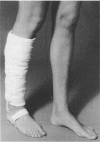
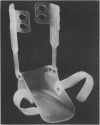
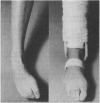
Abstract
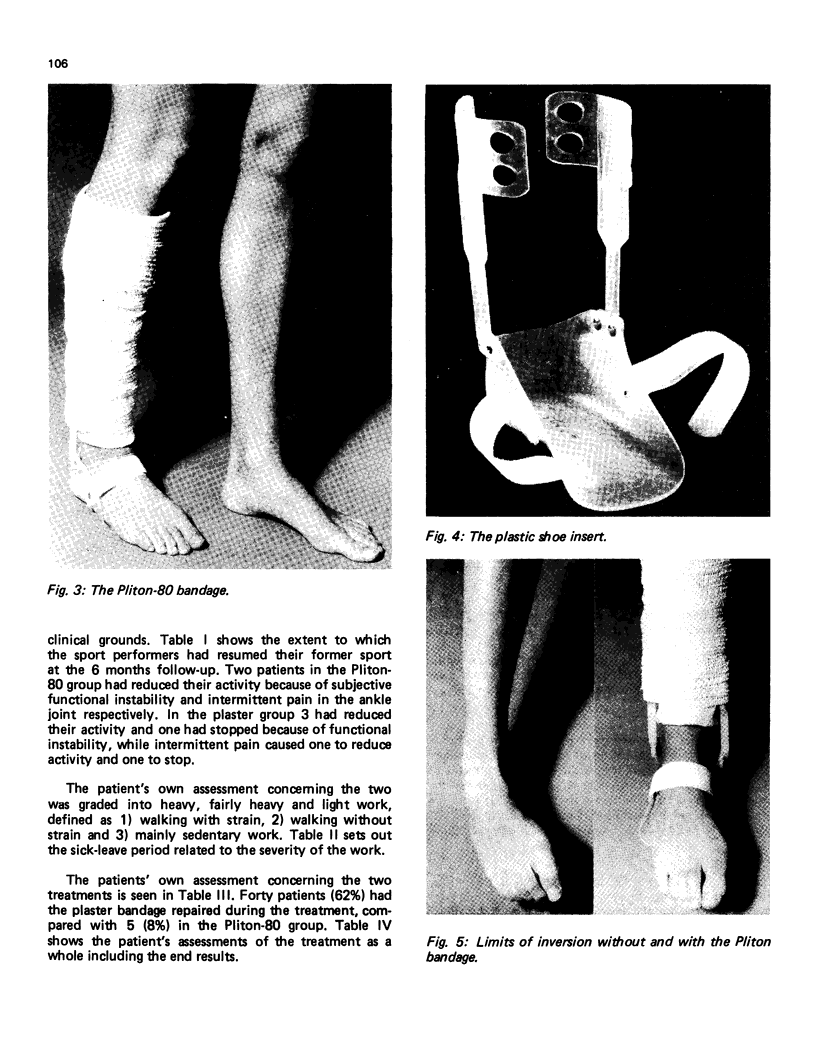
A prospective randomised study was performed in order to compare plaster cast with Pliton-80 cast brace with a mobile plastic shoe insert in the treatment of ruptured fibular ankle ligaments. The two treatment groups consisted of 65 patients in each and all were participating in the follow-up sixth months after the accident. There were no statistically significant differences in the overall results between the two treatment groups. Because 1) the mobile Pliton-80 bandage subjectively is more acceptable to the patients and -2) the disability time in the Pliton-80 group was considerably shorter than in the plaster group--it was concluded that the mobile Pliton-80 bandage can be recommended as the treatment of ruptures of the fibular ankle ligaments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. Therapie und Prognose der frischen Aussenknöchelbandläsion. Unfallheilkunde. 1976 Mar;79(3):101–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand R. L., Black H. M., Cox J. S. The natural history of inadequately treated ankle sprain. Am J Sports Med. 1977 Nov-Dec;5(6):248–249. doi: 10.1177/036354657700500609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broström L. Sprained ankles. V. Treatment and prognosis in recent ligament ruptures. Acta Chir Scand. 1966 Nov;132(5):537–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetti R. Conservative treatment of injury to the fibular ligaments of the ankle. Br J Sports Med. 1982 Mar;16(1):47–52. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.16.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. L., Derby A. C., Power G. R. Injuries of the lateral ligament of the ankle. Conservative vs. operative repair. Can J Surg. 1965 Oct;8(4):358–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Frenyo S. D. The stress-tenogram in the diagnosis of ruptures of the lateral ligament of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979 Aug;61-B(3):347–351. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.61B3.113414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. A., Dean M. R., Hanham I. W. The etiology and prevention of functional instability of the foot. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965 Nov;47(4):678–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. A. Treatment of ruptures of the lateral ligament of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965 Nov;47(4):661–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow M., Jackson A., Jamieson A. M. Instability of the ankle after injury to the lateral ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980 May;62-B(2):196–200. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.62B2.7364836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermann B., Andersen A., Andersen S. B., Funder V., Jørgensen J. P., Lindholmer E., Vuust M. Rupture of the lateral ligaments of the ankle: operation or plaster cast? A propective study. Acta Orthop Scand. 1981 Oct;52(5):579–587. doi: 10.3109/17453678108992150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders E. A. Ligamentous injuries of the ankle. Am Fam Physician. 1980 Aug;22(2):132–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber B. G., Hupfauer W. Zur Behandlung der frishen fibularen Bandruptur und der chronischen fibularen Bandinsuffizienz. Arch Orthop Unfallchir. 1969;65(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00415867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]