Abstract
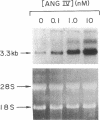
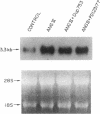
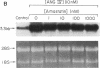
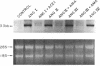
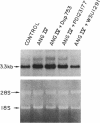
Recent studies from this laboratory have demonstrated that angiotensin II (Ang II) stimulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) in cultured endothelial cells. This response does not appear to be mediated via an interaction with either the AT1 or the AT2 receptor subtype. Since a novel angiotensin receptor has been identified in a variety of tissues that specifically binds the hexapeptide Ang IV (Ang II, [3-8]), we therefore examined the effects of Ang IV on the expression of PAI-1 mRNA in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Ang IV stimulated dose- and time-dependent increases in the expression of PAI-1 mRNA. The effect of Ang IV (10 nM) was not inhibited by Dup 753 (1.0 microM), a highly specific antagonist of the AT1 receptor, or by PD123177 (1.0 microM), a highly specific antagonist of the AT2 receptor. In contrast, the AT4 receptor antagonist, WSU1291 (1.0 microM), effectively prevented PAI-1 expression. Although larger forms of angiotensin (i.e., Ang I, Ang II, and Ang III) are capable of inducing PAI-1 expression, this property is lost in the presence of converting enzyme or aminopeptidase inhibitors. These results indicate that the hexapeptide Ang IV is the form of angiotensin that stimulates endothelial expression of PAI-1. This effect appears to be mediated via the stimulation of an endothelial receptor that is specific for Ang IV.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S., Ward P. E. Role of aminopeptidase activity in the regulation of the pressor activity of circulating angiotensins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):643–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Sedlak B. J., Rafelson M. E., Jr Culture of arterial endothelial cells: characterization and growth of bovine aortic cells. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):825–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braszko J. J., Kupryszewski G., Witczuk B., Wiśniewski K. Angiotensin II-(3-8)-hexapeptide affects motor activity, performance of passive avoidance and a conditioned avoidance response in rats. Neuroscience. 1988 Dec;27(3):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaki S., Inagami T. Identification and characterization of a new binding site for angiotensin II in mouse neuroblastoma neuro-2A cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 15;182(1):388–394. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichek D., Quertermous T. Thrombin regulation of mRNA levels of tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):222–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H. Corcoran Lecture. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and the heart. Hypertension. 1994 Jun;23(6 Pt 2):813–818. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.23.6.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H., Lever A. F., Brown J. J., Macadam R. F., Robertson J. I. Acute renal failure, tubular necrosis, and myocardial infarction induced in the rabbit by intravenous angiotensin II. Lancet. 1971 Jul 3;2(7714):19–22. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Sznycer-Laszuk R. Thrombin induction of plasminogen activator-inhibitor in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):165–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI112271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. R., Bradstreet T. E., McWilliams E. J., Tanaka W. K., Lipert S., Bjornsson T. D., Waldman S. A., Osborne B., Pivadori L., Lewis G. Biochemical effects of losartan, a nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 1995 Jan;25(1):37–46. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. R., Tanaka W., Barchowsky A., Bradstreet T. E., McCrea J., Lo M. W., McWilliams E. J., Jr, Bjornsson T. D. Effects of losartan on blood pressure, plasma renin activity, and angiotensin II in volunteers. Hypertension. 1993 May;21(5):704–713. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.21.5.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberl R. L., Decker P. J., Einhäupl K. M. Angiotensin degradation products mediate endothelium-dependent dilation of rabbit brain arterioles. Circ Res. 1991 Jun;68(6):1621–1627. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.6.1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K. L., Hanesworth J. M., Ball A. E., Felgenhauer G. P., Hosick H. L., Harding J. W. Identification and characterization of a novel angiotensin binding site in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells that is specific for the hexapeptide (3-8) fragment of angiotensin II, angiotensin IV. Regul Pept. 1993 Mar 19;44(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., de Faire U., Walldius G., Dahlén G., Szamosi A., Landou C., Blombäck M., Wiman B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma: risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1987 Jul 4;2(8549):3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanesworth J. M., Sardinia M. F., Krebs L. T., Hall K. L., Harding J. W. Elucidation of a specific binding site for angiotensin II(3-8), angiotensin IV, in mammalian heart membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Aug;266(2):1036–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. W., Cook V. I., Miller-Wing A. V., Hanesworth J. M., Sardinia M. F., Hall K. L., Stobb J. W., Swanson G. N., Coleman J. K., Wright J. W. Identification of an AII(3-8) [AIV] binding site in guinea pig hippocampus. Brain Res. 1992 Jun 26;583(1-2):340–343. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(10)80047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Gessner G. W., Ly C. Q. The angiotensin hexapeptide 3-8 fragment potently inhibits [125I]angiotensin II binding to non-AT1 or -AT2 recognition sites in bovine adrenal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 25;219(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90312-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Wing A. V., Hanesworth J. M., Sardinia M. F., Hall K. L., Wright J. W., Speth R. C., Grove K. L., Harding J. W. Central angiotensin IV binding sites: distribution and specificity in guinea pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1718–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A., Jr, Shiverick K. T., Ogilvie S., Buhi W. C., Raizada M. K. Angiotensin II induces secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and a tissue metalloprotease inhibitor-related protein from rat brain astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1928–1932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer M. A., Braunwald E., Moyé L. A., Basta L., Brown E. J., Jr, Cuddy T. E., Davis B. R., Geltman E. M., Goldman S., Flaker G. C. Effect of captopril on mortality and morbidity in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Results of the survival and ventricular enlargement trial. The SAVE Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 3;327(10):669–677. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209033271001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Moon B. J., Harbeson S. Inhibition of aminopeptidases by amastatin and bestatin derivatives. Effect of inhibitor structure on slow-binding processes. J Med Chem. 1984 Apr;27(4):417–422. doi: 10.1021/jm00370a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridker P. M., Gaboury C. L., Conlin P. R., Seely E. W., Williams G. H., Vaughan D. E. Stimulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor in vivo by infusion of angiotensin II. Evidence of a potential interaction between the renin-angiotensin system and fibrinolytic function. Circulation. 1993 Jun;87(6):1969–1973. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.6.1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford J. D., Pfeffer M. A., Moyé L. A., Davis B. R., Flaker G. C., Kowey P. R., Lamas G. A., Miller H. S., Packer M., Rouleau J. L. Effects of captopril on ischemic events after myocardial infarction. Results of the Survival and Ventricular Enlargement trial. SAVE Investigators. Circulation. 1994 Oct;90(4):1731–1738. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.4.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardinia M. F., Hanesworth J. M., Krishnan F., Harding J. W. AT4 receptor structure-binding relationship: N-terminal-modified angiotensin IV analogues. Peptides. 1994;15(8):1399–1406. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson G. N., Hanesworth J. M., Sardinia M. F., Coleman J. K., Wright J. W., Hall K. L., Miller-Wing A. V., Stobb J. W., Cook V. I., Harding E. C. Discovery of a distinct binding site for angiotensin II (3-8), a putative angiotensin IV receptor. Regul Pept. 1992 Aug 13;40(3):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(92)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. E., Lazos S. A., Tong K. Angiotensin II regulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured endothelial cells. A potential link between the renin-angiotensin system and thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):995–1001. doi: 10.1172/JCI117809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. A., Flapan A. D., Alberti K. G., Ludlam C. A., Fox K. A. Effects of captopril therapy on endogenous fibrinolysis in men with recent, uncomplicated myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Jul;24(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf S., Pepine C. J., Garces C., Pouleur H., Salem D., Kostis J., Benedict C., Rousseau M., Bourassa M., Pitt B. Effect of enalapril on myocardial infarction and unstable angina in patients with low ejection fractions. Lancet. 1992 Nov 14;340(8829):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92889-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen R. T., Kol A., Andreotti F., Kluft C., Maseri A., Sperti G. Angiotensin II increases plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and tissue-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 1994 Jul;90(1):362–368. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.1.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]