Abstract
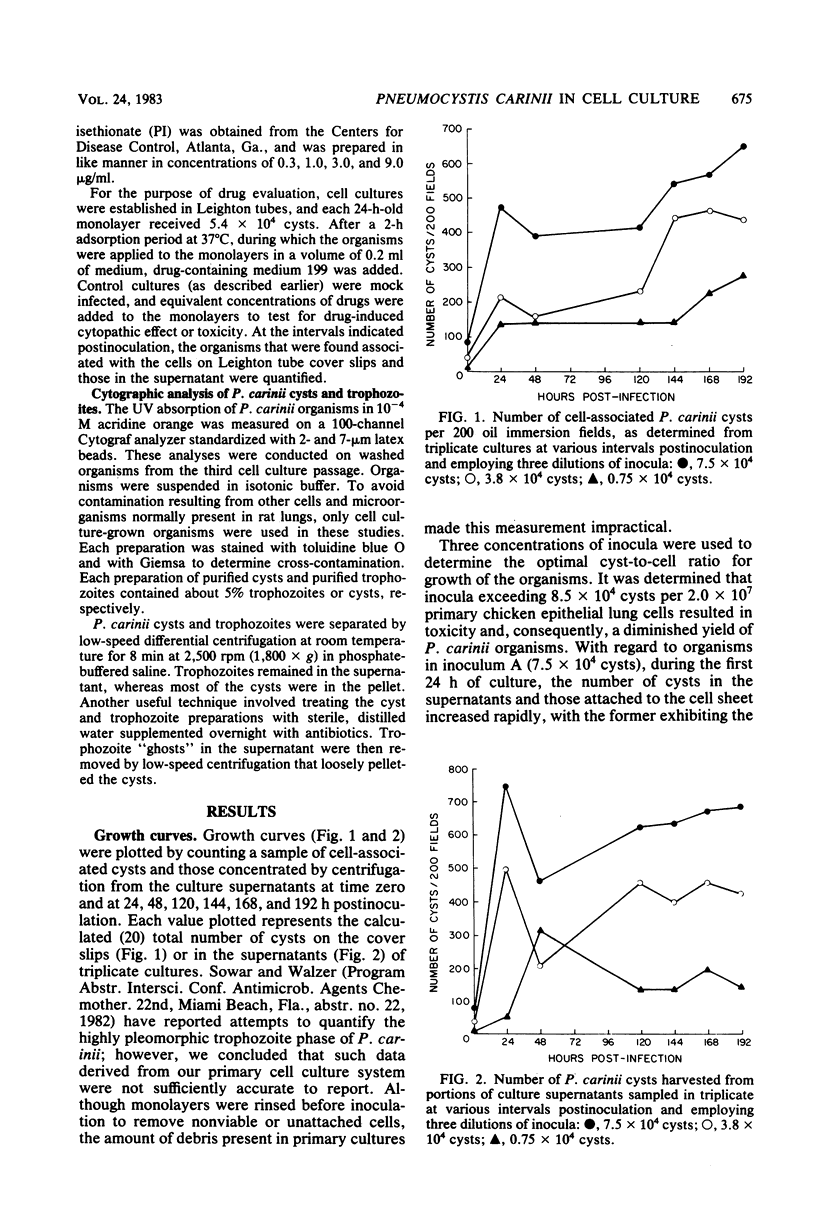
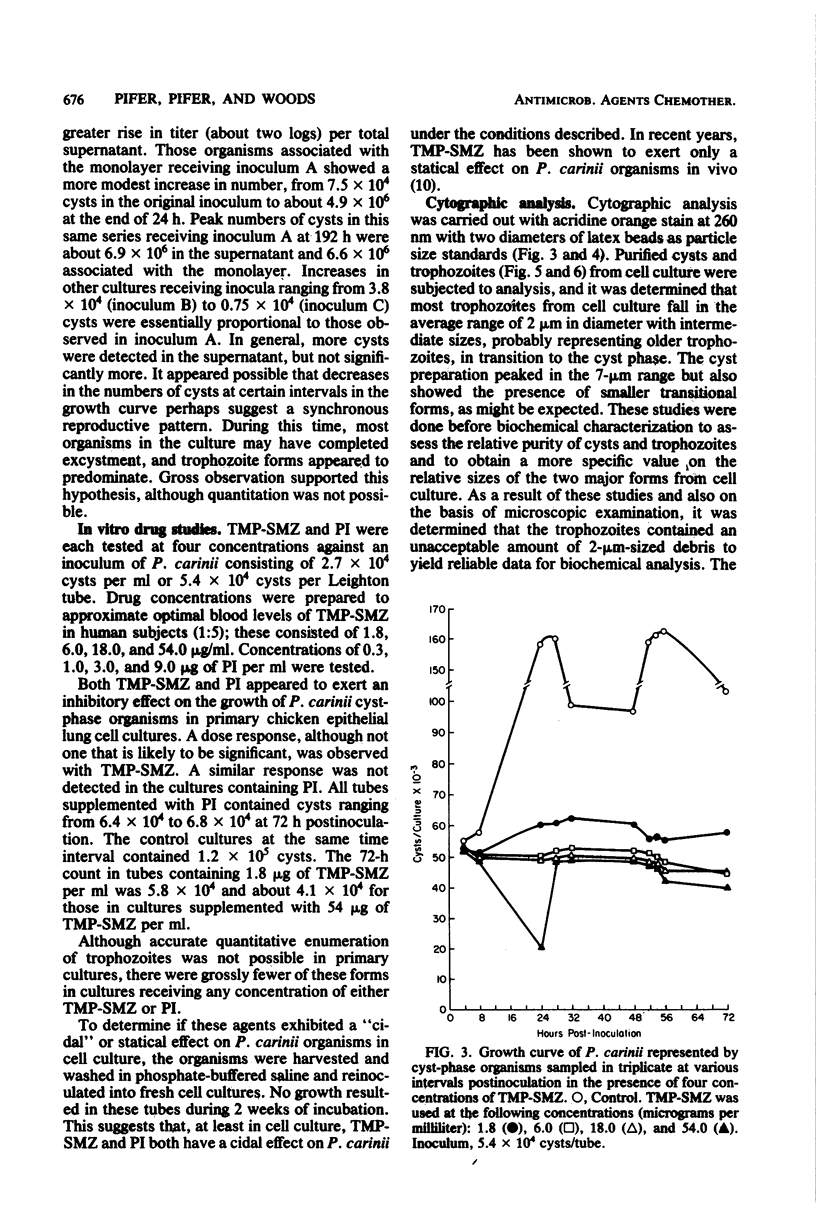
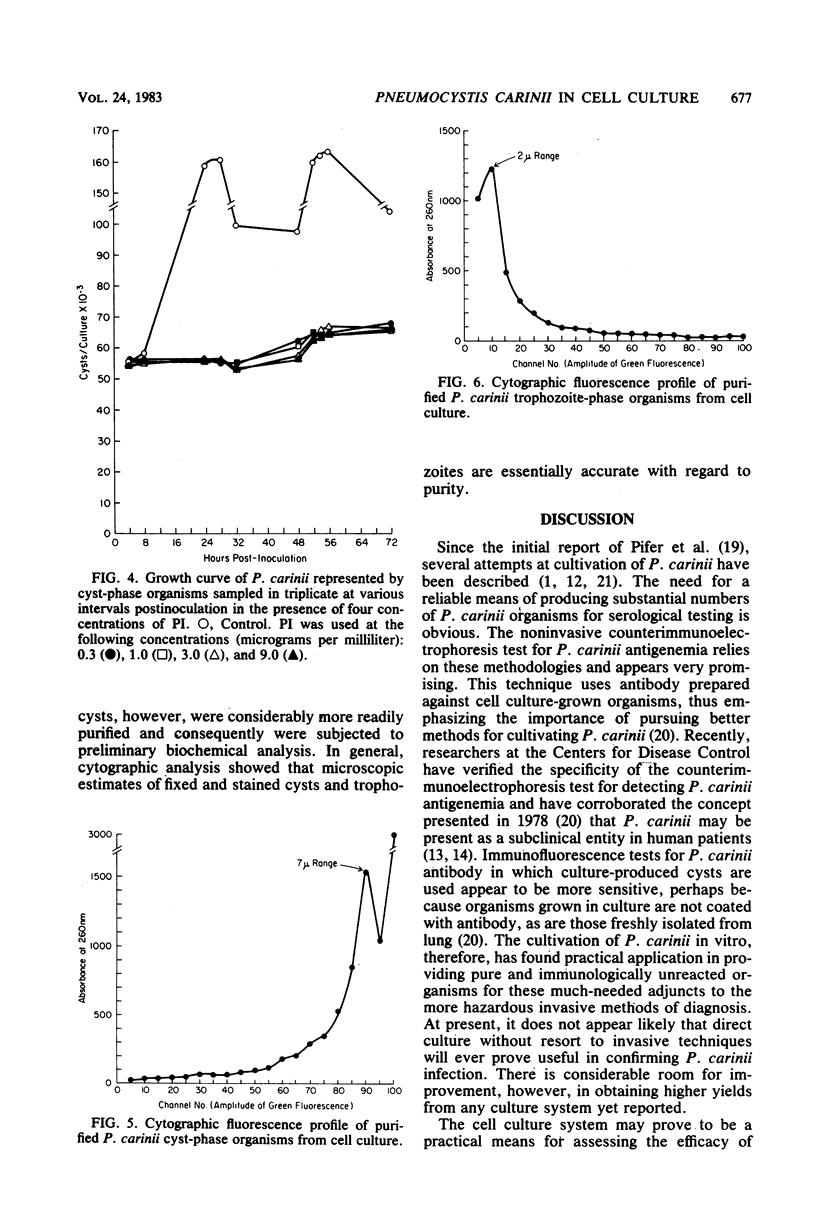
Although the growth characteristics of Pneumocystis carinii have been described in several cell culture systems, the response of this organism to the drugs of choice, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and pentamidine isethionate, have not been described in vitro. The effect of various concentrations of drugs against P. carinii on the growth of this potentially hazardous opportunistic organism as well as the methodology for in vitro assay of these agents have been detailed. Fluorescence profiles illustrating size ranges of trophozoites and cysts derived from cell culture are described.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHALVARDJIAN A. M., GRAWE L. A. A NEW PROCEDURE FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII CYSTS IN TISSUE SECTIONS AND SMEARS. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jul;16:383–384. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos H. W., Curran J. W. The current outbreak of Kaposi's sarcoma and opportunistic infections. CA Cancer J Clin. 1982 Nov-Dec;32(6):330–339. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.32.6.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kuhn S., Chaudhary S., Feldman S., Verzosa M., Aur R. J., Pratt C., George S. L. Successful chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 29;297(26):1419–1426. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712292972602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Limited effect of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis on Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):333–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Pneumocystis pneumonia: a plague of the immunosuppressed. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1978 Dec;143(6):184–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre C. R., Sulzer A. J., Norman L. G. Serial propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in cell line cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1204–1206. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1204-1206.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Hayes G. V., Ivey M. H., Tsang V. C., Slemenda S. B., Norman L. G. Fractionation of Pneumocystis carinii antigens used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies and in the production of antiserum for detecting Pneumocystis carinii antigenemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1029–1035. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1029-1035.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Hayes G. V., Slemenda S. B., Norman L. G., Ivey M. H. Detection of specific antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and antigenemia by counterimmunoelectrophoresis in humans infected with Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1036–1043. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1036-1043.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Michelis M. A., Wormser G. P., Lewin S., Gold J., Tapper M. L., Giron J., Lerner C. W., Armstrong D., Setia U. Opportunistic infection in previously healthy women. Initial manifestations of a community-acquired cellular immunodeficiency. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):533–539. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L., Cox C. Metabolic and synthetic activities of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):908–914. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.908-914.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Hughes W. T., Murphy M. J., Jr Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1977 Apr;11(4):305–316. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifer L. L., Woods D., Hughes W. T. Propagation of Pneumocystis carinii in Vero cell culture. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):66–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.66-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


