. Ribozyme-mediated attenuation of pancreatic beta-cell glucokinase expression in transgenic mice results in impaired glucose-induced insulin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Korbutt G. S., Hellerström C. Prolonged exposure of human pancreatic islets to high glucose concentrations in vitro impairs the beta-cell function. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1263–1268. doi: 10.1172/JCI115989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Pipeleers D. G., Ling Z., Welsh N., Hellerström C., Andersson A. Major species differences between humans and rodents in the susceptibility to pancreatic beta-cell injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9253–9256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein S. C., Hoffman M. D., Matsutani A., Permutt M. A. Linkage analysis of GLUT1 (HepG2) and GLUT2 (liver/islet) genes in familial NIDDM. Diabetes. 1992 Dec;41(12):1660–1667. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.12.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber S., BeltrandelRio H., Johnson J. H., Noel R. J., Cassidy L. E., Clark S., Becker T. C., Hughes S. D., Newgard C. B. GLUT-2 gene transfer into insulinoma cells confers both low and high affinity glucose-stimulated insulin release. Relationship to glucokinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11523–11529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorus F. K., Malaisse W. J., Pipeleers D. G. Differences in glucose handling by pancreatic A- and B-cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1196–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Brant A. M., Kahn B. B., Shepherd P. R., McCoid S. C., Gibbs E. M. Expression of the brain-type glucose transporter is restricted to brain and neuronal cells in mice. Diabetologia. 1992 Apr;35(4):304–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00401196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Thomas H. M., Jess T. J., Bell G. I. Expression of human glucose transporters in Xenopus oocytes: kinetic characterization and substrate specificities of the erythrocyte, liver, and brain isoforms. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5139–5145. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimberg H., De Vos A., Pipeleers D., Thorens B., Schuit F. Differences in glucose transporter gene expression between rat pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells are correlated to differences in glucose transport but not in glucose utilization. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 14;270(15):8971–8975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimberg H., De Vos A., Vandercammen A., Van Schaftingen E., Pipeleers D., Schuit F. Heterogeneity in glucose sensitivity among pancreatic beta-cells is correlated to differences in glucose phosphorylation rather than glucose transport. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2873–2879. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. D., Johnson J. H., Quaade C., Newgard C. B. Engineering of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and biosynthesis in non-islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):688–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. D., Quaade C., Johnson J. H., Ferber S., Newgard C. B. Transfection of AtT-20ins cells with GLUT-2 but not GLUT-1 confers glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Relationship to glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15205–15212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Möbius G., Seitz H. J., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Tissue-specific expression of glucokinase: identification of the gene product in liver and pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):1998–2001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Newgard C. B., Milburn J. L., Lodish H. F., Thorens B. The high Km glucose transporter of islets of Langerhans is functionally similar to the low affinity transporter of liver and has an identical primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6548–6551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Ogawa A., Chen L., Orci L., Newgard C. B., Alam T., Unger R. H. Underexpression of beta cell high Km glucose transporters in noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.2237405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Katz N. Functional specialization of different hepatocyte populations. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):708–764. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. J. Elusive proximal signals of beta-cells for insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1990 Dec;39(12):1461–1466. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.12.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M. Glucokinase as glucose sensor and metabolic signal generator in pancreatic beta-cells and hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):647–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F., Liang Y., Kesavan P., Wang L., Froguel P., Velho G., Cohen D., Permutt M. A., Tanizawa Y., Jetton T. L. Glucokinase as pancreatic beta cell glucose sensor and diabetes gene. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2092–2098. doi: 10.1172/JCI116809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Kruse M., Strube M., Riggs A. C., Chiu K. C., Permutt M. A. A mutation in the Glut2 glucose transporter gene of a diabetic patient abolishes transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):17765–17767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa A., Johnson J. H., Ohneda M., McAllister C. T., Inman L., Alam T., Unger R. H. Roles of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction in dexamethasone-induced diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):497–504. doi: 10.1172/JCI115886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Noma Y., Davalli A. M., Wu Y. J., Thorens B., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Loss of glucose-induced insulin secretion and GLUT2 expression in transplanted beta-cells. Diabetes. 1995 Jan;44(1):75–79. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H., Ravazzola M., Ogawa A., Komiya I., Baetens D., Lodish H. F., Thorens B. Reduced beta-cell glucose transporter in new onset diabetic BB rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1615–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI114883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permutt M. A., Koranyi L., Keller K., Lacy P. E., Scharp D. W., Mueckler M. Cloning and functional expression of a human pancreatic islet glucose-transporter cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8688–8692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnedl W. J., Ferber S., Johnson J. H., Newgard C. B. STZ transport and cytotoxicity. Specific enhancement in GLUT2-expressing cells. Diabetes. 1994 Nov;43(11):1326–1333. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.11.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino Y., Yamamoto T., Inoue K., Imamura M., Kadowaki S., Kojima H., Fujikawa J., Imura H. Abnormal facilitative glucose transporter gene expression in human islet cell tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jan;76(1):75–78. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.1.8421107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slieker L. J., Sundell K. L., Heath W. F., Osborne H. E., Bue J., Manetta J., Sportsman J. R. Glucose transporter levels in tissues of spontaneously diabetic Zucker fa/fa rat (ZDF/drt) and viable yellow mouse (Avy/a). Diabetes. 1992 Feb;41(2):187–193. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Liang Y., Najafi H., Lodish H. F., Matschinsky F. M. Expression and function of GLUT-1 and GLUT-2 glucose transporter isoforms in cells of cultured rat pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17241–17247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Lodish H. F., Brown D. Differential localization of two glucose transporter isoforms in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C286–C294. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Wu Y. J., Leahy J. L., Weir G. C. The loss of GLUT2 expression by glucose-unresponsive beta cells of db/db mice is reversible and is induced by the diabetic environment. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):77–85. doi: 10.1172/JCI115858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trus M. D., Zawalich W. S., Burch P. T., Berner D. K., Weill V. A., Matschinsky F. M. Regulation of glucose metabolism in pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1981 Nov;30(11):911–922. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.11.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Diabetic hyperglycemia: link to impaired glucose transport in pancreatic beta cells. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1200–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.2006409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Solanes G., Fernández-Alvarez J., Pujol A., Ferrer J., Asins G., Gomis R., Bosch F. Expression of GLUT-2 antisense RNA in beta cells of transgenic mice leads to diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28543–28546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velho G., Froguel P., Clement K., Pueyo M. E., Rakotoambinina B., Zouali H., Passa P., Cohen D., Robert J. J. Primary pancreatic beta-cell secretory defect caused by mutations in glucokinase gene in kindreds of maturity onset diabetes of the young. Lancet. 1992 Aug 22;340(8817):444–448. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91768-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. C., McDaniel M. L., Lacy P. E. Alloxan uptake by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1978 Jun;102(6):1847–1855. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-6-1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Hinkle P. C. Kinetic properties of the reconstituted glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8907–8914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]