Abstract
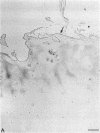
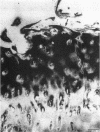
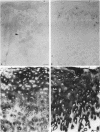
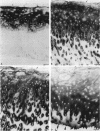
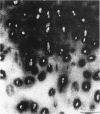
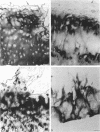
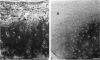
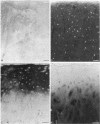
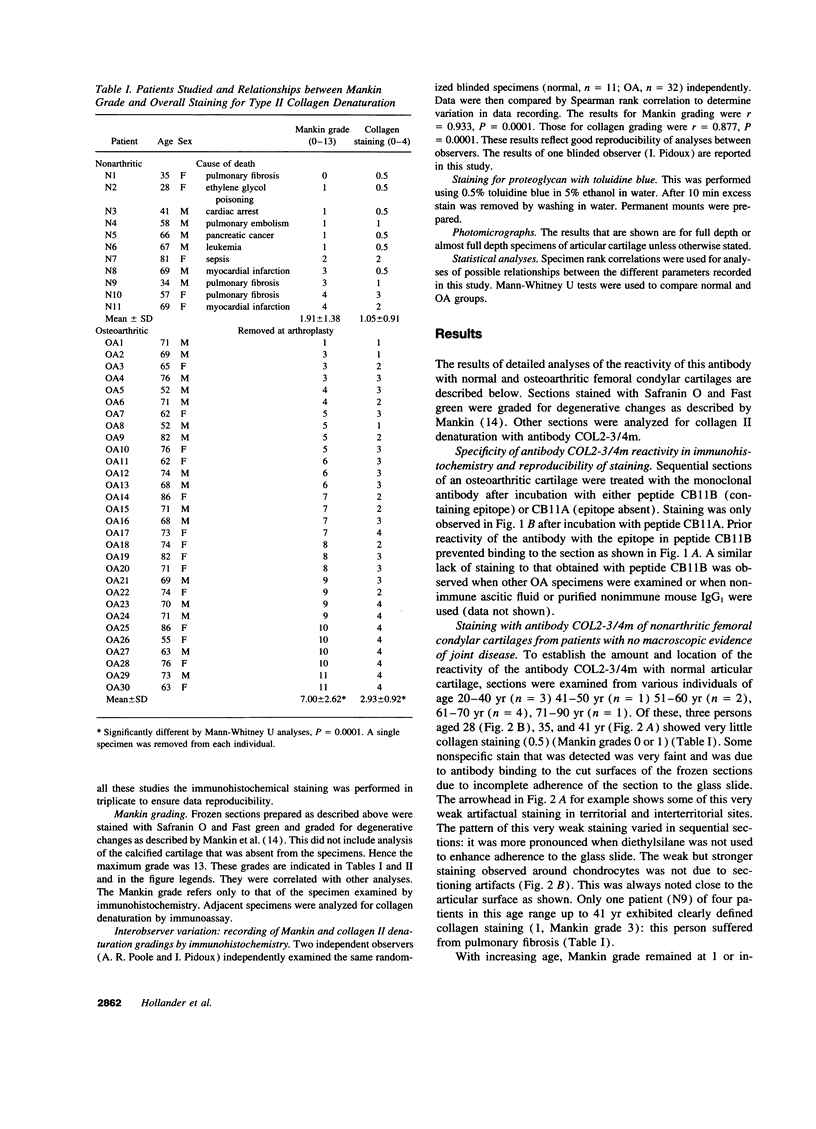
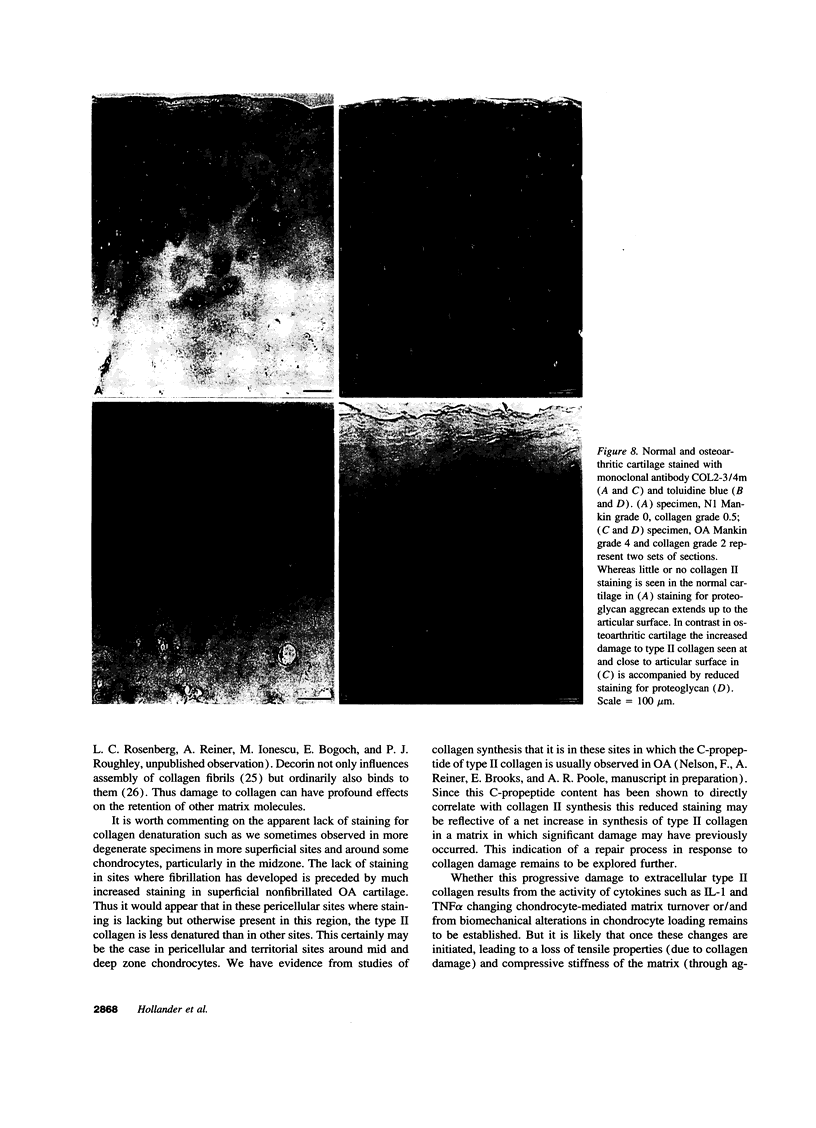
Enhanced denaturation of type II collagen fibrils in femoral condylar cartilage in osteoarthritis (OA) has recently been quantitated immunochemically (Hollander, A.P., T.F. Heathfield, C. Webber, Y. Iwata, R. Bourne, C. Rorabeck, and A.R. Poole. 1994. J. Clin. Invest. 93:1722-1732). Using the same antibody that only reacts with denatured type II collagen, we investigated with immunoperoxidase histochemistry (results were graded for analysis) the sites of the denaturation (loss of triple helix) of this molecule in human aging (at autopsy, n= 11) and progressively degenerate (by Mankin grade [MG]) OA (at arthroplasty, n= 51) knee condylar cartilages. Up to 41 yr, most aging cartilages (3 of 4) (MG 0-4) showed very little denaturation. In most older cartilages, (4 of 7) (MG 2-4), staining was observed in the superficial and mid zones. This pattern of collagen II denaturation was also seen in all OA specimens with increased staining extending to the deep zone with increasing MG. Collagen II staining correlated directly both with MG and collagen II denaturation measured by immunoassay. Cartilage fibrillation occurred in OA cartilages with increased penetration of the staining for collagen II denaturation into the mid and deep zones and where denaturation was more pronounced by immunoassay. Thus in both aging and OA the first damage to type II collagen occurs in the superficial and upper mid zone (low MG) extending to the lower mid and deep zones with increasing degeneration (increasing MG). Initial damage is always seen around chondrocytes implicating them in the denaturation of type II collagen.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akizuki S., Mow V. C., Müller F., Pita J. C., Howell D. S., Manicourt D. H. Tensile properties of human knee joint cartilage: I. Influence of ionic conditions, weight bearing, and fibrillation on the tensile modulus. J Orthop Res. 1986;4(4):379–392. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100040401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. D., Martel-Pelletier J., Pelletier J. P., Howell D. S., Woessner J. F., Jr Evidence for metalloproteinase and metalloproteinase inhibitor imbalance in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):678–685. doi: 10.1172/JCI114215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge G. R., Poole A. R. Immunohistochemical detection and immunochemical analysis of type II collagen degradation in human normal, rheumatoid, and osteoarthritic articular cartilages and in explants of bovine articular cartilage cultured with interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):647–661. doi: 10.1172/JCI113929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T. Epidemiology of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Epidemiol Rev. 1988;10:1–28. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freije J. M., Díez-Itza I., Balbín M., Sánchez L. M., Blasco R., Tolivia J., López-Otín C. Molecular cloning and expression of collagenase-3, a novel human matrix metalloproteinase produced by breast carcinomas. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16766–16773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallyas F., Merchenthaler I. Copper-H2O2 oxidation strikingly improves silver intensification of the nickel-diaminobenzidine (Ni-DAB) end-product of the peroxidase reaction. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Jul;36(7):807–810. doi: 10.1177/36.7.2898497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C. Interaction of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronic acid. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(1):101–120. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
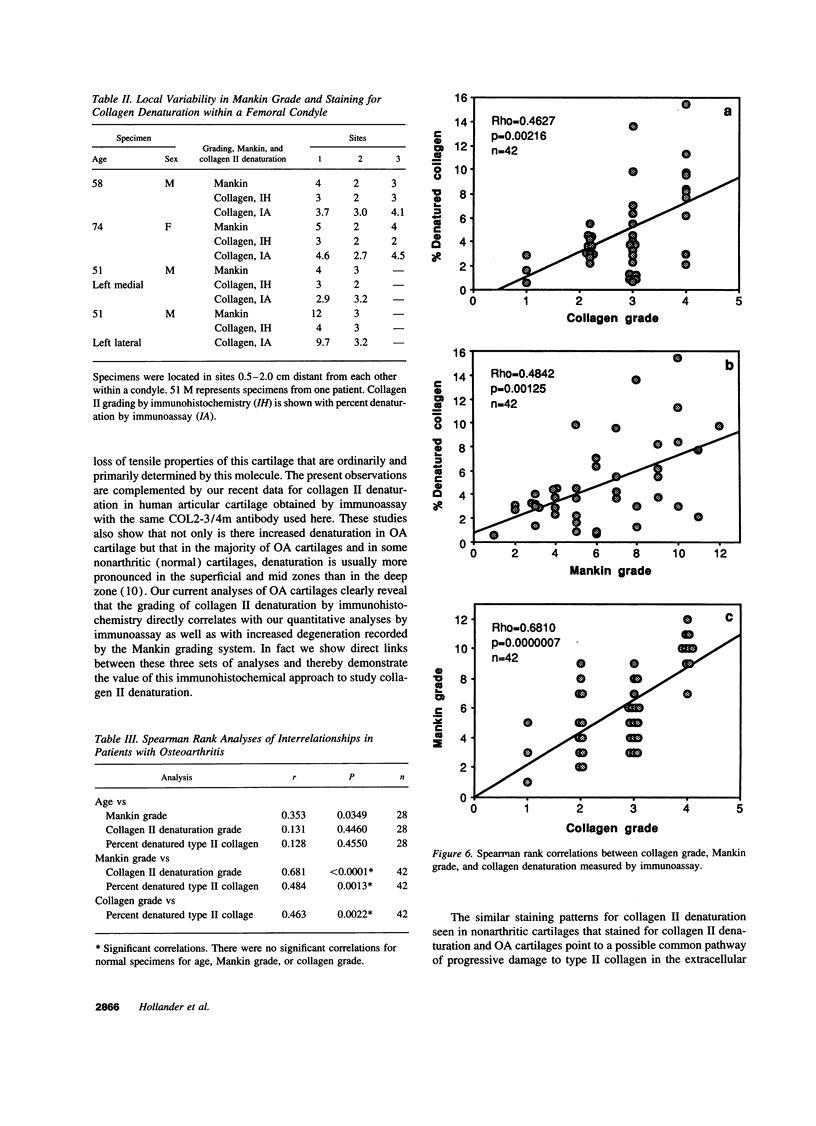
- Hollander A. P., Heathfield T. F., Webber C., Iwata Y., Bourne R., Rorabeck C., Poole A. R. Increased damage to type II collagen in osteoarthritic articular cartilage detected by a new immunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1722–1732. doi: 10.1172/JCI117156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E. Age-related changes in the tensile properties of human articular cartilage: a comparative study between the femoral head of the hip joint and the talus of the ankle joint. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 31;1075(3):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90270-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E., Muir H., Pollard C., Tuke M. The tensile properties of the cartilage of human femoral condyles related to the content of collagen and glycosaminoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):456–472. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E., Muir H., Swanson S. A., Freeman M. A. Correlations between stiffness and the chemical constituents of cartilage on the human femoral head. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E. Relationship between the tensile properties of articular cartilage from the human knee and age. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Oct;41(5):508–511. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.5.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Dorfman H., Lippiello L., Zarins A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Apr;53(3):523–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohtai M., Smith R. L., Schurman D. J., Tsuji Y., Torti F. M., Hutchinson N. I., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Goldberg G. I. Expression of 92-kD type IV collagenase/gelatinase (gelatinase B) in osteoarthritic cartilage and its induction in normal human articular cartilage by interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):179–185. doi: 10.1172/JCI116547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Dodge G. R., Roughley P. J., Liu J., Finch S. J., DiPasquale G., Poole A. R. Direct evidence for active metalloproteinases mediating matrix degradation in interleukin 1-stimulated human articular cartilage. Matrix. 1993 Mar;13(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mow V. C., Ratcliffe A., Poole A. R. Cartilage and diarthrodial joints as paradigms for hierarchical materials and structures. Biomaterials. 1992;13(2):67–97. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(92)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Q., Mort J. S., Roughley P. J. Preferential mRNA expression of prostromelysin relative to procollagenase and in situ localization in human articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1189–1197. doi: 10.1172/JCI115702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Shinmei M., Tanaka O., Naka K., Kimura A., Nakanishi I., Bayliss M. T., Iwata K., Nagase H. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) in osteoarthritic cartilage and synovium. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):680–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmoski M. J., Brandt K. D. Effects of static and cyclic compressive loading on articular cartilage plugs in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Jun;27(6):675–681. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Pidoux I., Reiner A., Rosenberg L. An immunoelectron microscope study of the organization of proteoglycan monomer, link protein, and collagen in the matrix of articular cartilage. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):921–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Pidoux I., Reiner A., Tang L. H., Choi H., Rosenberg L. Localization of proteoglycan monomer and link protein in the matrix of bovine articular cartilage: An immunohistochemical study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Jul;28(7):621–635. doi: 10.1177/28.7.6156200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Webber C., Pidoux I., Choi H., Rosenberg L. C. Localization of a dermatan sulfate proteoglycan (DS-PGII) in cartilage and the presence of an immunologically related species in other tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 May;34(5):619–625. doi: 10.1177/34.5.3701029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah R. L., Doong J. Y., Grodzinsky A. J., Plaas A. H., Sandy J. D. Effects of compression on the loss of newly synthesized proteoglycans and proteins from cartilage explants. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Apr;286(1):20–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E. Proteoglycan-fibrillar collagen interactions. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):313–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2520313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K. G., Paulsson M., Heinegård D. Specific inhibition of type I and type II collagen fibrillogenesis by the small proteoglycan of tendon. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):587–597. doi: 10.1042/bj2230587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kampen G. P., Veldhuijzen J. P., Kuijer R., van de Stadt R. J., Schipper C. A. Cartilage response to mechanical force in high-density chondrocyte cultures. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Apr;28(4):419–424. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]