Abstract
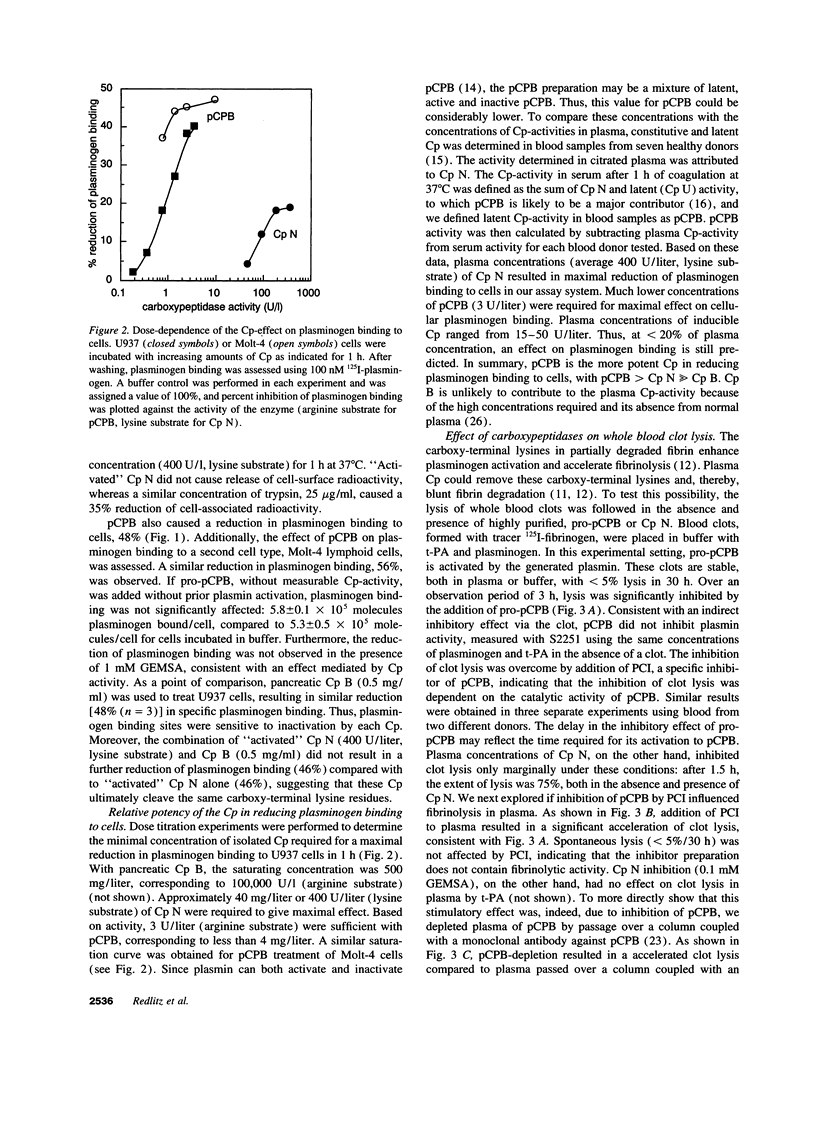
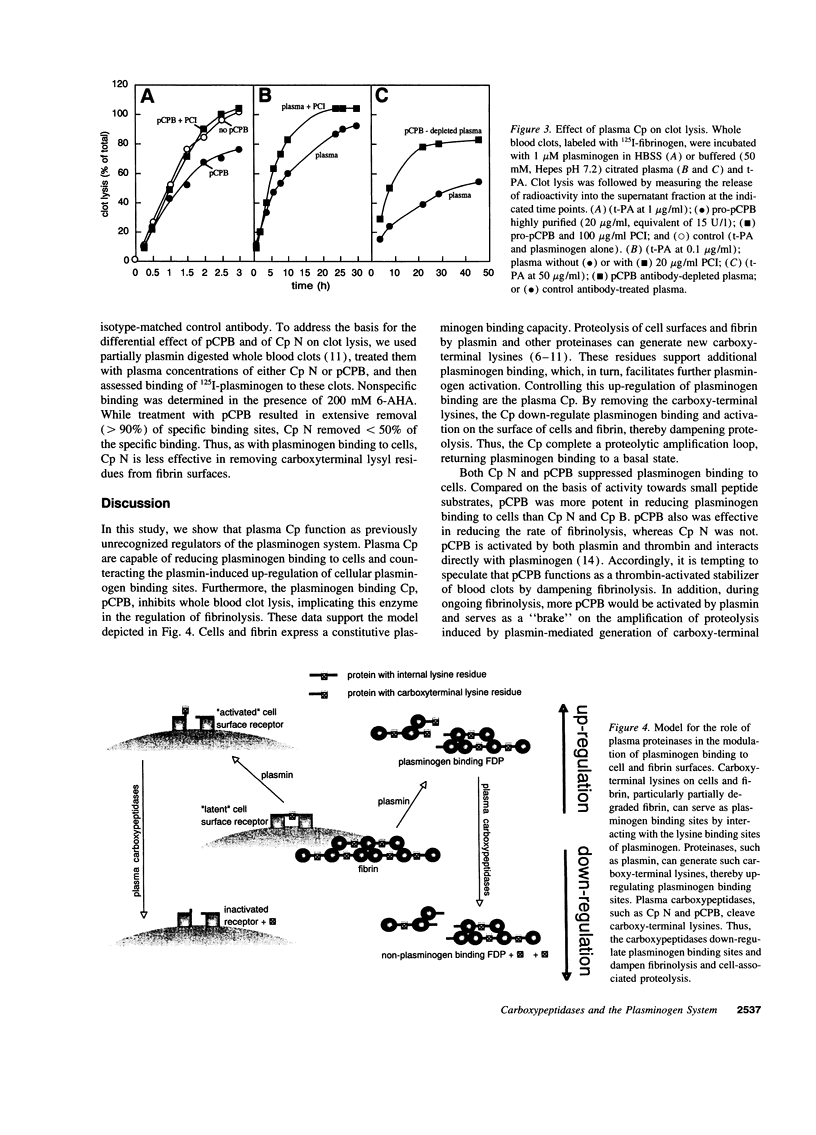
Carboxy-terminal lysine residues on the surface of cells and fibrin bind plasminogen and control its activation. Since plasma contains basic carboxypeptidases, which remove carboxy-terminal lysines from protein substrates, we investigated if these enzymes are involved in the regulation of plasminogen binding sites. Plasma reduced plasminogen binding to cells, and this effect could be ascribed to the activity of the plasma carboxypeptidases. Purified carboxypeptidase N, which is constitutively active, and plasma carboxypeptidase B, which circulates as a zymogen, were both capable of significantly reducing plasminogen binding to cells. Dose titration experiments verified that plasma concentrations of either carboxypeptidase were sufficient to maximally affect plasminogen binding to cells. Furthermore, plasma carboxypeptidase B, but not carboxypeptidase N, reduced the rate of whole blood clot lysis induced by tissue-type plasminogen activator. These findings establish that plasma carboxypeptidases can modulate plasminogen binding to cells and control the rate of fibrinolysis. These functions delineate a novel role for the plasma carboxypeptidases in the regulation of the plasminogen system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camacho M., Fondaneche M. C., Burtin P. Limited proteolysis of tumor cells increases their plasmin-binding ability. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W., Yonezu K., Shinohara T., Okada H. An arginine carboxypeptidase generated during coagulation is diminished or absent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 May;115(5):610–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen U. C-terminal lysine residues of fibrinogen fragments essential for binding to plasminogen. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 11;182(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Lijnen H. R. Basic and clinical aspects of fibrinolysis and thrombolysis. Blood. 1991 Dec 15;78(12):3114–3124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delk A. S., Durie P. R., Fletcher T. S., Largman C. Radioimmunoassay of active pancreatic enzymes in sera from patients with acute pancreatitis. I. Active carboxypeptidase B. Clin Chem. 1985 Aug;31(8):1294–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Malloy B. E., Tsai S. P., Henzel W., Drayna D. Isolation, molecular cloning, and partial characterization of a novel carboxypeptidase B from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21833–21838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felez J., Miles L. A., Plescia J., Plow E. F. Regulation of plasminogen receptor expression on human monocytes and monocytoid cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1673–1683. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleury V., Anglés-Cano E. Characterization of the binding of plasminogen to fibrin surfaces: the role of carboxy-terminal lysines. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7630–7638. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Stack S., Pizzo S. V. Plasmin binding to the plasminogen receptor enhances catalytic efficiency and activates the receptor for subsequent ligand binding. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 May 1;286(2):625–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Jacovina A. T., Chacko J. An endothelial cell receptor for plasminogen/tissue plasminogen activator. I. Identity with annexin II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21191–21197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Chang T. S., Verderber E. Tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase mediate the binding of Glu-plasminogen to plasma fibrin I. Evidence for new binding sites in plasmin-degraded fibrin I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4432–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks D., Scharpé S., van Sande M., Lommaert M. P. Characterisation of a carboxypeptidase in human serum distinct from carboxypeptidase N. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1989 May;27(5):277–285. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1989.27.5.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin Y., Skidgel R. A., Erdös E. G. Isolation and characterization of the subunits of human plasma carboxypeptidase N (kininase i). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4618–4622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguerie G. A., Edgington T. S., Plow E. F. Interaction of fibrinogen with its platelet receptor as part of a multistep reaction in ADP-induced platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):154–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay T. J., Plummer T. H., Jr By-product analogues for bovine carboxypeptidase B. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):401–405. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Dahlberg C. M., Plescia J., Felez J., Kato K., Plow E. F. Role of cell-surface lysines in plasminogen binding to cells: identification of alpha-enolase as a candidate plasminogen receptor. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1682–1691. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Plow E. F. Receptor mediated binding of the fibrinolytic components, plasminogen and urokinase, to peripheral blood cells. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Oct 28;58(3):936–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannell R., Black J., Gurewich V. Complementary modes of action of tissue-type plasminogen activator and pro-urokinase by which their synergistic effect on clot lysis may be explained. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):853–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI113394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Hurwitz M. Y. Human plasma carboxypeptidase N. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3907–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Kimmel M. T. An improved spectrophotometric assay for human plasma carboxypeptidase N1. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 1;108(2):348–353. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabovic M., Lijnen H. R., Keber D., Collen D. Effect of retraction on the lysis of human clots with fibrin specific and non-fibrin specific plasminogen activators. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Dec 29;62(4):1083–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A. Basic carboxypeptidases: regulators of peptide hormone activity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A. Human carboxypeptidase N: lysine carboxypeptidase. Methods Enzymol. 1995;248:653–663. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)48042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan A. K., Eaton D. L. Activation and characterization of procarboxypeptidase B from human plasma. Biochemistry. 1995 May 2;34(17):5811–5816. doi: 10.1021/bi00017a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Hendriks D. F., Scharpé S. S. Carboxypeptidase U, a plasma carboxypeptidase with high affinity for plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15937–15944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



