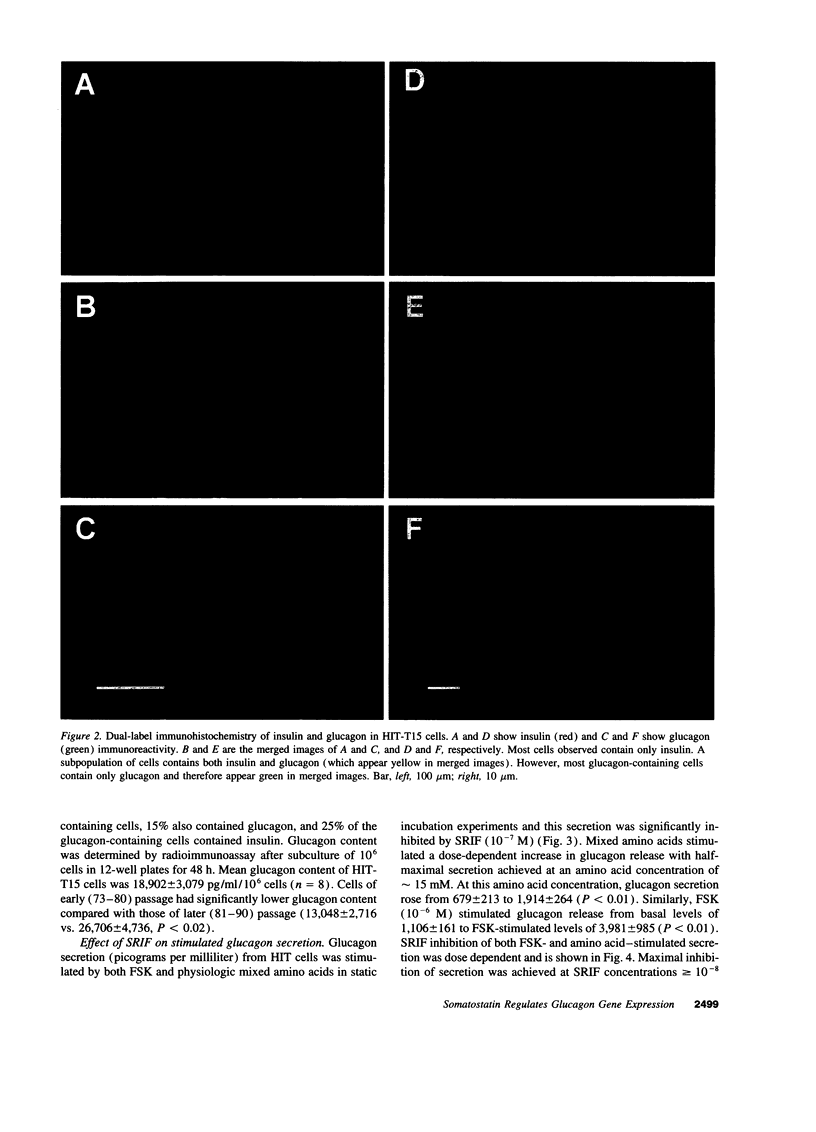
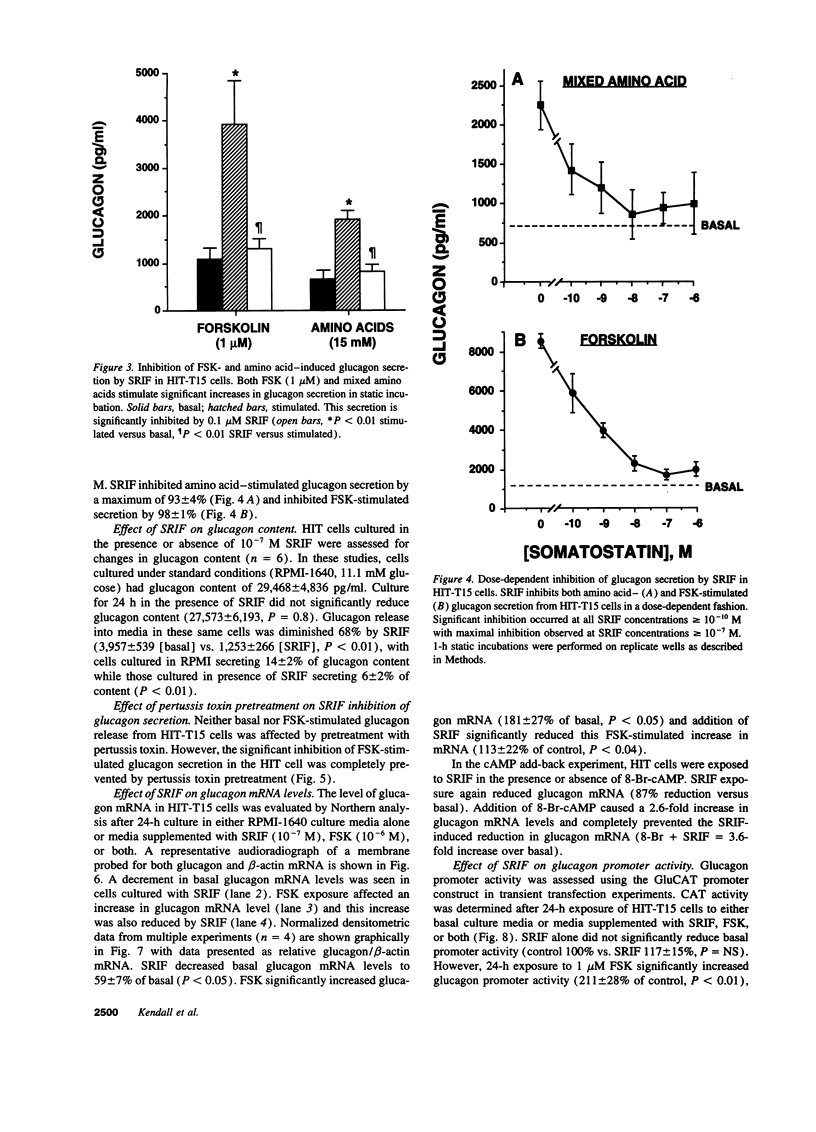
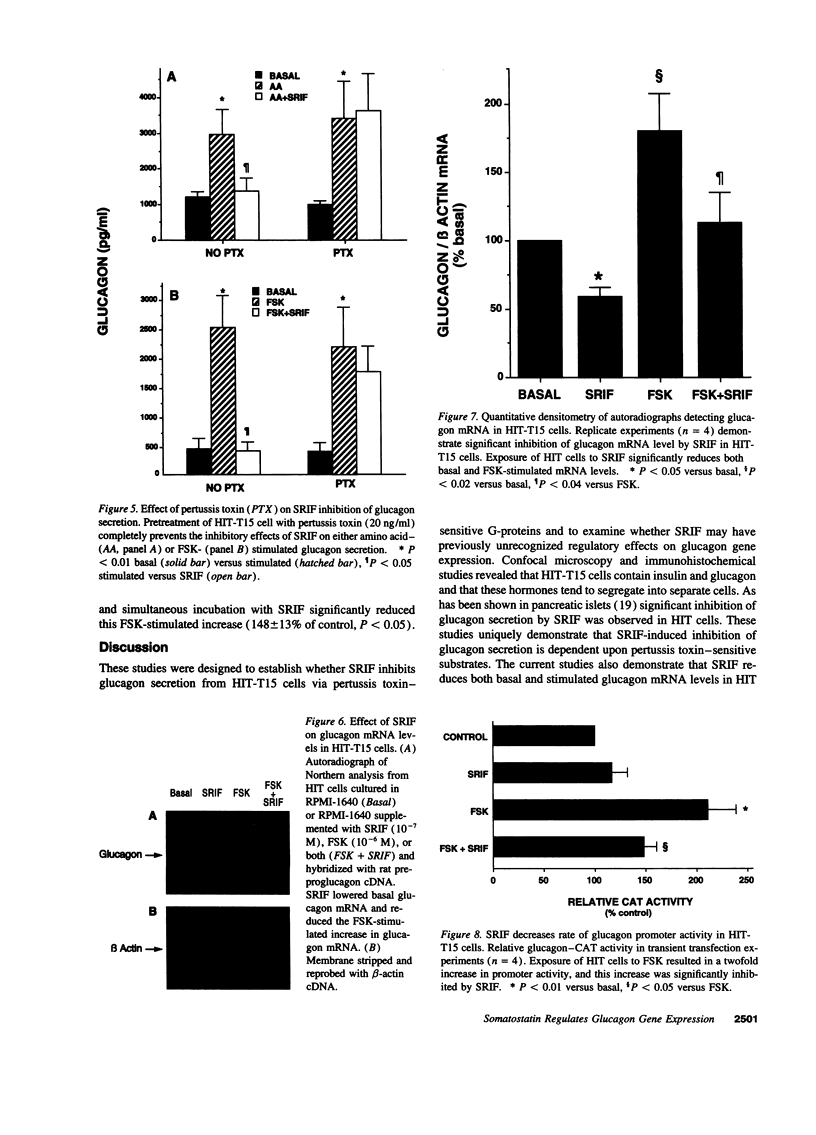
Abstract
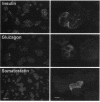
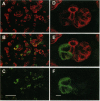
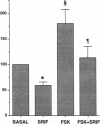
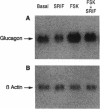
Somatostatin (SRIF) regulates secretion from several endocrine cell types. SRIF inhibits both insulin and glucagon secretion and reduces insulin gene expression. However, whether SRIF inhibition of glucagon secretion from the pancreatic alpha cell is mediated via pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins is not presently known, nor has it been determined whether SRIF can regulate glucagon gene expression. Consequently, we performed studies in the transformed islet cell line HIT-T15 to determine whether the inhibitory effect of SRIF on glucagon exocytosis is preserved in this cell line, whether this effect is mediated through a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism, and whether SRIF has an inhibitory effect on glucagon gene expression. Confocal microscopy with immunostaining revealed that 15-25% of HIT-T15 cells contained glucagon. In static incubations forskolin (FSK, 1 microM) increased glucagon secretion 3.6 +/- 0.9-fold (P < 0.01) and mixed amino acids (15 mM) increased glucagon secretion 2.8 +/- 0.4-fold (P < 0.01). Addition of SRIF significantly inhibited both forskolin- and amino acid-stimulated secretion. Maximal inhibition of both FSK- and amino acid-stimulated secretion occurred at SRIF concentrations > or = 10(-8) M and these inhibitory effects were completely prevented by pertussis toxin pretreatment. In addition to inhibiting glucagon secretion, SRIF significantly reduced both basal and FSK-stimulated glucagon mRNA levels and this reduction in glucagon mRNA was completely prevented by the addition of cyclic AMP analogue. Glucagon gene promoter activity, as assessed by transient transfection experiments, was stimulated 2.1 +/- 0.25-fold by forskolin (P < 0.01). This effect was significantly inhibited by SRIF (71 +/- 4% reduction from FSK alone, P < 0.04) suggesting that SRIF inhibition of the glucagon promoter may, at least in part, account for the observed decrease in glucagon mRNA levels. These studies uniquely demonstrate that glucagon secretion from the HIT-T15 cell line is inhibited by SRIF through a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism and that SRIF also inhibits glucagon gene expression in part by reducing glucagon promoter activity. These findings indicate that SRIF can coordinately regulate glucagon delivery by the alpha cell both at the level of gene expression and hormone exocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brelje T. C., Scharp D. W., Sorenson R. L. Three-dimensional imaging of intact isolated islets of Langerhans with confocal microscopy. Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):808–814. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diem P., Walseth T. F., Zhang H. J., Robertson R. P. Secretion and degradation of glucagon by HIT cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Oct;127(4):1609–1612. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-4-1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Campos R., Reynolds R., Stobie K., Brubaker P. L. The rat glucagon gene is regulated by a protein kinase A-dependent pathway in pancreatic islet cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):394–400. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Lee Y. C., Asa S. L., Brubaker P. L. Inhibition of pancreatic glucagon gene expression in mice bearing a subcutaneous glucagon-producing GLUTag transplantable tumor. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2175–2184. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knepel W., Chafitz J., Habener J. F. Transcriptional activation of the rat glucagon gene by the cyclic AMP-responsive element in pancreatic islet cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6799–6804. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Ruch W., Chideckel E., Palmer J., Goodner C. J., Ensinck J., Gale C. C. Somatostatin: hypothalamic inhibitor of the endocrine pancreas. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):482–484. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. K., Redmon J. B., Towle H. C., Robertson R. P. Chronic exposure of HIT cells to high glucose concentrations paradoxically decreases insulin gene transcription and alters binding of insulin gene regulatory protein. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):514–519. doi: 10.1172/JCI116596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Drucker D. J., Knepel W., Jepeal L., Misulovin Z., Habener J. F. Alpha-cell-specific expression of the glucagon gene is conferred to the glucagon promoter element by the interactions of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4877–4888. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J. Glucagon gene transcription is negatively regulated by insulin in a hamster islet cell line. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):672–677. doi: 10.1172/JCI114214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J. Insulin regulation of the glucagon gene is mediated by an insulin-responsive DNA element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7224–7227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmon J. B., Towle H. C., Robertson R. P. Regulation of human insulin gene transcription by glucose, epinephrine, and somatostatin. Diabetes. 1994 Apr;43(4):546–551. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Seaquist E. R., Walseth T. F. G proteins and modulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):1–6. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronner P., Matschinsky F. M., Hang T. L., Epstein A. J., Buettger C. Sulfonylurea-binding sites and ATP-sensitive K+ channels in alpha-TC glucagonoma and beta-TC insulinoma cells. Diabetes. 1993 Dec;42(12):1760–1772. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.12.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Cook R. A., Crisel R. M., Sharp J. D., Schmidt R. J., Williams D. C., Wilson C. P. Insulin synthesis in a clonal cell line of simian virus 40-transformed hamster pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4339–4343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaninger M., Lux G., Blume R., Oetjen E., Hidaka H., Knepel W. Membrane depolarization and calcium influx induce glucagon gene transcription in pancreatic islet cells through the cyclic AMP-responsive element. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5168–5177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaquist E. R., Neal A. R., Shoger K. D., Walseth T. F., Robertson R. P. G-proteins and hormonal inhibition of insulin secretion from HIT-T15 cells and isolated rat islets. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1390–1399. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaquist E. R., Neal A. R., Shoger K. D., Walseth T. F., Robertson R. P. G-proteins and hormonal inhibition of insulin secretion from HIT-T15 cells and isolated rat islets. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1390–1399. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. J., Redmon J. B., Andresen J. M., Robertson R. P. Somatostatin and epinephrine decrease insulin messenger ribonucleic acid in HIT cells through a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism. Endocrinology. 1991 Nov;129(5):2409–2414. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-5-2409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. J., Walseth T. F., Robertson R. P. Insulin secretion and cAMP metabolism in HIT cells. Reciprocal and serial passage-dependent relationships. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):44–48. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]