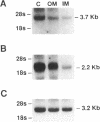
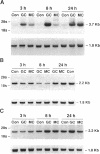
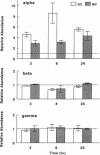
Abstract
The terminal nephron segment, the inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD), absorbs Na+ by an electrogenic process that involves the entry through an apical (luminal) membrane Na+ channel. To understand the nature of this Na+ channel, we employed the patch clamp technique on the apical membrane of primary cultures of rat IMCD cells grown on permeable supports. We found that all ion channels detected in the cell-attached configuration were highly selective for Na+ (Li+) over K+. The open/closed transitions showed slow kinetics, had a slope conductance of 6-11 pS, and were sensitive to amiloride and benzamil. Nonselective cation channels with a higher conductance (25-30 pS), known to be present in IMCD cells, were not detected in the cell-attached configuration, but were readily detected in excised patches. The highly selective channels had properties similar to the recently described rat epithelial Na+ channel complex, rENaC. We therefore asked whether rENaC mRNA was present in the IMCD. We detected mRNA for all three rENaC subunits in rat renal papilla and also in primary cultures of the IMCD. Either glucocorticoid hormone or mineralocorticoid hormone increased the amount of alpha-rENaC subunit mRNA but had no effect on the mRNA level of the beta-rENaC or gamma-rENaC subunits. From these data, taken in the context of other studies on the characteristics of Na+ selective channels and the distribution of rENaC mRNA, we conclude that steroid stimulated Na+ absorption by the IMCD is mediated primarily by Na+ channels having properties of the rENaC subunit complex.
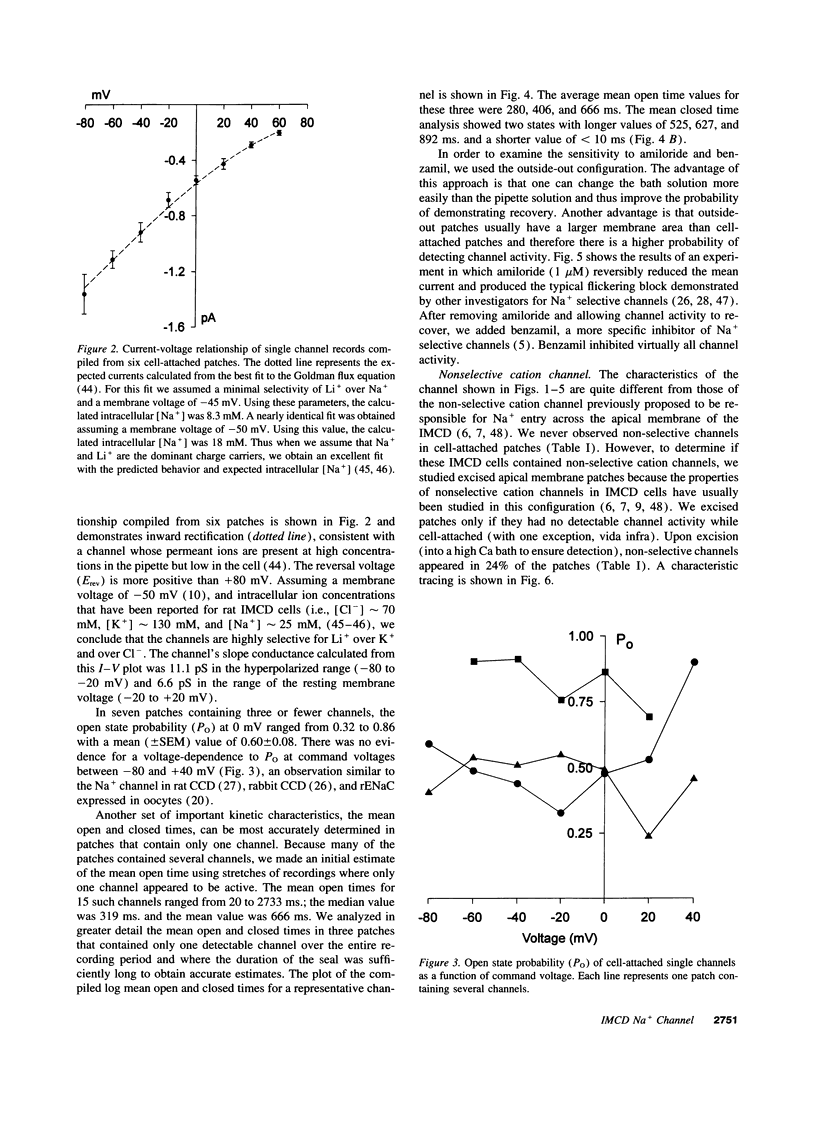
Full text
PDF

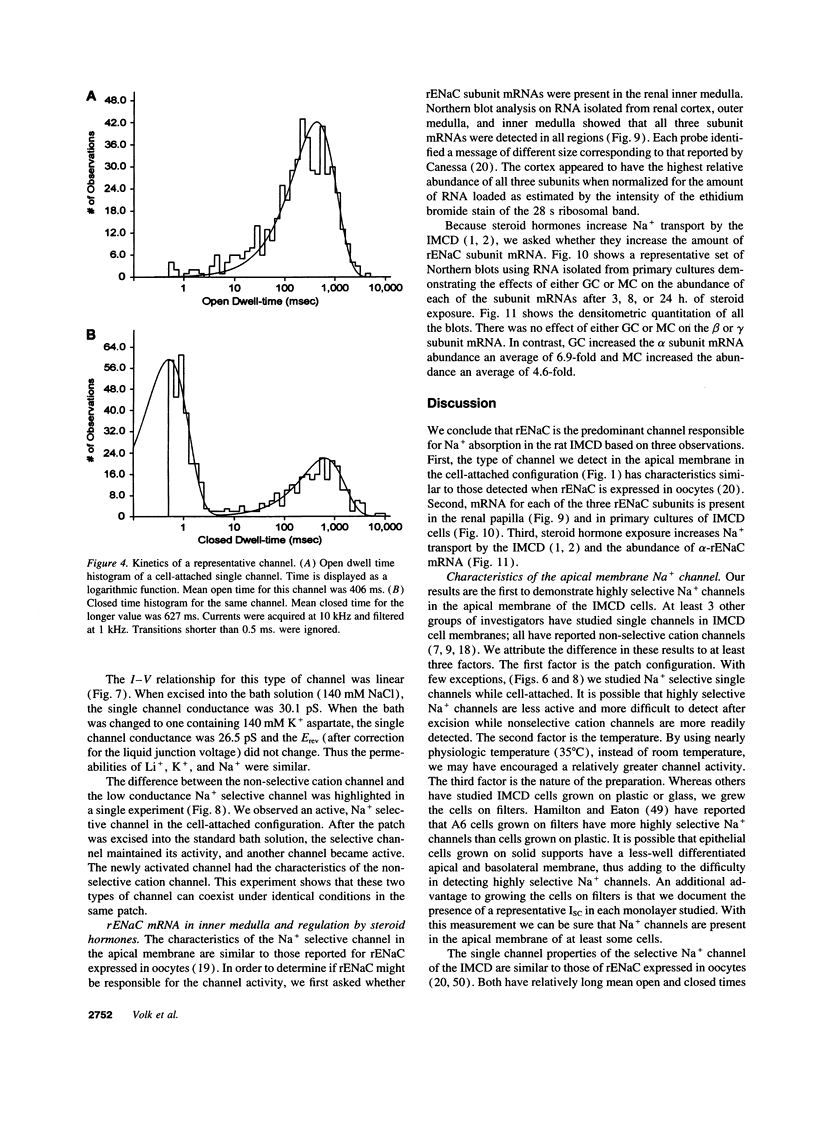



Images in this article
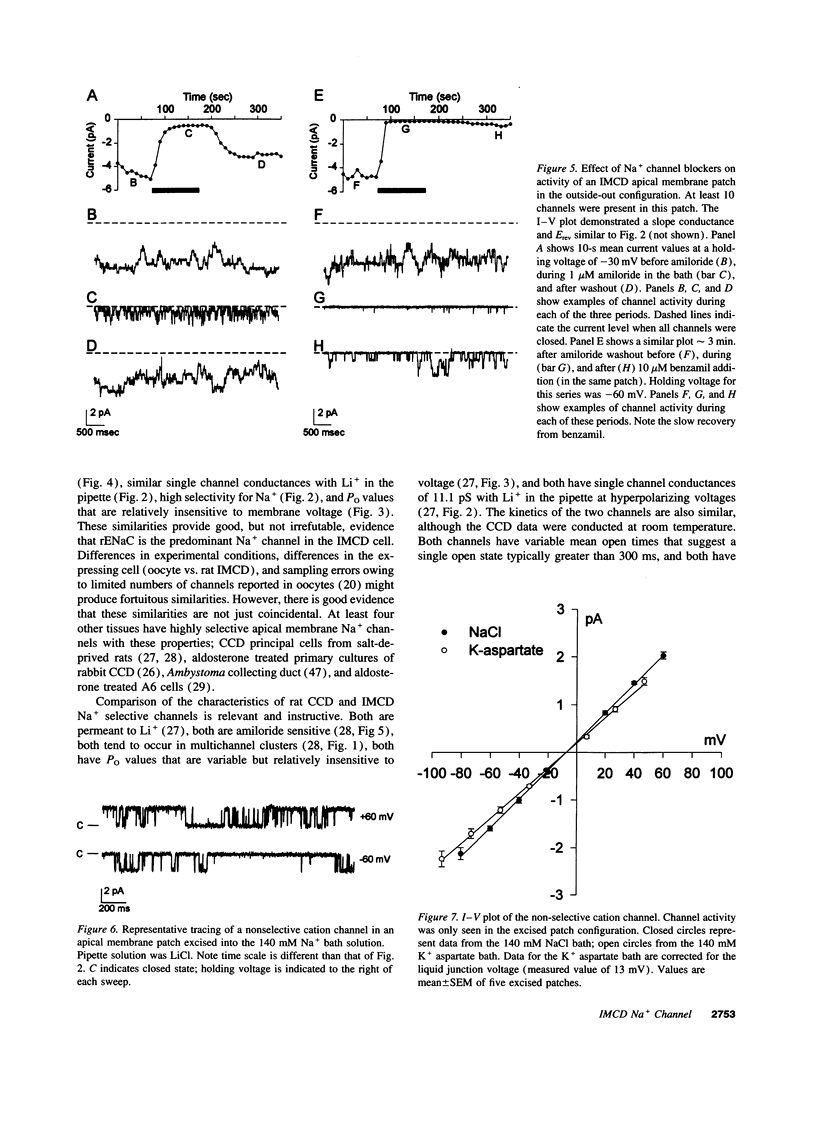
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck F., Dörge A., Rick R., Thurau K. Intra- and extracellular element concentrations of rat renal papilla in antidiuresis. Kidney Int. 1984 Feb;25(2):397–403. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Awayda M. S., Ismailov I. I., Johnson J. P. Structure and function of amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels. J Membr Biol. 1995 Jan;143(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00232519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
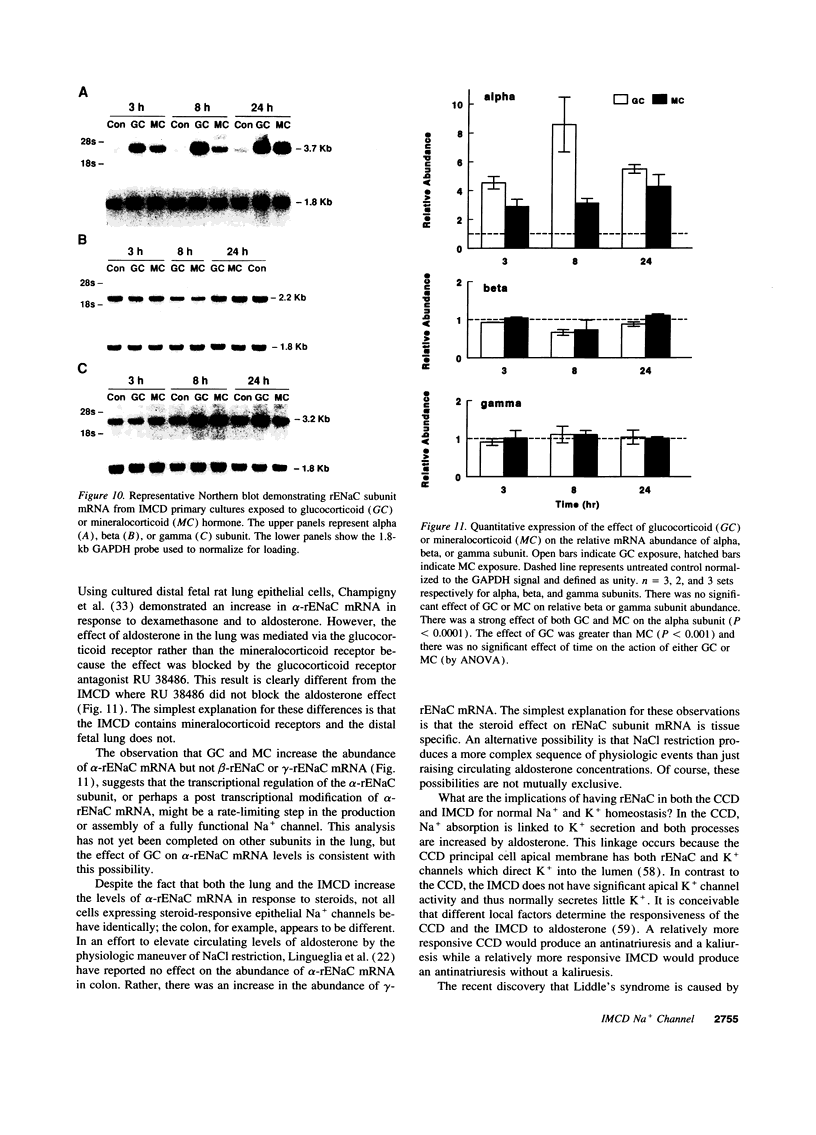
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigny G., Voilley N., Lingueglia E., Friend V., Barbry P., Lazdunski M. Regulation of expression of the lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel by steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2177–2181. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chraïbi A., Van den Abbeele T., Guinamard R., Teulon J. A ubiquitous non-selective cation channel in the mouse renal tubule with variable sensitivity to calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Nov;429(1):90–97. doi: 10.1007/BF02584034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diezi J., Michoud P., Aceves J., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of electrolyte transport across papillary collecting duct of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):623–634. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc C., Farman N., Canessa C. M., Bonvalet J. P., Rossier B. C. Cell-specific expression of epithelial sodium channel alpha, beta, and gamma subunits in aldosterone-responsive epithelia from the rat: localization by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1907–1921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchatelle P., Ohara A., Ling B. N., Kemendy A. E., Kokko K. E., Matsumoto P. S., Eaton D. C. Regulation of renal epithelial sodium channels. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992 Sep 8;114(1-2):27–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00240294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Palmer L. G. Low-conductance K channels in apical membrane of rat cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F143–F151. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamati H. F., Britton E. L., Carey D. J. Inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis alters extracellular matrix deposition, proliferation, and cytoskeletal organization of rat aortic smooth muscle cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2495–2505. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. L., Eaton D. C. Single-channel recordings from two types of amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels. Membr Biochem. 1986;6(2):149–171. doi: 10.3109/09687688609065447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy D. P., Fanestil D. D. Localization of atrial natriuretic peptide binding sites within the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F573–F578. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Laplace J. R., Stokes J. B. Enhancement of electrogenic Na+ transport across rat inner medullary collecting duct by glucocorticoid and by mineralocorticoid hormones. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):498–506. doi: 10.1172/JCI114736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Matsushita K., Stokes J. B. Induction of resistance to mineralocorticoid hormone in cultured inner medullary collecting duct cells by TGF-beta 1. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 2):F767–F775. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.5.F767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Volk K. A., Sigmund R. D., Stokes J. B. Anion secretion by the inner medullary collecting duct. Evidence for involvement of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):644–650. doi: 10.1172/JCI117709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Yoshitomi K. Electrophysiological study of inner medullary collecting duct of hamsters. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):180–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00370240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemendy A. E., Kleyman T. R., Eaton D. C. Aldosterone alters the open probability of amiloride-blockable sodium channels in A6 epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):C825–C837. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.4.C825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D. O., Rudigier J. F., Bischoff E., Decker K. F. The trapping of uridine phosphates by D-galactosamine. D-glucosamine, and 2-deoxy-D-galactose. A study on the mechanism of galactosamine hepatitis. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):246–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizer N. L., Lewis B., Stanton B. A. Electrogenic sodium absorption and chloride secretion by an inner medullary collecting duct cell line (mIMCD-K2). Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 2):F347–F355. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.2.F347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplace J. R., Husted R. F., Stokes J. B. Cellular responses to steroids in the enhancement of Na+ transport by rat collecting duct cells in culture. Differences between glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormones. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1370–1378. doi: 10.1172/JCI116003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Corbin J. D., Stanton B. A. Dual ion-channel regulation by cyclic GMP and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):336–339. doi: 10.1038/344336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., McCann F. V., Keller T. M., Stanton B. A. Amiloride-sensitive cation channel in apical membrane of inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F278–F286. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Schwiebert E. M., Karlson K. H., Stanton B. A. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits a cation channel in renal inner medullary collecting duct cells. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):383–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2463673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Hinton C. F., Eaton D. C. Amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in rabbit cortical collecting tubule primary cultures. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F933–F944. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Renard S., Waldmann R., Voilley N., Champigny G., Plass H., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Different homologous subunits of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel are differently regulated by aldosterone. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13736–13739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald F. J., Snyder P. M., McCray P. B., Jr, Welsh M. J. Cloning, expression, and tissue distribution of a human amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 1):L728–L734. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1994.266.6.L728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka T., Matsuzaki K., Kawahara K., Suzuki K., Hoshino M. Monovalent cation selective channel in the apical membrane of rat inner medullary collecting duct cells in primary culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Feb 15;1233(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)00241-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Sands J. M., Knepper M. A. ANF inhibits NaCl and fluid absorption in cortical collecting duct of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F179–F186. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H., Canessa C., Ueda J., Rafii B., Rossier B. C., Edelson J. Expression of the epithelial Na+ channel in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):C491–C496. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.2.C491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Mougouris T., DuBose T. D., Jr, Sansom S. C. ATP and calcium modulation of nonselective cation channels in IMCD cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):F558–F565. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.4.F558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G. Epithelial Na channels: function and diversity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:51–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Conductance and gating of epithelial Na channels from rat cortical collecting tubule. Effects of luminal Na and Li. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):121–138. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pácha J., Frindt G., Antonian L., Silver R. B., Palmer L. G. Regulation of Na channels of the rat cortical collecting tubule by aldosterone. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jul;102(1):25–42. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif M. C., Troutman S. L., Schafer J. A. Sodium transport by rat cortical collecting tubule. Effects of vasopressin and desoxycorticosterone. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1291–1298. doi: 10.1172/JCI112433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. M., Nonoguchi H., Knepper M. A. Hormone effects on NaCl permeability of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F421–F428. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. J., Husted R. F., Stokes J. B. Steroid hormone stimulation of Na+ transport in A6 cells is mediated via glucocorticoid receptors. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):C875–C884. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.4.C875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on cation transport by cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):F576–F585. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets R. A., Warnock D. G., Bositis C. M., Nelson-Williams C., Hansson J. H., Schambelan M., Gill J. R., Jr, Ulick S., Milora R. V., Findling J. W. Liddle's syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H. Collecting duct function in deoxycorticosterone acetate-escaped, normal, and salt-deprived rats. Response to hypervolemia. Circ Res. 1976 Aug;39(2):282–288. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.2.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Honrath U., Chong C. K., Wilson D. R. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits sodium transport in medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 2):F963–F966. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.6.F963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A. Characterization of apical and basolateral membrane conductances of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F862–F868. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Grupp C., Kinne R. K. Purification of rat papillary collecting duct cells: functional and metabolic assessment. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F251–F262. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Ingram M. J., Williams A. D., Ingram D. Heterogeneity of the rabbit collecting tubule: localization of mineralocorticoid hormone action to the cortical portion. Kidney Int. 1981 Sep;20(3):340–347. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Engbretson B. G., Viggiano S. C., Benos D. J., Smith P. R. Amiloride-sensitive apical membrane sodium channels of everted Ambystoma collecting tubule. J Membr Biol. 1995 Mar;144(2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00232800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Pisano J. J., Knepper M. A. Control of sodium and potassium transport in the cortical collecting duct of the rat. Effects of bradykinin, vasopressin, and deoxycorticosterone. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):132–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI111935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich E., Baldamus C. A., Ullrich K. J. Einfluss von Aldosteron auf den Natriumtransport in den Sammelrohren der Säugetierniere. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):111–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00587019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voilley N., Lingueglia E., Champigny G., Mattéi M. G., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. The lung amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel: biophysical properties, pharmacology, ontogenesis, and molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Champigny G., Lazdunski M. Functional degenerin-containing chimeras identify residues essential for amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel function. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):11735–11737. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.11735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Kikeri D., Silva P., Burrowes M., Brenner B. M. Atrial natriuretic peptides inhibit conductive sodium uptake by rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1172/JCI113663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]