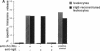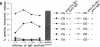Abstract
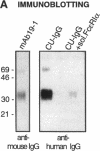
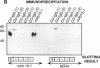
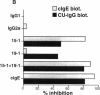
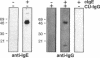
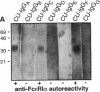
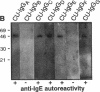
While it is well established that acute allergic urticaria is caused by degranulation of skin mast cells occurring after allergen/IgE-dependent cross-linking of high affinity IgE receptors (FcepsilonRI), the pathophysiologic mechanisms operative in chronic urticaria (CU) are less well understood. Some evidence points to the existence of histamine-releasing activity in the serum of CU patients which possibly acts via triggering of FcepsilonRI. In this study, we aimed to better characterize this anti-FcepsilonRIalpha reactivity of CU patients using affinity-purified, IgE-depleted IgG fractions of such individuals (CU-IgG). Using immobilized, recombinant soluble FcepsilonRIalpha as a a reaction target for Western blot studies, we found that 12/32 (37%) CU-IgG serum samples exhibited IgG autoreactivity against FcepsilonRI- alpha. These findings were confirmed by experiments demonstrating that immunoblot-reactive, but not immunoblot-nonreactive, CU-IgG preparations precipitated the FcepsilonRIalpha from FcepsilonRI- alphagamma-transfected cells. No anti-FcepsilonRIalpha reactivity was observed in IgG fractions from atopic dermatitis (AD) patients (0/15) or healthy control individuals (CO:0/15). As opposed to the selective occurrence of IgG anti-Fc epsilon RI alpha autoantibodies in CU patients, IgG anti-IgE antibodies were detected in all groups investigated (CU: 69%; AD: 73%; CO: 26%). While both types of autoantibodies can exhibit histamine-releasing properties, not all of the autoantibodies proved to be functional in vitro. Our results indicate that the occurrence of IgG anti-FcepsilonRIalpha reactivity defines an autoimmune-mediated subentity of CU and provide a basis for the development of new diagnostic procedures and, perhaps, therapeutic strategies for this disease.
Full text
PDF

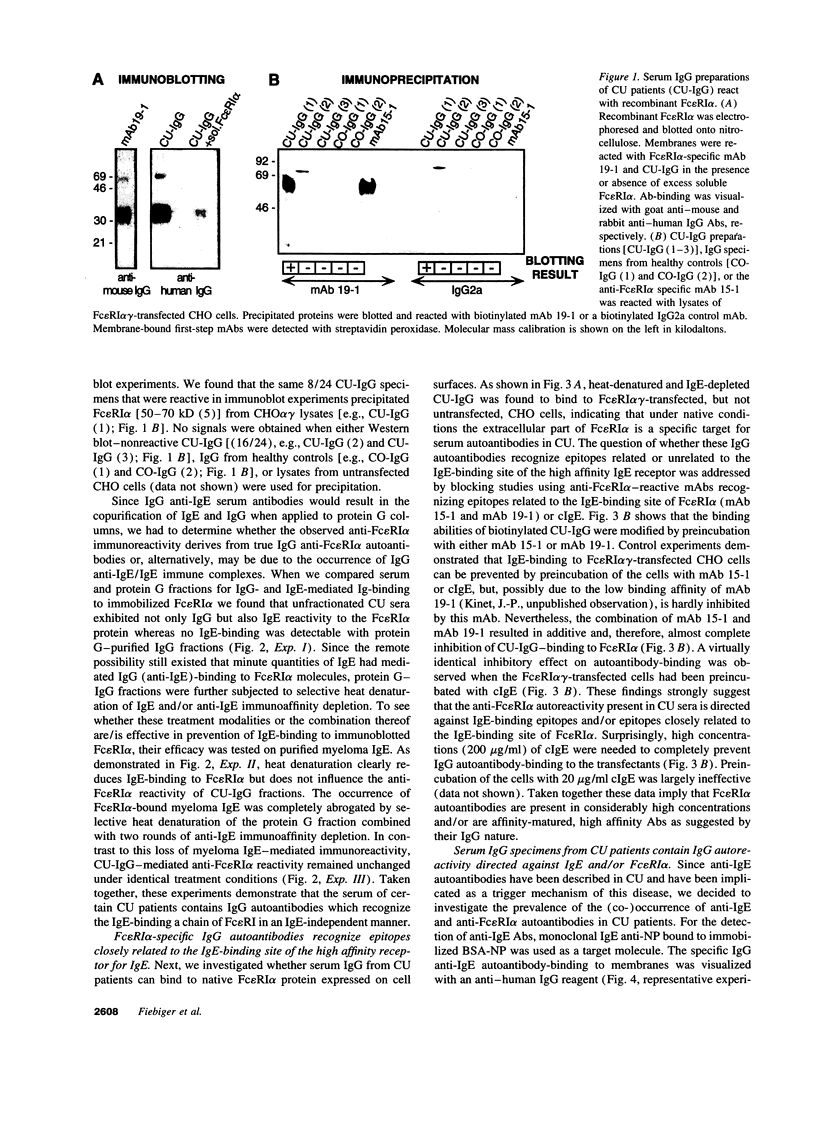
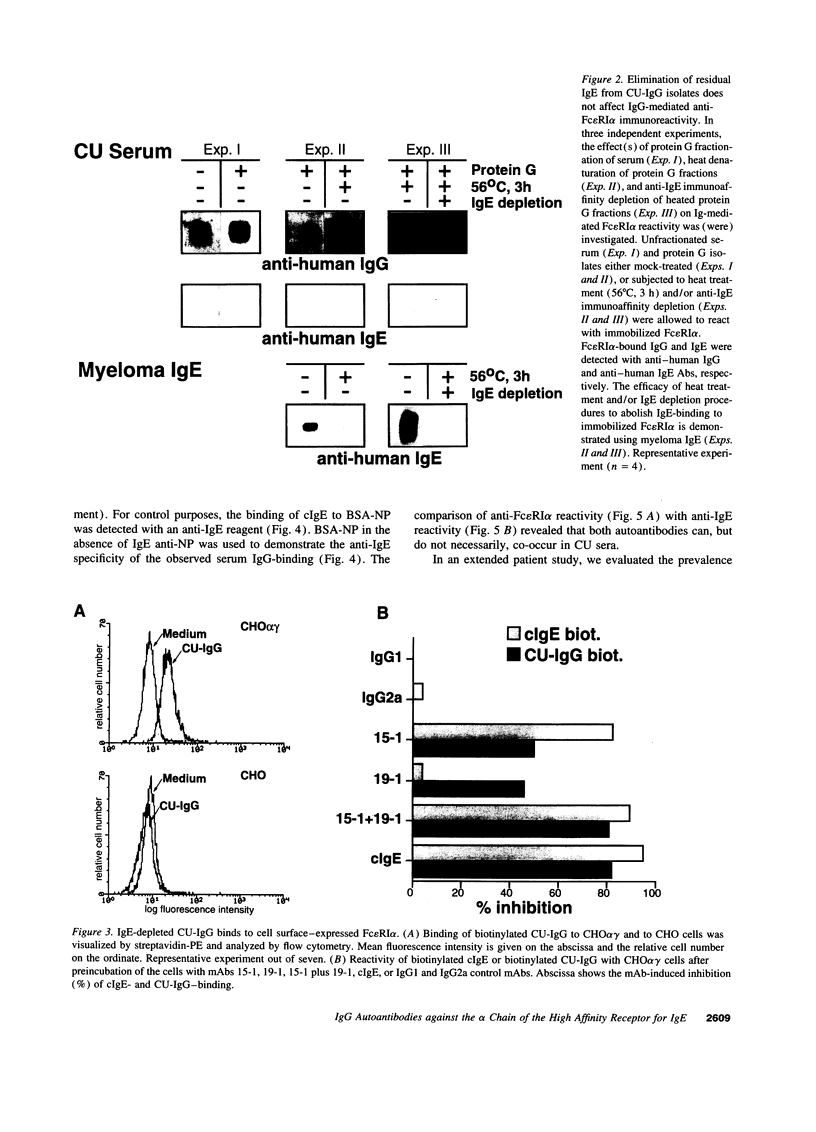
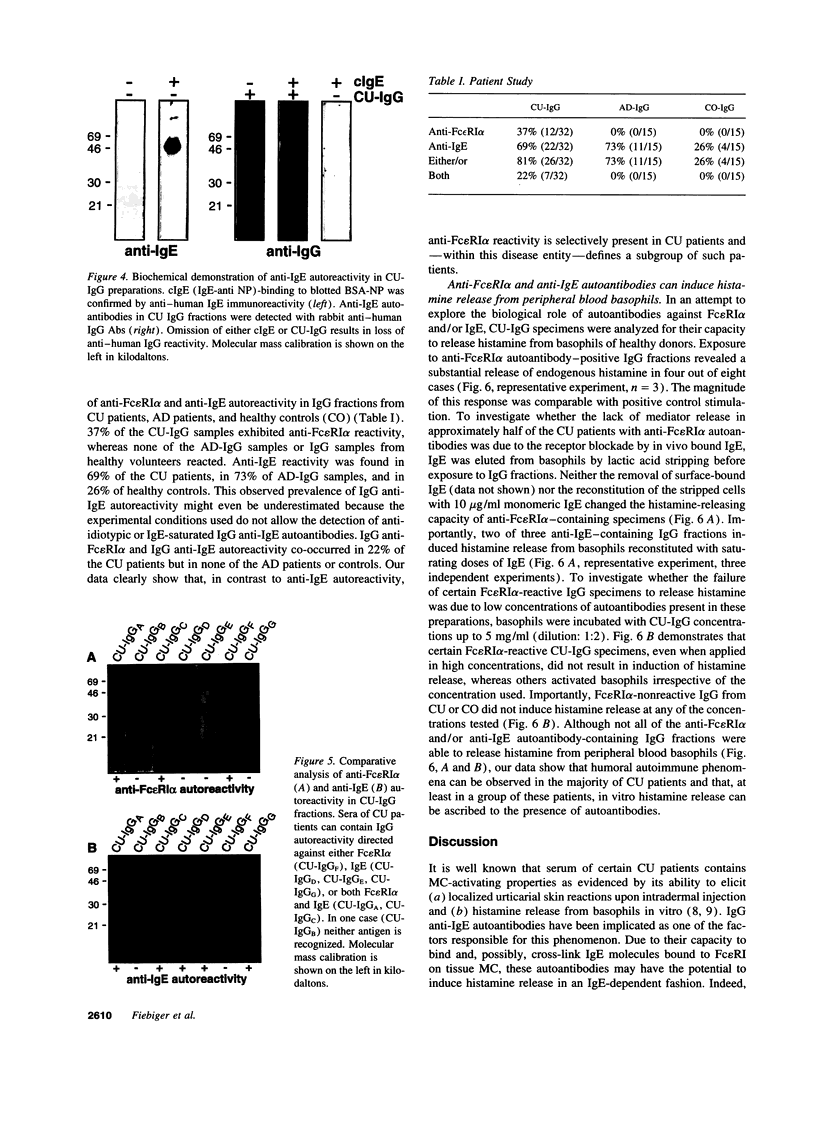
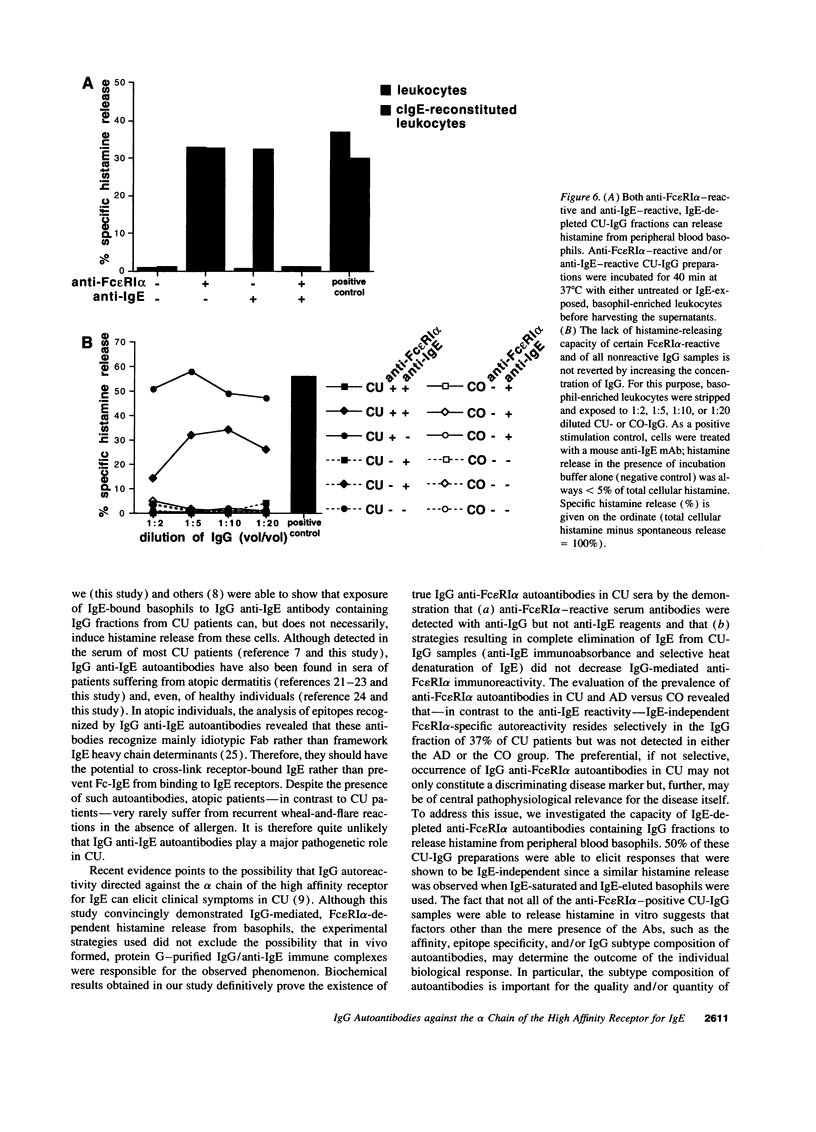

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bischoff S. C., Brunner T., De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. Interleukin 5 modifies histamine release and leukotriene generation by human basophils in response to diverse agonists. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1577–1582. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Capron M., Bazin H. Specific IgE antibodies in immune adherence of normal macrophages to Schistosoma mansoni schistosomules. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):474–475. doi: 10.1038/253474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion R. H. A practical approach to the urticarial syndromes--a dermatologist's view. Clin Exp Allergy. 1990 Mar;20(2):221–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1990.tb02671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Bennich H. Thermally induced structural changes in immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8378–8384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grattan C. E., Francis D. M., Hide M., Greaves M. W. Detection of circulating histamine releasing autoantibodies with functional properties of anti-IgE in chronic urticaria. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Nov;21(6):695–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb03198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grattan C. E., Francis D. M., Slater N. G., Barlow R. J., Greaves M. W. Plasmapheresis for severe, unremitting, chronic urticaria. Lancet. 1992 May 2;339(8801):1078–1080. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90666-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber B. L., Baeza M. L., Marchese M. J., Agnello V., Kaplan A. P. Prevalence and functional role of anti-IgE autoantibodies in urticarial syndromes. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Feb;90(2):213–217. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide M., Francis D. M., Grattan C. E., Hakimi J., Kochan J. P., Greaves M. W. Autoantibodies against the high-affinity IgE receptor as a cause of histamine release in chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun 3;328(22):1599–1604. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199306033282204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston D. P., Bressler R. B. Urticaria and angioedema. Med Clin North Am. 1992 Jul;76(4):805–840. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inganäs M., Johansson S. G., Bennich H. Anti-IgE antibodies in human serum: occurrence and specificity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;65(1):51–61. doi: 10.1159/000232737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P. Chronic urticaria. Possible causes, suggested treatment alternatives. Postgrad Med. 1983 Sep;74(3):209-15, 218-22. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1983.11698427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marone G., Casolaro V., Paganelli R., Quinti I. IgG anti-IgE from atopic dermatitis induces mediator release from basophils and mast cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Aug;93(2):246–252. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer D., Ebner C., Reininger B., Fiebiger E., Kraft D., Kinet J. P., Stingl G. The high affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) mediates IgE-dependent allergen presentation. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 15;154(12):6285–6290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer D., Fiebiger E., Reininger B., Wolff-Winiski B., Jouvin M. H., Kilgus O., Kinet J. P., Stingl G. Expression of functional high affinity immunoglobulin E receptors (Fc epsilon RI) on monocytes of atopic individuals. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):745–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. The high affinity receptor for IgE on mast cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 May;21(3):269–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb01658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawata Y., Koike T., Hosokawa H., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Anti-IgE autoantibody in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):478–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky J. J., Grammer L. C., Patterson R., Roberts M. Dissociation of IgE from receptors on human basophils. I. Enhanced passive sensitization for histamine release. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1949–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinti I., Brozek C., Wood N., Geha R. S., Leung D. Y. Circulating IgG autoantibodies to IgE in atopic syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Apr;77(4):586–594. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B. Mast cells and their role in urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Jul;25(1 Pt 2):190–204. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Tepler I., Benfey P. N., Berenstein E. H., Siraganian R. P., Leder P. Human and rat mast cell high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptors: characterization of putative alpha-chain gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M. H., Smith R. I., Morrison S. L. Structural features of human immunoglobulin G that determine isotype-specific differences in complement activation. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):661–667. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twena D. M., Marshall J. S., Haeney M. R., Bell E. B. A survey of nonatopic and atopic children and adults for the presence of anti-IgE autoantibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Oct;53(1):40–51. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel M., Miescher S., Biaggi C., Stadler B. M. Human anti-IgE antibodies by repertoire cloning. Eur J Immunol. 1994 May;24(5):1200–1207. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Rieger A., Kilgus O., Ochiai K., Maurer D., Födinger D., Kinet J. P., Stingl G. Epidermal Langerhans cells from normal human skin bind monomeric IgE via Fc epsilon RI. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1353–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]