Abstract
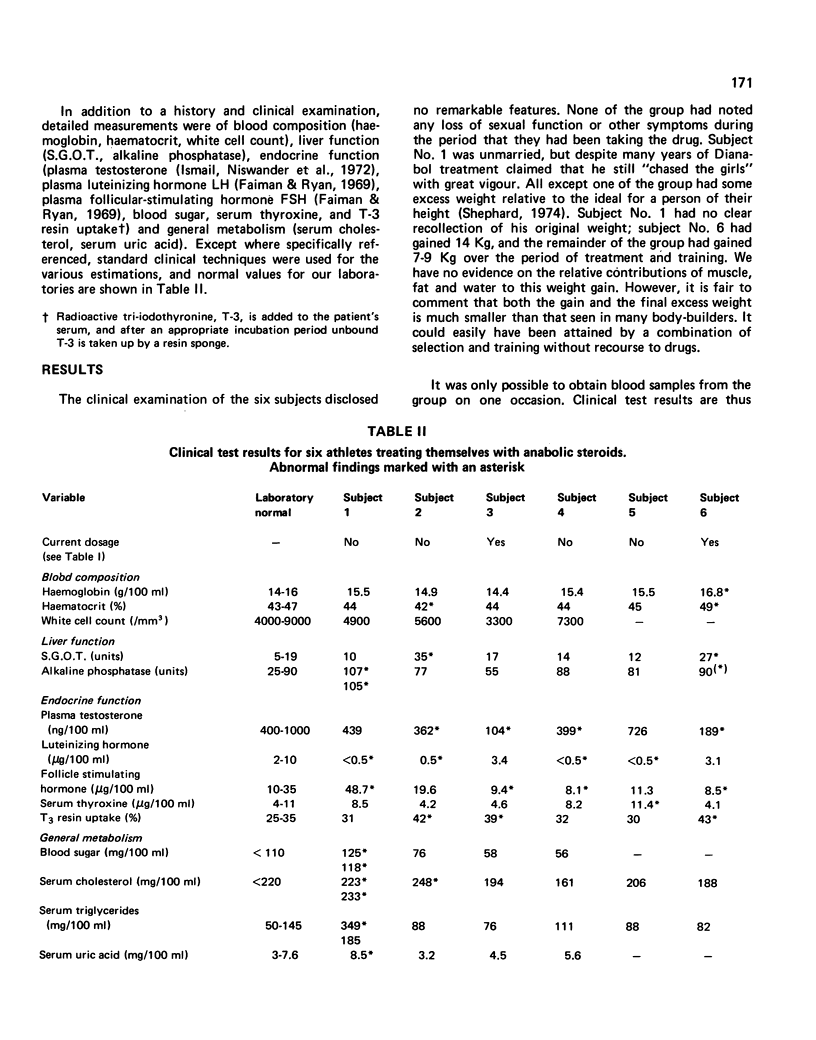
Description is given of six body-builders who had been taking Methandrostenolone (up to 20 mg/day in intermittent courses for a year or more). At the time of examination there was no subjective disturbance of sexual function, but testosterone levels were low relative to laboratory standards and luteinizing hormone levels were also reduced - particularly in relation to testosterone concentrations. Abnormal liver function tests were seen in three of the six subjects, and one had mild diabetes with high serum cholesterol, triglycerides and uric acid. The weight gain of the group was not outstanding, and the only possible finding was a high haemoglobin and haematocrit in one of the six subjects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Faiman C., Ryan R. J. Mechanism of specificity in radioimmunoassay for human FSH after HCG adsorption of antisera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):691–695. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness R. A., Kilshaw B. H., Hobson B. M. Effects of large doses of anabolic steroids. Br J Sports Med. 1975 Jul;9(2):70–73. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.9.2.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervey G. R. Are athletes wrong about anabolic steroids? Br J Sports Med. 1975 Jul;9(2):74–77. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.9.2.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail A. A., Niswender G. D., Midgley A. R., Jr Radioimmunoassay of testosterone without chromatography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):177–184. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynn V. Metabolic effects of anabolic steroids. Br J Sports Med. 1975 Jul;9(2):60–64. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.9.2.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



