Abstract
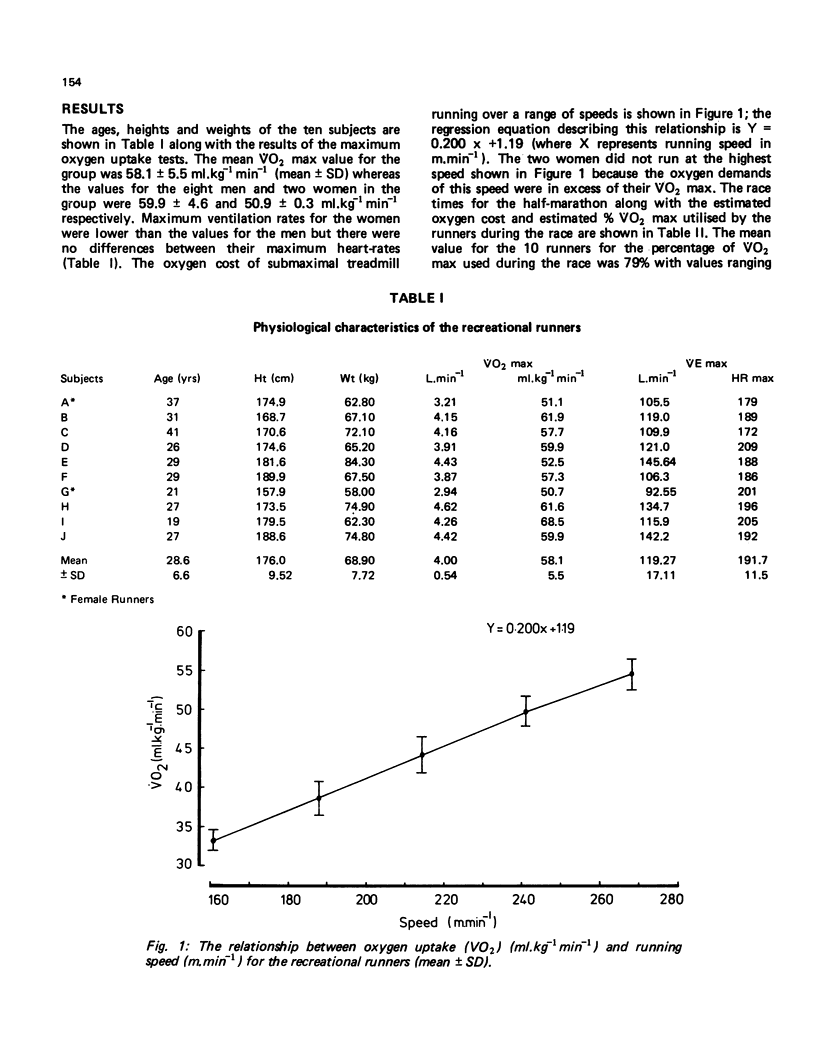
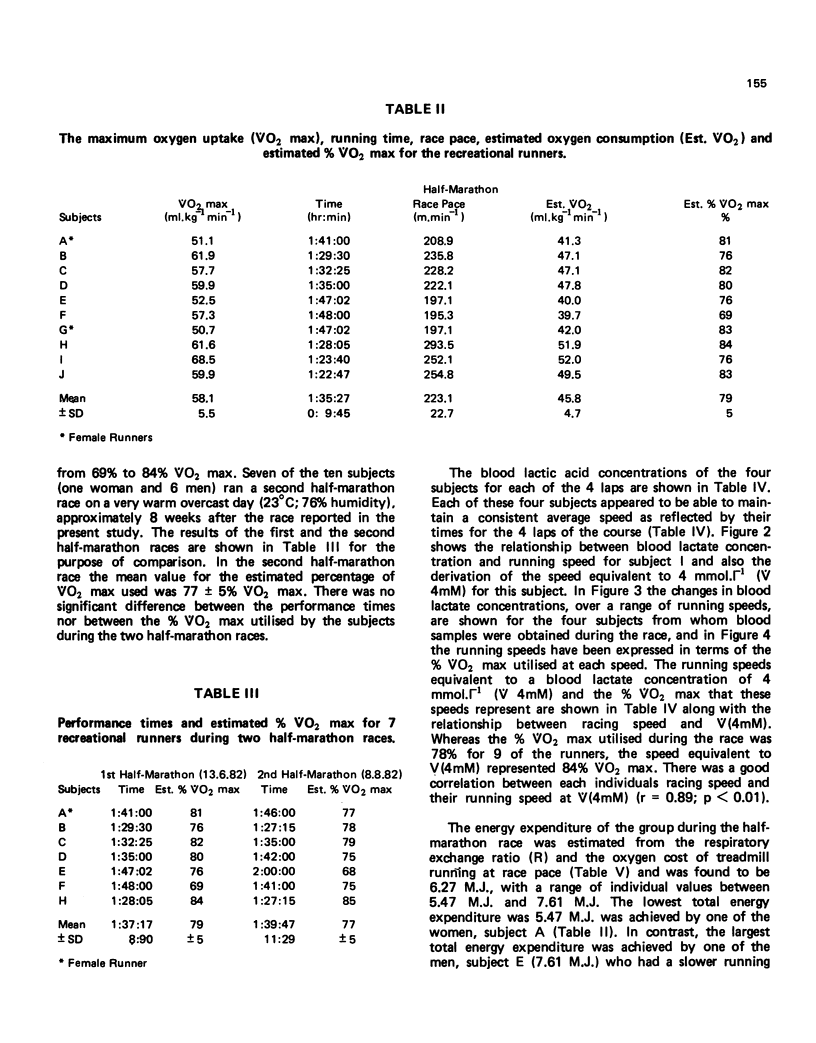
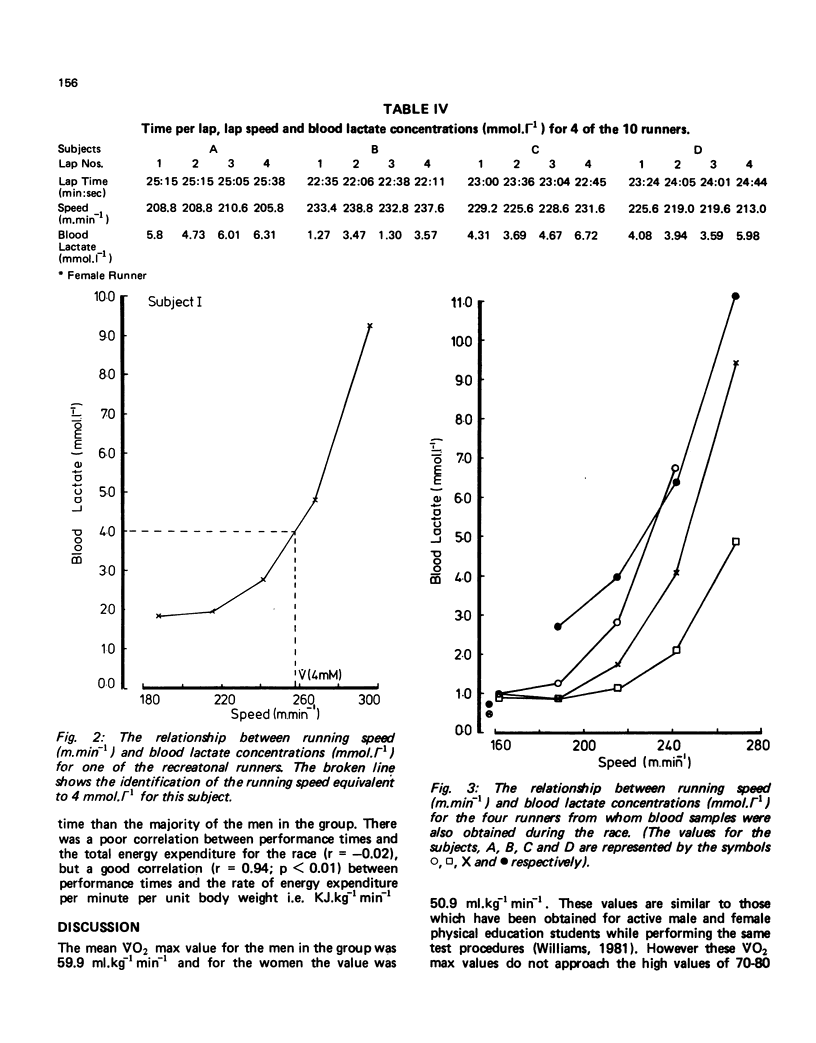
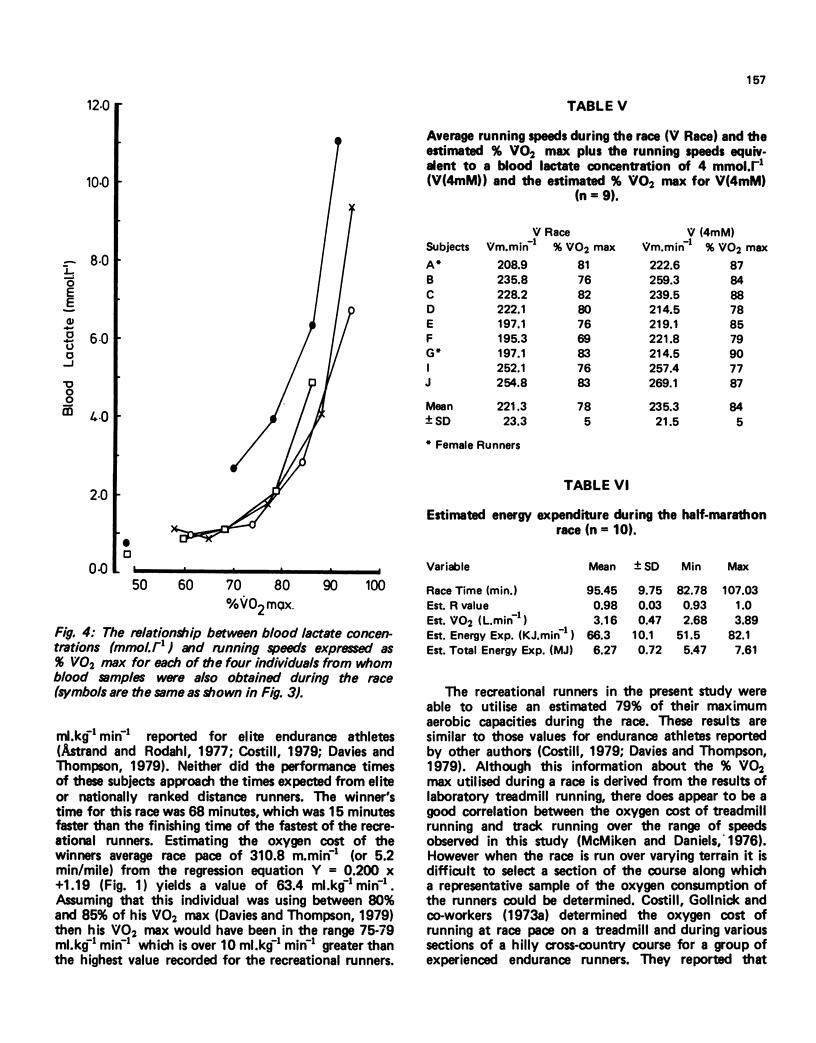
The purpose of this study was to assess the physiological demands of a half-marathon race on a group of ten recreational runners (8 men and 2 women). The average running speed was 223.1 +/- 22.7 m.min-1 (mean +/- SD) for the group and this represented 79 +/- 5% VO2 max for these runners. There was a good correlation between VO2 max and performance time for the race (4 = -0.81; p less than 0.01) and an even better correlation between running speed equivalent to a blood lactate concentration of 4 mmol.l-1 and performance times (r = -0.877; p less than 0.01). The blood lactate concentration os 4 of the runners at the end of the race was 5.65 +/- 1.42 mmol.l-1 (mean +/- SD) and the estimated energy expenditure for the group was 6.22 M.J. While there was only a poor correlation between total energy expenditure and performance time for the race, the correlation coefficient was improved when the energy expenditure of each individual was expressed in KJ.kg-1 min-1 (r = 0.938; p less than 0.01).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conley D. L., Krahenbuhl G. S. Running economy and distance running performance of highly trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1980;12(5):357–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costill D. L., Gollnick P. D., Jansson E. D., Saltin B., Stein E. M. Glycogen depletion pattern in human muscle fibres during distance running. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Nov;89(3):374–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costill D. L. Metabolic responses during distance running. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Mar;28(3):251–255. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costill D. L., Thomason H., Roberts E. Fractional utilization of the aerobic capacity during distance running. Med Sci Sports. 1973 Winter;5(4):248–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels J., Oldridge N. The effects of alternate exposure to altitude and sea level on world-class middle-distance runners. Med Sci Sports. 1970 Fall;2(3):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. T., Thompson M. W. Aerobic performance of female marathon and male ultramarathon athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1979 Aug;41(4):233–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00429740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. A., Vodak P., Wilmore J. H., Vodak J., Kurtz P. Anaerobic threshold and maximal aerobic power for three modes of exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):544–550. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. A., Wilmore J. H., Coyle E. F., Billing J. E., Costill D. L. Plasma lactate accumulation and distance running performance. Med Sci Sports. 1979 Winter;11(4):338–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster C., Costill D. L., Daniels J. T., Fink W. J. Skeletal muscle enzyme activity, fiber composition and VO2 max in relation to distance running performance. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1978 Aug 15;39(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00421711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralambie G., Senser L., Sierra-Chàvez R. Physiological and metabolic effects of a 25 km race in female athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1981;47(2):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00421664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakeman P., Davies B. The characteristics of a low resistance breathing valve designed for the measurement of high aerobic capacity. Br J Sports Med. 1979 Jun;13(2):81–83. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.13.2.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindermann W., Simon G., Keul J. The significance of the aerobic-anaerobic transition for the determination of work load intensities during endurance training. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1979 Sep;42(1):25–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00421101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai S., Tanaka K., Matsuura Y., Matsuzaka A., Hirakoba K., Asano K. Relationships of the anaerobic threshold with the 5 km, 10 km, and 10 mile races. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1982;49(1):13–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00428959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMiken D. F., Daniels J. T. Aerobic requirements and maximum aerobic power in treadmill and track running. Med Sci Sports. 1976 Spring;8(1):14–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen C. An enzymatic fluorimetric micromethod for the determination of acetoacetate, -hydroxybutyrate, pyruvate and lactate. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jul;33(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90486-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard R. J., Allen C., Benade A. J., Davies C. T., Di Prampero P. E., Hedman R., Merriman J. E., Myhre K., Simmons R. The maximum oxygen intake. An international reference standard of cardiorespiratory fitness. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(5):757–764. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjödin B., Jacobs I. Onset of blood lactate accumulation and marathon running performance. Int J Sports Med. 1981 Feb;2(1):23–26. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1034579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. S., McLellan T. M., McLellan T. H. The transition from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1980 Mar;51(1):234–248. doi: 10.1080/02701367.1980.10609285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR H. L., BUSKIRK E., HENSCHEL A. Maximal oxygen intake as an objective measure of cardio-respiratory performance. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jul;8(1):73–80. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman K., Whipp B. J., Koyl S. N., Beaver W. L. Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Aug;35(2):236–243. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.35.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Hecht L. H., Krahenbuhl G. S. Physical characteristics and oxygen utilization of male and female marathon runners. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1981 May;52(2):281–285. doi: 10.1080/02701367.1981.10607869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. The biological basis of aptitude: the endurance runner. J Biosoc Sci Suppl. 1981;7:103–115. doi: 10.1017/s0021932000024603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




