Abstract
Skin adnexal neoplasms comprise a wide spectrum of benign and malignant tumours that exhibit morphological differentiation towards one or more types of adnexal structures found in normal skin. Most adnexal neoplasms are relatively uncommonly encountered in routine practice, and pathologists can recognise a limited number of frequently encountered tumours. In this review, the first of two, the normal histology of the skin adnexal structures is reviewed, and the histological features of selected but important benign and malignant tumours and tumour‐like lesions of pilosebaceous origin discussed, with emphasis on the diagnostic approach and pitfalls in histological diagnosis.
Skin adnexal tumours (SAT) are a large and diverse group of benign and malignant neoplasms, which exhibit morphological differentiation towards one of the different types of adnexal epithelium present in normal skin: pilosebaceous unit, eccrine and apocrine. SAT may display more than one line of differentiation (hybrid/composite tumours), rendering precise classification of these neoplasms difficult.1 The diagnosis of these mixed SAT relies on histological evaluation, and they are usually classified according to the predominant morphological component. The histogenesis of mixed adnexal tumours is still uncertain; however, the possibility of origin from a pluripotent stem cells is suggestive.2
Most SAT are benign, and local complete surgical excision is curative. However, diagnosing some of these tumours has important implications, as they might be markers for syndromes associated with internal malignancies, such as trichilemmomas in Cowden disease and sebaceous tumours in Muir–Torre syndrome. A malignant counterpart of almost every SAT has been described. These tumours are rare, locally aggressive, and have the potential for nodal involvement and distant metastasis, with a poor clinical outcome. Therefore, establishing a diagnosis of malignancy in SAT is important for therapeutic and prognostic purposes. Because pathologists may not frequently encounter SAT, and owing to their different derivation and broad histogenesis, diagnosing these tumours may be challenging even to an experienced pathologist. In this article, we review the histological features of selected benign, malignant and tumour‐like lesions of pilosebaceous origin (box 1), with emphasis on the diagnostic approach and morphological pitfalls in histological evaluation.
Normal histology of skin appendages
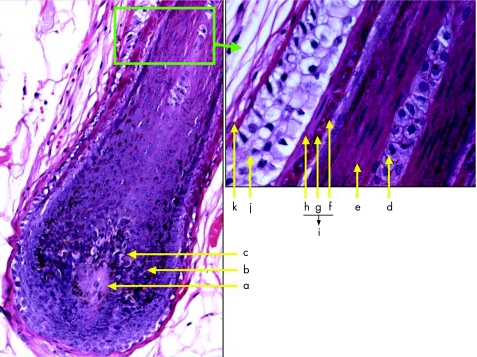
Skin appendages are derived from the ectoderm, and start to develop early during the embryological life. During the fourth week of development, a single‐cell‐thick ectoderm and underlying mesoderm begin to proliferate, and differentiate towards various structures, including skin appendages. These specialised skin structures are located within the dermis, including the deep dermis, and focally within the subcutaneous fatty tissue. They are represented by three histologically distinct structures: (1) the pilosebaceous unit; (2) the eccrine sweat glands; and (3) the apocrine glands. The distribution and arrangement of these appendages vary from one part of the skin to another, but the overall general basic morphogenesis is maintained. The pilosebaceous units (hair follicle and sebaceous glands) originate from the primary epithelial germs in the epidermis, a collection of deeply basophilic cells in the basal cell layer of the epidermis, protruding into the dermis and surrounded by an aggregate of mesenchymal cells. The hair follicle is a tubular invagination from the epidermis, responsible for the formation of hair, a highly modified keratinised structure. Highly vascular connective tissue papillae, enclosed by bulbous expansion (the hair bulb), are located in the reticular dermis or in the superficial subcutaneous fatty tissue, and form the lower portion of the hair follicle. The inner, mitotically active cells lining the dermal papillae undergo keratinisation to form the hair shaft and internal root sheath. Each hair shaft consists of an innermost medulla, surrounded by a broad, highly keratinised cortical layer, and an outermost thin layer of overlapping keratin, the cuticle. The outer two epidermal cell layers of hair bulb form the external root sheath, which consists of large, glycogen‐rich (clear) cells and is separated from the surrounding dermal connective tissue by a thick glassy membrane composed of homogenised fibrous tissue (fig 1).
Figure 1 Structure of hair bulb: (a) dermal papilla, (b) matrix, (c) melanocytes, (d) medulla, (e) cortex of hair, (f) area of hair cuticle, (g) Huxley's layer (prominent keratohyalin granules), (h) Henle's layer (one cell layer), (i) inner root sheath composed of cuticle, Huxley's and Henle's layers, (j) outer root sheath and (k) glassy basement membrane.
Box 1 Skin adnexal neoplasms and neoplastic‐like lesions of pilosebaceous origin
Hyperplastic and hamartomatous lesions
-
Hair and hair follicle
-
-
Basaloid follicular hamartoma
-
-
Basaloid epidermal proliferation
-
-
Overlying dermal mesenchymal lesions
-
-
Trichofolliculoma
-
-
Sebaceous trichofolliculoma
-
-
Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma
-
-
Trichodiscoma/fibrofolliculoma
-
-
Pilar sheath acanthoma
-
-
-
Sebaceous glands
-
-
Sebaceous hyperplasia
-
-
Nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn
-
-
Benign neoplasms
-
Hair and hair follicle
-
-
Trichofolliculoma
-
-
Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma
-
-
Trichoblastoma
-
-
Trichoblastic fibroma
-
-
Trichoadenoma
-
-
Proliferating trichilemmal cyst/pilar tumour
-
-
Trichilemmoma
-
-
Desmoplastic trichilemmoma
-
-
Pilomatricoma/proliferative pilomatricoma
-
-
-
Sebaceous glands
-
-
Sebaceous adenoma
-
-
Sebaceoma/sebaceous epithelioma
-
-
Malignant neoplasms
-
Hair and hair follicle
-
-
Trichilemmal carcinoma
-
-
Trichoblastic carcinoma
-
-
Malignant proliferating trichilemmal cyst
-
-
Pilomatrix carcinoma
-
-
-
Sebaceous glands
-
-
Sebaceous carcinoma
-
-
Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation
-
-
Developmentally, all sebaceous glands are hair follicle‐dependent (except those of the labia minora and glans penis), and originate as a budding of sebaceous glands primordium. The sebaceous glands consist of multiple lobules of rounded cells (sebocytes), filled with lipid‐containing vacuoles, and rimmed by a single layer of small, dark germinative cells. The lobules converge on a short duct, which empties the lipid content of degenerated sebocytes into the hair follicle. Sebaceous glands are immunoreactive to low‐molecular weight cytokeratin (LMWK), epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) and, to a lesser extent, to the lymphatic marker D2‐40. They are negative for S100 protein and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
Eccrine sweat glands originate from epidermal epithelial germs protruding into the dermis similar to those of pilosebaceous units, but contain less mesenchymal condensation. They are distributed almost everywhere in the skin. The sweat‐secreting coil glands are tubular and consist of two anatomical portions:
The secretory coil, located in the deep dermis at the junction with the subcutaneous tissue and composed of clear pyramidal cells, and darkly stained cells that are often difficult to identify on light microscopy. These cells express the immunohistochemical stains LMWK, EMA, CEA and S100 protein (basal layer only). A single outer, discontinuous layer of myoepithelial cells resting on a well‐defined basement membrane is present, and can be highlighted by immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis for smooth muscle actin (SMA), p63 and calponin.
The excretory part is composed of a straight intradermal portion and an intraepidermal spiral portion (acrosyringium), and consists of a double layer of small cuboidal cells with no underlying myoepithelial layer. The cells in this part may stain with high molecular weight keratin (HMWK) and cytokeratin (CK) 14.
Apocrine glands are seen mainly in the axillae, groin, pubic and perineal regions. In contrast with eccrine glands, apocrine glands develop from an upper bulge in hair follicles that are in the early bulbous peg stage. They have a coiled, tubular excretory portion with widely dilated lumen, lined by cuboidal epithelial cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and apical snouts (representing decapitation secretion), and an outer discontinuous layer of myoepithelial cells, resting on a prominent basement membrane. The cytoplasm of apocrine glandular cells might contain iron, which can be illustrated using Prussian blue stain. The luminal cells are characteristically immunoreactant to gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP‐15). These glands also express androgen receptors, which may be useful in the assessment of lesions suspected to be apocrine carcinoma. The excretory duct of apocrine glands is histologically similar to that of eccrine glands, and drains into the hair shaft. A third type of sweat gland is “apoeccrine” glands. These are atrichial glands which open directly to the skin surface, but their secretory coil is similar to that of apocrine glands.3 These glands are mostly found in the axillary region, and within lesions of the nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn (NSJ)4; they are considered to be the origin of some adnexal lesions, such as syringocystadenoma papilliferum (SCAP),5 and Fox–Fordyce disease.6 The occurrence of mammary‐like glands mainly in the anogenital region has been elucidated in recent years and will be discussed further in the second review of cutaneous sweat gland tumours.
Practical considerations in the pathological evaluation of skin adnexal tumours
In the pathological evaluation of skin specimens for SAT, the pathologist should be provided with sufficient clinical data that may prove to be useful in achieving accurate diagnosis. These include patient's age and sex, location(s) of the lesion, the rate of tumour growth, whether the lesion is solitary or multiple, and, if present, any associated inherited or systemic diseases. The specimen should be examined grossly and meticulously; the size, growth pattern (nodular or plaque), colour, presence of ulceration, and status of the surgical resection margins should be recorded. The specimen should be thoroughly sampled after painting its resection margins; the lesion should be serially sectioned at 0.3–0.5‐cm intervals and submitted in its entirety for histological examination. Sections including tumoral and grossly uninvolved surrounding tissue are relevant to evaluate the growth pattern of the tumour. The deep and peripheral surgical resection margins should be submitted to assure complete excision. It is important to note that a small/superficial biopsy may preclude accurate diagnosis of skin adnexal lesions, and is therefore not advised.
After proper fixation and processing, haematoxylin and eosin (H&E)‐stained sections are considered sufficient for routine microscopic evaluation. The presence of cells with coarsely vacuolated cytoplasm and starry nuclei (mulberry cells) within a tumour is indicative of sebaceous differentiation. Follicular differentiation in adnexal tumours is characterised by the presence of proliferation of basaloid bulbar follicular germinative cells, peripheral nuclear palisading and adjacent papillary mesenchymal cells. Follicular differentiation may also be suspected in the presence of matrical shadow (ghost) cells, and if tumour is attached to normal follicular structures. Apocrine cells have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric, basally located nuclei. Although the presence of decapitation secretion is deemed evidence for apocrine differentiation, this finding is considered useful but not very specific.
Thorough morphological evaluation should be performed to reach proper classification and correct diagnosis (tables 1 and 2). Benign SAT are usually multilobulated, and have symmetric and smooth borders, and uniform collections of epithelial cells, usually with no tumour necrosis or ulceration. There is usually no atypia, and the mitotic activity is generally minimal. Dense fibrotic stromal reaction occurs frequently in these tumours. Malignant features in SAT include asymmetrical growth, jagged/infiltrative borders, irregular arrangement of neoplastic cells, cytonuclear atypia and increased mitotic activity. Tumour necrosis and superficial ulcerations are commonly seen. The tumour‐associated sclerotic stroma is usually diminished. The presence of these worrisome features should prompt wide excision of these tumours, with meticulous examination of all resection margins. Sentinel lymph node biopsy may be indicated in some cases; however, the role of sentinel node biopsy in malignant SAT is not yet fully defined. The patients should be closely followed up for potential regional and distant metastasis.
Table 1 Histopathological diagnostic features to consider in the evaluation of benign skin adnexal lesions.
| Category | Feature description | Common examples |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Intraepidermal | Basaloid epidermal proliferations |
| Pilar sheath acanthoma | ||
| Hidroacanthoma simplex (intraepidermal poroma) | ||
| Dermal with epidermal connection | Trichofolliculoma | |
| Trichilemmoma | ||
| Poroma | ||
| Hidradenoma (rarely) | ||
| Dermal without epidermal connection | Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma | |
| Sebaceous tumours | ||
| Pilomatricoma | ||
| Hidradenoma | ||
| Morphology | Nests and/or cords | Syringoma |
| Syringofibradenoma | ||
| Solid sheets, nodular | Hidradenoma | |
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Cylindroma | ||
| Jigsaw puzzle‐like pieces | Cylindroma | |
| Ductal‐tubular formation | Syringoma | |
| Syringofibradenoma | ||
| Papillary structures | Syringocystadenoma papilliferum | |
| Hidradenoma papilliferum | ||
| Tubulopapillary hidradenoma (papillary eccrine adenoma and tubular apocrine adenoma) | ||
| Partially cystic | Pilomatricoma | |
| Pilar tumour | ||
| Hidradenoma | ||
| Chondroid syringoma | ||
| Fully cystic | Hidrocystoma | |
| Trichilemmal cyst | ||
| Steatocystoma | ||
| Borders | Well‐defined, round and lobulated | Pilomatricoma |
| Hidradenoma papilliferum | ||
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Cylindroma | ||
| Pushing | Pilar tumour | |
| Infiltrative | A feature suspicious of malignant transformation | |
| Cellular details | Basaloid | Basaloid follicular hamartoma |
| Basaloid epidermal proliferations | ||
| Sebaceoma | ||
| Pilomatricoma | ||
| Hidradenoma | ||
| Poroma | ||
| Cylindroma | ||
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Epidermoid/squamoid | Hidradenoma papilliferum | |
| Hidradenoma | ||
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Syringocystadenoma papilliferum | ||
| Shadow (ghost) cells | Pilomatricoma | |
| Clear | Trichilemmoma | |
| Hidradenoma | ||
| Poroma | ||
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Syringoma | ||
| Mulberry cells | Lesions with sebaceous differentiation | |
| Presence of more than one population of cells | Spiradenoma | |
| Cylindroma | ||
| Apical snouts | Most lesions with apocrine differentiation | |
| Peripheral palisading | Basaloid follicular hamartoma | |
| Trichoepitheliomas | ||
| Trichoblastoma | ||
| Trichilemmomas | ||
| Sebaceoma | ||
| Pilar tumour | ||
| Evidence of differentiation | Trichilemmal keratinisation (without granular layer) | Pilar tumour |
| Follicular germ and hair shaft formation | Trichoblastoma | |
| Trichoepitheliomas | ||
| Glandular formation | Syringoma | |
| Tubulopapillary hidradenoma | ||
| Syringofibroadenoma | ||
| Hidradenoma papilliferum | ||
| Syringocystadenoma papilliferum | ||
| Sebaceous differentiation | Sebaceous tumours and lesions with sebaceous differentiation | |
| Spindle cell differentiation (rare) | Hidradenoma | |
| Stroma | Stromal desmoplasia | Most adnexal lesions |
| Mucinous change | Trichoblastic fibroma | |
| Chondroid syringoma | ||
| Chondroid change | Chondroid syringoma | |
| Vascular component | Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma | |
| Trichodiscoma/fibrofolliculoma | ||
| Poromas | ||
| Syringofibroadenoma | ||
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Neural component | Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma | |
| Prominent stromal plasma cell infiltrate | Syringocystadenoma papilliferum | |
| Other morphological associations | Epidermal verrucous hyperplasia | Trichilemmoma |
| Sebaceoma | ||
| Nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn | ||
| Melanocytic hyperplasia | Trichoblastoma | |
| Ulceration | Suspicious feature for malignancy | |
| Dystrophic calcification/ossification | Trichoepitheliomas | |
| Trichoblastoma | ||
| Pilomatricoma | ||
| Pilar tumour | ||
| Hyaline basement membrane | Trichilemmomas | |
| Cylindroma | ||
| Steatocystoma | ||
| Foreign body granuloma | Trichoepithelioma | |
| Pilomatricoma | ||
| Pilar tumour | ||
| Presence of rare Merkel cells | Basaloid epidermal proliferation | |
| Trichofolliculoma | ||
| Trichoepitheliomas | ||
| Trichoblastoma |
Table 2 Morphological patterns and useful observations in evaluating skin adnexal tumours.
| Pattern | Examples | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Tumours with sebaceous elements | Sebaceous hyperplasia, sebaceous adenoma and sebaceoma | Sebaceous differentiation is indicated by “mulberry” cells with coarsely vacuolated cytoplasm and starry nuclei |
| Sebaceous carcinoma | EMA is positive in sebaceous cells | |
| Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation | ||
| Trichoblastoma with sebaceous differentiation | ||
| A variety of tumours of the “pilosebaceous‐apocrine” unit | ||
| Sebaceous hyperplasia, sebaceous adenoma and sebaceoma | ||
| Sebaceous carcinoma | ||
| Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation | ||
| Trichoblastoma with sebaceous differentiation | ||
| A variety of tumours of the “pilosebaceous‐apocrine” unit | ||
| Tumours with elements of follicular differentiation | Trichoepithelioma | Proliferation of basaloid bulbar follicular germinative cells (with peripheral palisading) or lesions with matrical cells |
| Tumours with elements of follicular differentiation | Trichoblastoma | |
| Trichofolliculoma pilomatricoma | ||
| Tumours with clear cell change | Trichilemmoma | Clear cell change is indicative of trichilemmal differentiation in follicular lesions |
| Poroma and porocarcinoma | Clear cells are glycogen rich and PAS positive | |
| Hidradenoma | Clear cell change is indicative of trichilemmal differentiation in follicular lesions. Clear cells are glycogen rich and PAS positive | |
| Tumours with ductal/tubuloglandular elements | Syringoma poroma and porocarcinoma | Mostly in eccrine/apocrine lesions |
| Syringoma | Ducts have a dense eosinophilic cuticle, and may contain amorphous material. PAS and CEA are usually positive | |
| Cylindroma | Mostly in eccrine/apocrine lesions. Ducts have a dense eosinophilic cuticle, and may contain amorphous material. PAS and CEA are usually positive | |
| Hidradenoma | ||
| Microcystic adnexal carcinoma | ||
| Tumours with small keratin cysts | Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma | Mostly in lesions with follicular differentiation |
| Trichoblastoma | Cysts lack a cuticle, do not stain with PAS or CEA, and may contain keratin | |
| Trichoadenoma | Mostly in lesions with follicular differentiation. Cysts lack a cuticle, do not stain with PAS or CEA, and may contain keratin | |
| Microcystic adnexal carcinoma | ||
| Tumours with predominant small/basaloid elements | Trichoblastoma/trichoepithelioma | This pattern should be interpreted in conjunction with other features such as sebaceous or follicular differentiation, the presence of cysts/ductal elements or clear cell change, etc |
| Pilomatricoma | ||
| Sebaceous tumours | ||
| Poroma | ||
| Spiradenoma | ||
| Acrospiroma | ||
| Cylindroma |
CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; EMA, epithelial membrane antigen; PAS, periodic acid Schiff.
The need for special and/or immunohistochemical stains in the evaluation of SAT varies from one case to another, and can be used when necessary. Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) stain, with and without diastase, can be helpful to demonstrate cytoplasmic glycogen contents and stromal hyalinised basement membrane that present in certain cutaneous adnexal lesions. Hale's colloidal iron stain for acid mucin is useful to highlight stromal mucinous degeneration in certain adnexal tumours. Prussian blue may be useful in demonstrating iron deposits within apocrine lesions. IHC and ultrastructural ancillary studies may aid in establishing the tumour differentiation, but they have limited diagnostic value and yield. Most SATs express different types of cytokeratins. Monoclonal CEA and EMA can be seen in tumours with ductal differentiation. EMA is expressed in tumours with sebaceous differentiation. GCDFP‐15 and androgen receptors are seen in apocrine lesions, whereas oestrogen and progesterone receptors are seen in different sweat glands lesions and are not considered specific.
Tumours of hair follicle (pilar) origin
Basaloid follicular hamartoma
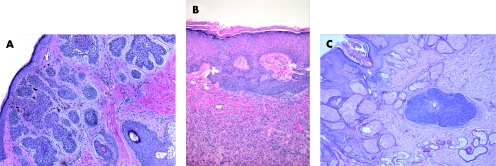
Basaloid follicular hamartoma (BFH) is a unique benign lesion, characterised by variable clinical presentation, and association with cutaneous and systemic diseases. It can be acquired or inherited as an autosomal dominant disease.7 The acquired BFH can present as a solitary lesion that affects middle‐aged and elderly people. The lesion mostly involves the scalp and face, or can be generalised, which is characteristically associated with other clinical conditions such as myasthenia gravis, basal cell carcinoma (BCC),8 systemic lupus erythematosus and alopecia.9,10 Inherited familial BFH presents during adulthood as numerous, widely spread, small flesh‐coloured or pigmented papules, and may be associated with alopecia and cystic fibrosis.11 Histologically, the lesion consists of multifocal proliferation of small basaloid cells admixed with squamous cells, forming anastomosing strands, branching cords or lobules extending from hair follicles, and embedded in loose, occasionally mucinous or densely fibrous stroma (fig 2A). Peripheral palisading of the basaloid cells, foci of keratinisation and horn cyst formation, and abortive hair follicles can be present, making BFH histologically indistinguishable from trichoepithelioma. Histological features of BFH are not always diagnostic, especially in superficial or inadequate biopsies, and should be differentiated from other cutaneous lesions with basaloid proliferation, particularly BCC. Fewer mitoses, decreased single‐cell necrosis and absence of artifactual retraction are helpful discriminating features from BCC.8 It is also worth mentioning that differentiating BFH from other lesions with basaloid proliferation (such as BCC) can be difficult on frozen sections, especially during Mohs surgery, and may require an experienced pathologist to assess the margins.
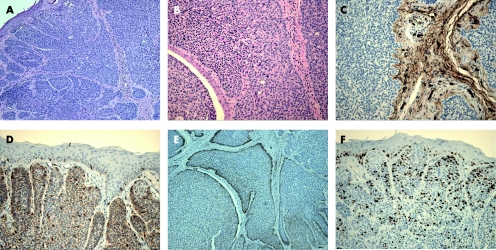
Figure 2 (A) Basaloid follicular hamartoma, (B) basaloid epidermal proliferation (BEP) overlying cutaneous fibrous histiocytoma and (C) BEP in nevus sebaceous.
Basaloid epidermal proliferation overlying dermal mesenchymal lesions
Basaloid epidermal proliferations (BEPs), morphologically resembling superficial BCC, have been described overlying cutaneous mesenchymal lesions such as fibrous histiocytoma (dermatofibroma)13 (fig 2B) and cutaneous myxomas.14 Not uncommonly, BEP is also present in the epidermis overlying NSJ (fig 2C). The pathogenesis of BEP is not clear. It is currently believed that BEP represents benign adnexal proliferation with follicular differentiation, and that it may be stimulated and maintained by the underlying proliferating mesenchymal lesion.15 Although in most cases BEPs behave in a benign fashion, and can even regress, the possibility of these lesions possessing a malignant potential is controversial.16,17 Distinguishing BEP from BCC is important because of the current differences in therapeutic approach and expected clinical outcome. In comparison to BCC, BEPs are limited to the epidermis overlying the dermal lesion, have no infiltrative growth pattern, contain sparse mitotic figures, express no or inconspicuous p53 immunoreactivity,13,18 and may occasionally contain Merkel cells (detected by anti‐CK 20 IHC staining).19 Conflicting results about the immunoexpression of proliferative marker MIB‐1 (Ki‐67)15,17 and bcl‐213,17 in BEP have been reported in the literature. Basaloid proliferations arising in hair follicles may also be seen within fibrous papules (angiofibromas) of the nose.
Trichofolliculoma, folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma, trichodiscoma/fibrofolliculoma and other closely related lesions
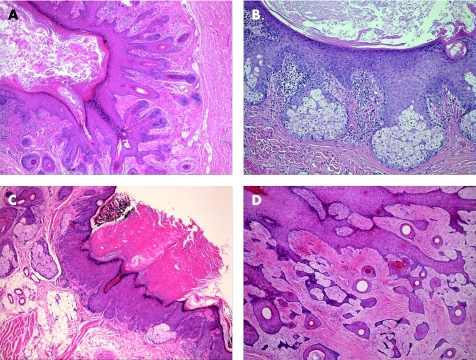
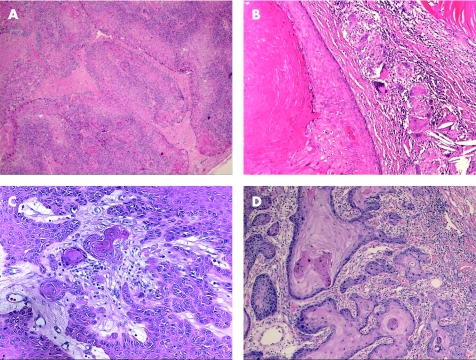
Trichofolliculomas are benign hamartomatous lesions that develop at any age, and typically involve the face. It is believed that trichofolliculomas represent abortive differentiation of cutaneous pluripotent stem cells towards hair follicles. They usually present as skin‐coloured, single or multiple small nodules with central epidermal ostium, in which hair emerge. Histologically, trichofolliculomas consist of centrally located, keratin‐filled, unilocular or multilocular cystic cavities, usually connected to the epidermis, and lined by infundibular squamous epithelium with prominent granular layer (fig 3A). Numerous secondary and tertiary hair follicles surrounded by variable numbers of sebaceous glands bud out and branch radially from the central cavity into a fibrotic stroma, giving it a “caput medusa” appearance. Characteristically, a large number of Merkel cells can easily be identified within the tumour cells by IHC examination.20 A single case of trichofolliculoma with perineural invasion has been reported in the literature.21 Sebaceous trichofolliculoma (fig 3B) is a rare variant of trichofolliculoma, and is characterised by prominent lobules of well‐differentiated sebaceous glands within the tumours, but lacking the vellus hair component.22 A differential diagnosis of sebaceous trichofolliculoma is folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma (FSCH), which is a very rare hamartomatous lesion, histologically consisting of a prominent epithelial component characterised by folliculosebaceous proliferation with cyst‐like infundibular dilatation,23,24 without connection to the overlying epidermis. Cleft‐like spaces separate the epithelial component from the surrounding stroma, which is characteristically composed of dense collagenous tissue, and can contain variable amounts of mature adipose tissue, and exhibit vascular and neural proliferation. Both the lack of epidermal connection and prominent stromal component are important morphological features discriminating FSCH from trichofolliculoma.
Figure 3 (A) Trichofolliculoma, (B) sebaceous trichofolliculoma, (C) pilar sheath acanthoma and (D) trichodiscoma/fibrofolliculoma.
Another differential diagnosis of trichofolliculoma is pilar sheath acanthoma, which is a benign follicular tumour, usually seen in adults as small single papules, mostly on the upper lip. Characteristically, it has a tiny central punctum, and lacks clinically identifiable hair structures. Histologically, it has a superficial broad invagination of cells, which often have clear (glycogenated) cytoplasm, producing a crater‐like cavity (fig 3C). The lesion is associated with epidermal/infundibular and isthmic differentiation. Hence, solid lobules of basophilic and eosinophilic cells are present within the superficial dermis, similar to the epithelium of the infundibulum and isthmus, respectively. Although dilated pore of Winer might be a differential diagnosis of trichofolliculoma and pilar sheath acanthoma, it is an infundibular cyst that shows invagination of the surface epithelium, lined by relatively thin stratified squamous epithelium, and lacking isthmus differentiation.
In trichodiscoma/fibrofolliculoma (fig 3D), the lesion is characterised by dilated follicular infundibulum, from which there is proliferation of thin, trabeculated strands of basophilic infundibular epithelium within a prominent fibrous stroma. The stroma contains a large number of small vascular channels, and stromal mucinous change is often present. Multiple lesions are seen in Birt–Hogg–Dube syndrome, which is an autosomal dominant condition characterised by trichodiscomas/fibrofolliculomas, and associated with benign and malignant renal neoplasms, lung cysts and spontaneous pneumothorax.25
Trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic trichoepithelioma
Classical trichoepithelioma is a benign tumour that can occur as: (1) a sporadic, solitary lesion that can be found on any portion of hair‐bearing skin, with a predilection for the head and neck region in adults, or (2) an autosomal dominant familial disorder characterised by multiple, small lesions, with a predilection for the head and neck, and upper trunk regions in adolescence. The gene associated with multiple familial trichoepithelioma (MFT) links to the short arm of chromosome 9, in which several tumour suppressor genes are located.26 Recently, mutations in the CYLD gene have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of MFT.27,28 Histologically, trichoepithelioma is a well‐circumscribed and symmetric lesion with or without connection to the epidermis. It consists predominantly of uniform basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, arranged in variably sized nests, trabeculae or cribriform patterns, and surrounded by dense stroma that contains fibroblasts resembling follicular germs and bulbs, and follicular papillae. In contrast with BCC (table 3), a major histological differential diagnosis, artefactual retraction is uncommon, and is present within the fibrotic stroma. Small horn cysts filled with keratin are usually present within the epithelial nests (fig 4). Immunohistochemically, trichoepithelioma expresses CK 5, 6, 7, 14, 17, and 15; the latter is found to be expressed in most trichoepithelioma but not in BCC.29 Positive immunostaining for bcl‐2 may be helpful in differentiating TE from BCC; it tends to be diffuse in BCC, whereas it is peripheral in trichoepithelioma.30,31 In addition, CD34 is found to be positive in the stroma of trichoepithelioma, but absent in BCC.32 Trichoepithelioma and BCC also have different patterns of CD10 positivity and MIB‐1 (Ki‐67) labelling index.33,34 Rarely, a BCC may develop within a trichoepithelioma in which case features of both tumours may be seen in the same lesion (fig 5).
Table 3 Useful histological and immunohistochemical features for distinguishing between basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma.
| Feature | BCC | TE |
|---|---|---|
| Histology | Increased mitoses | Mitoses not increased |
| Retraction spaces | Retraction spaces not present | |
| Usually no horn cysts | Horn cysts usually present | |
| Stromelysin 3 | Positive in stroma | Negative |
| CD10 | Positive in basaloid cells | Positive in stroma |
| CD34 | Negative | Positive in stroma |
| Bcl‐2 | Diffusely positive in basaloid cells | Positive in peripheral cells only |
| Ki‐67 | Increased (20–40%) | Normal (rare cells) |
| CK 15 | Negative | Focally positive |
| CK 20 | Negative | Focally positive |
BCC, basal cell carcinoma; CK, cytokeratin; TE, trichoepithelioma.
Figure 4 Trichoepithelioma, with keratin cysts and tubular/eccrine differentiation (arrows).
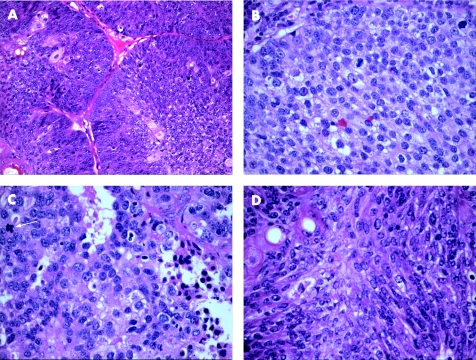
Figure 5 An adnexal tumour with features of trichoepithelioma on haematoxylin and eosin stain (A and B) and CD34‐positive stroma (C), shown to have the immunostaining pattern of basal cell carcinoma with diffusely positive bcl‐2 (D), peripheral layer positivity with CD10 (E) and increased MIB‐1 labelling index (F).
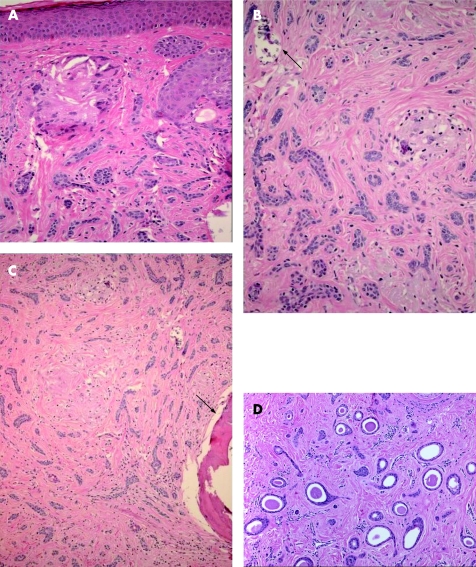
Trichoadenoma is a rare benign follicular neoplasm characterised by proliferation of follicular germ cells with inconspicuous basaloid cells, predominance of keratin cysts and without hair shaft formation. In contrast with trichoadenoma, keratin cysts do not predominate in trichoepithelioma. Rare cases of malignant transformation of trichoepithelioma have been reported, in which there is an infiltrative growth pattern associated with cytological pleomorphism, mitotic activity and necrosis.35 Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE) variant occurs most commonly on the faces of young females. Histologically, it is characterised by narrow, compressed strands of basaloid germinative epithelium, with or without small horn cysts, embedded in densely sclerotic stroma within the upper dermis36 (fig 6A–C). It is important to differentiate DTE from morphoea‐like BCC. The presence of horn cysts and CD34 positivity in stromal cells, and the absence of peripheral palisading, mitoses, retraction artefact and stromal expression of stromelysin‐3 are useful discriminating features.32,37,38,39 CK 20 may identify occasional Merkel cells within DTE, which are absent in BCC.40 In comparison with syringoma, trichoepithelioma exhibits peripheral palisading, horn cyst formation, foreign body granuloma and more calcification (fig 6A–C). Syringoma is characterised by proliferation of small ducts, which are composed of two layers of cells, embedded in a sclerotic connective tissue stroma (fig 6D). There is no keratinisation. Other differential diagnoses of DTE are metastatic breast carcinoma and microcystic adnexal carcinoma; both, in comparison with DTE, are usually immunoreactant to CK 7.
Figure 6 Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (DTE): (A) desmoplastic stroma and giant cell reaction; (B) calcification (arrow); (C) ossification (arrow); and (D) syringoma. Note the sclerotic stroma similar to that seen in DTE.
Trichoblastoma
Trichoblastoma is a benign tumour of follicular germinative epithelium, closely related to trichoepithelioma and DTE. The latter two lesions are traditionally distinguished from trichoblastoma by their characteristic morphological appearance, and prominent superficial follicular differentiation. Clinically, TB is a solitary, well‐circumscribed lesion that occurs in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue, most commonly in elderly individuals, with a predilection to the head and neck region, trunk and extremities. It consists of nodules of cords and nests formed of solid basaloid germinative epithelial cells that exhibit peripheral palisading and brisk mitotic activity (fig 7A,B). Follicular papillae are characteristically present, and small keratin cysts may be found. Numerous melanocytes and melanin pigment are also frequently seen within the epithelial component (pigmented TB; fig 7C). The minimal intervening stromal component separates the epithelial nodules, with absent or inconspicuous cleft artefact. Trichoblastoma is the most common neoplasm that develops in association with NSJ.41,42 Merkel cells, identified by CK 20, are frequently seen in trichoblastoma. An important differential diagnosis of trichoblastoma is BCC, as the two tumours share many histological features (table 4). Trichoblastic fibroma is a morphological variant of trichoblastoma, which can present as a well‐circumscribed nodular or less commonly poorly defined plaque lesion,43 and histologically consists of lobules of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and brisk mitotic activity, with or without keratin cysts (fig 7D). It is characterised by a prominent fibromyxoid stromal component, which contains spindle and stellate fibroblasts and papillary mesenchymal bodies (primitive hair papilla formation).44 Occasionally, some lesions of trichoblastoma contain features of trichoepithelioma (such as keratin cysts and ductal differentiation), and these are referred to as trichoepitheliomatous trichoblastoma.
Figure 7 Trichoblastoma: (A) nodules of basaloid germinative epithelial cells with peripheral palisading and (B) brisk mitotic activity (arrows). (C) Pigmented trichoblastoma. (D) Trichoblastic fibroma.
Table 4 General features comparing basal cell carcinoma with trichoblastoma.
| Feature | BCC | TB |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Older | Younger |
| Site | Sun‐exposed areas | Not limited to sun‐exposed areas |
| Location | Usually limited to within dermis | Usually within deep dermis and subcutaneous fat |
| Peripheral palisading | Present | Present |
| Artefactual clefting | Present | Absent/inconspicuous |
| Keratin cysts | Usually absent | Usually present (small) |
| Mitotic activity | Present | Brisk |
| Stroma | Sclerotic and “normal” in amount | Sclerotic and “minimal” in amount |
| Calcification | Present | Present |
| Follicular papillae | Uncommonly seen | Usually present |
BCC, basal cell carcinoma; TB, trichoblastoma.
Based on the current understanding of the origin of BCC as a tumour of skin adnexal structures, many authors consider trichoblastic carcinoma as a synonym for BCC. However, unlike classic BCC, the very rare trichoblastic carcinoma arising in trichoblastoma seems to have a higher potential for distant metastasis.45,46 Trichoblastic carcinoma is characterised by its “bottom heavy” configuration and the restricted tumour stroma, and may infiltrate into underlying muscles.
Trichilemmoma
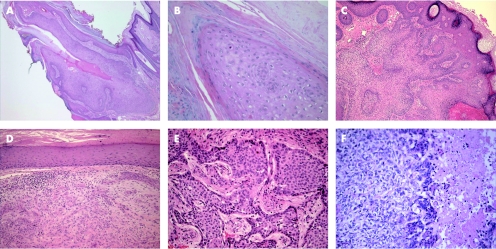
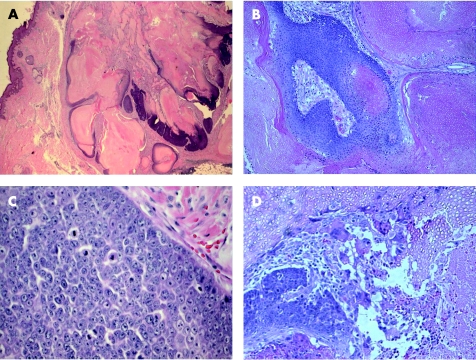
Trichilemmomas are benign tumours that arise from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle, mainly of the bulb region. They usually present as a solitary small skin‐coloured papule, or verrucous lesion, and have a predilection for faces of older adults, particularly over the nose. Multiple facial trichilemmomas characteristically occur in association with Cowden syndrome (multiple hamartoma syndrome).47 This genodermatosis is an autosomal dominant disorder, characterised by multiple hamartomas in the skin, breast, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract, endometrium and brain, and is associated with significantly increased risk of malignancy in these organs. Histologically, trichilemmoma is a well‐circumscribed and symmetric lesion, with broad connection with the epidermis, which is hyperplastic and may show verruca vulgaris‐like changes; however, this connection may not be identified in some cases. The prototypical early lesion shows hyperplasia of the infundibular epithelium, with differentiation towards the outer root sheath (fig 8A,B). In fully developed lesions (fig 8C), trichilemmoma consists of lobules or plates of uniform cells with glycogenated, periodic acid Schiff (PAS)‐positive/diastase‐sensitive clear cytoplasm. The cells at the periphery of tumour lobules are more basophilic, arranged in a palisading pattern, and surrounded by thick, hyaline, PAS‐positive/diastase‐resistant basement membrane material. Foci of keratin microcysts and squamous eddies may be seen. Trichilemmoma should be distinguished from inverted follicular keratosis, clear BCC and hidroacanthoma simplex (HAS; epidermal poroma). The presence of palisading and hyaline basement membrane material, and the absence of ductal differentiation are helpful features in separating trichilemmoma from HAS. Inverted follicular keratosis is characterised by squamous and basaloid epithelial expansion of the infundibular portion of the hair follicle, associated with squamous eddies similar to irritated seborrhoeic keratosis. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma is a histological variant characterised by the presence of strands of tumour cells, entrapped in dense, hypocellular and fibrotic dermis (fig 8D,E), and resembling desmoplastic BCC and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).48,49 The presence of features of conventional trichilemmoma at the periphery of a desmoplastic lesion, presence of PAS‐positive/diastase‐resistant and Alcian blue‐positive material in dermal stroma, and the immunohistochemical expression of CD34 are important features that favour the diagnosis of desmoplastic trichilemmoma.50 Very rare cases of trichilemmal carcinoma (fig 8F) have been described.51,52 These cases exhibit only trichilemmal differentiation, and should not be confused with BCC, particularly in a superficial biopsy.
Figure 8 Trichilemmoma. (A) An early lesion (B) with verruca‐like changes. (C) An established lesion. (D,E) Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. (F) Trichilemmal carcinoma, with atypia and tumour necrosis.
Proliferating trichilemmal cyst (pilar tumour)
Proliferating trichilemmal cyst (PTC) is a benign lesion, most commonly occurring on the scalps of elderly women. PTC presents as a solitary nodulocystic lesion, usually ranging in size from 1 to 10 cm in diameter, and very rarely reaching up to 25 cm in size.53 Occasional patients may develop multiple tumours.54 PTC is believed to originate from a pre‐existing trichilemmal cyst. Histologically, PTC exhibits differentiation towards the follicular outer root sheath, consists of well‐defined lobulated, solid and cystic mass of proliferating squamous epithelium, surrounded by thick hyalinised basement membrane, and involves the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue (fig 9A). Extension of epithelial growths into the lumen, central trichilemmal keratinisation, and peripheral palisading of small basaloid cells may be seen. The squamous cells exhibit bland or mildly atypical cytonuclear features, and inconspicuous, basally located mitotic activity. Individual cell keratinisation and squamous eddies are characteristic findings. Focal necrosis and calcification can be present in large tumours. Stromal reactive multinucleated giant cell reaction is frequently present (fig 9B). Foci of residual, simple pilar cyst(s) may be identified. It is important to distinguish PTC from SCC (box 2). Malignant transformation in PTC is uncommon. Desmoplasia and/or squamous budding into the tumour stroma within the lesion should not be confused with SCC (fig 9C), as it represents pseudoinvasion. Features of malignant PTC include a combination of non‐scalp locations, size >5 cm, recent rapid increase in size, infiltrative growth pattern (fig 9D), significant cytonuclear atypia and brisk mitotic activity.55 Particularly large and long‐standing lesions can potentially recur if not adequately excised by wide local excision,56 and involvement of lymph nodes and distant metastases are reported.57,58
Figure 9 Pilar tumour (A) characteristic lobulation, (B) trichilemmal keratinisation and associated cholesterol clefts and foreign body type giant cell reaction, (C) keratin pearls and budding into the stroma within the tumour should be recognised as pseudoinvasion, compared with true malignant change, which is seen at the infiltrative peripheral margins (D).
Pilomatricoma (pilomatrixoma)
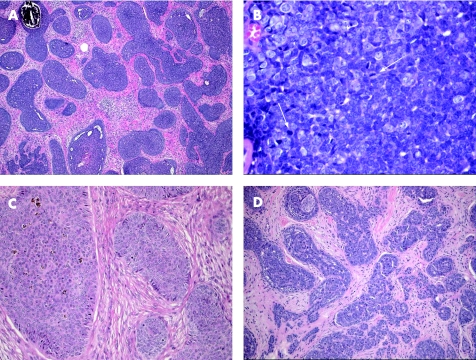
Pilomatricoma or calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe is a benign dermal and/or subcutaneous tumour, most commonly affecting children and adolescents; it is slightly more common in females. Pilomatricoma usually occurs as a solitary firm lesion with predilection for head and neck, and upper extremities. Rare cases of multiple pilomatricoma are associated with different conditions such as myotonic dystrophy,59 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome60 and Turner syndrome.61 Activation mutations of β‐catenin are found to contribute to tumorigenesis of pilomatricoma.62 Classic pilomatricoma is readily identified by light microscopic examination, which shows a well‐circumscribed nodular lesion in the dermis and/or subcutis, surrounded by fibrous stroma (fig 10A). Early lesions are usually cystic, and consist of mitotically active, uniform, basaloid cells lining the cystic cavity, and contiguously transformed into pale eosinophilic anucleated shadow/ghost cells admixed with keratin (fig 10B,C). The shadow cells represent faulty attempts to produce a hair shaft. Older pilomatricomas become solid, and are characterised by prominent shadow cell component, keratin debris, secondary multinucleated giant cells (fig 10D) and dystrophic calcification. Less commonly, bone formation with extramedullary haematopoiesis may also occur.63 Perforating pilomatricoma is a histological variant characterised by transepidermal elimination of shadow cells and keratin. Proliferating pilomatricoma is another variant, occurring in the middle‐aged and elderly, and is characterised by prominent lobulation and proliferation of basaloid cells, and inconspicuous foci of shadow cells.
Figure 10 Pilomatricoma: (A) a multilobulated mass in fibrous stroma reaching the subcutis; (B) basaloid and ghost cells; (C) mitoses in an early lesion; and (D) giant cell reaction in an established lesion.
Box 2 Histological features distinguishing proliferating trichilemmal cyst from squamous cell carcinoma
Presence of pre‐existing simple pilar cyst
Good circumscription
Smooth peripheral margins
Trichilemmal keratinisation
Absent or inconspicuous cytonuclear atypia and minimal mitotic activity
Presence of peripheral palisading
Hyaline basement membrane
Pilomatrix carcinoma is very rare, and mostly occurs in head and neck, upper limbs, and buttocks. It is locally aggressive, with great tendency for local recurrence, and, potentially, can metastasise to regional lymph nodes and distant organs.64,65 Histologically, it differs from pilomatricoma in asymmetrical growth pattern, poor circumscription, significant cytonuclear atypia, markedly increased mitotic activity and infiltration to the adjacent tissue. Tumour necrosis, calcification and ossification may also be seen. The presence of lymphovascular and perineural invasion, extension into the bone, and distant metastasis are definitive features of malignancy.
Tumours of sebaceous glands
Sebaceous hyperplasia, sebaceous adenoma, sebaceoma and sebaceous carcinoma
Sebaceous adenoma, and, more frequently, sebaceous hyperplasia are common benign skin adnexal lesions that principally affect middle‐aged and elderly individuals. They are usually solitary, and present as a small, yellow, lobulated papule with a predilection to the forehead and cheeks. Multiple sebaceous lesions (hyperplasia, adenoma, sebaceoma and carcinoma) can occur in association with Muir–Torre syndrome, an autosomal dominantly inherited disorder characterised by visceral malignancies (colorectal, upper gastrointestinal, endometrial and urological malignant neoplasms), and tumours of sebaceous glands or keratoacanthoma.66 Sebaceous hyperplasia represents a single enlarged sebaceous gland and shows five or more lobules of bland, immature sebocytes that open into a single dilated follicular infundibulum (fig 11A). The peripheries of the lobules have one or two cell layers of basaloid germinative cells. Sebaceous hyperplasia should be differentiated from rhinophyma, in which the sebaceous gland hyperplasia is associated with perifollicular inflammation and dermal fibrosis, and not confined to one focal area.
Figure 11 Benign sebaceous neoplasms: (A) sebaceous hyperplasia; (B) sebaceous adenoma; (C) sebaceoma; (D) peripheral palisading and sebaceous ductal differentiation in sebaceoma (arrow); (E) sebaceoma with squamous metaplasia (arrow).
Sebaceous adenoma is a well‐circumscribed dermal nodule, histologically formed of lobules of predominate mature, bland sebaceous cells, and peripherally located in one or two layers of germinal basaloid epithelial cells (fig 11B). There is no central draining duct. Sebaceoma (formerly known as sebaceous epithelioma) is a histological variant of SA, in which the basaloid epithelial cells constitute ⩾50% of the SA (fig 11C). It is characterised by variably sized lobules, which are composed predominantly of basaloid cells, admixed with single or clustered mature sebaceous cells, and exhibit sebaceous ductal differentiation (fig 11D). Foci of squamous metaplasia may rarely be seen (fig 11E). Some authors believe that sebaceoma is synonymous with BCC with sebaceous differentiation. However, we agree with others67 that these two entities should be separate, as there are well‐defined histological differences (table 5). A verrucous variant of sebaceoma characterised by connection with a hyperplastic infundibulum in the upper portion of the lesion, prominent granular layer and basosquamous differentiation, similar to those seen in seborrhoeic keratosis, has been described.68 Superficial epithelioma with sebaceous differentiation is a rare slow‐growing tumour, characterised by anastomosing basaloid cells mixed with sebaceous cells broadly attached to the overlying surface epithelium. As many of these tumours also have peripheral palisading, many authors believe the term to be synonymous with superficial BCC with sebaceous differentiation.
Table 6 Useful histological features for distinguishing between sebaceoma and basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation.
| Feature | Sebaceoma | BCC with sebaceous differentiation |
|---|---|---|
| Overall morphology | Similar to sebaceous adenoma, but with more basaloid component | Similar to classical BCC, but with a component of sebaceous differentiation |
| Main components | Aggregates of basaloid germinative cells admixed with single units or clusters of mature vacuolated sebocytes | Aggregate of follicular germinative basaloid cells |
| Architectural pattern | Benign | Malignant |
| Cytological features | Monomorphous basaloid cells, with small oval nuclei and non‐prominent nucleoli | Pleomorphic basaloid cells, with slightly elongated nuclei |
| Mitotic activity | Mild/absent | Brisk |
| Sebaceous differentiation | Prominent | Focal and associated with apocrine differentiation in many cases |
| Peripheral palisading | Usually absent | Present |
| Artefactual clefting | Absent | Often present |
| Basaloid tumour necrosis | Rare | Frequent |
| Other associated features | Sebaceous duct‐like structures, rare squamous differentiation, and dense eosinophilic dermal sclerosis | Sebaceous duct‐like structures, individual cell necrosis, keratinization and mucinous stroma |
BCC, basal cell carcinoma.
Sebaceous carcinoma most frequently affects the eyelid (ocular, palpebral sebaceous carcinoma), and has potential for local recurrence and distant metastases. Sebaceous carcinoma of the eyelid is derived from the modified sebaceous glands (Meibomian glands or glands of Zeis). When associated with Muir–Torre syndrome, sebaceous carcinoma appears to have a better prognosis. Histologically, sebaceous carcinoma differs from sebaceous adenoma and sebaceoma in its asymmetry, poor circumscription, infiltrative growth pattern, and preponderance of pleomorphic, basaloid cells that are arranged in solid sheets, and shows marked cytonuclear atypia and high mitotic activity (fig 12A,B). Scattered sebocytes are often present within the basaloid tumour mass. Peripheral palisading and artefactual clefting are absent. The presence of tumour necrosis denotes bad prognosis68 (fig 12C). Superficial spread resembling Bowen‐like disease and/or pagetoid pattern, involving the overlying epidermis, particularly in ocular sebaceous carcinoma may occasionally be identified.69 IHC shows sebaceous carcinoma to be immunopositive for AE1/AE3 cytokeratin, LMWCK, EMA, anti‐breast carcinoma associated antigen‐225 antibody (CU18), anti‐CA 15.3 antibody, and androgen receptor protein, and immunonegative for CEA, S100 protein and GCDFP‐15.70,71 Immature and mature neoplastic sebocytes can also express CK 14.72
Figure 12 Sebaceous carcinoma: (A) lobulated mass of basaloid cells and inconspicuous sebocytes, (B) cellular atypia and brisk mitotic activity, (C) tumour necrosis and mitoses (arrow) and (D) focal spindle cell differentiation.
Different histological variants of sebaceous carcinoma are recognised, the most important being the basaloid, spindle cell, squamoid and dedifferentiated (pleomorphic) variants. Basaloid sebaceous carcinoma is composed of small basaloid cells, with palisading at the periphery of the epithelial lobules, and inconspicuous sebocytes. The spindle cell variant is predominantly formed of spindle cells with foci of squamous metaplasia (fig 12D). In these cases, EMA can be used to identify sebocytes; LMWK and D2‐40 can help as they may be positive, but they are not specific.
Nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn
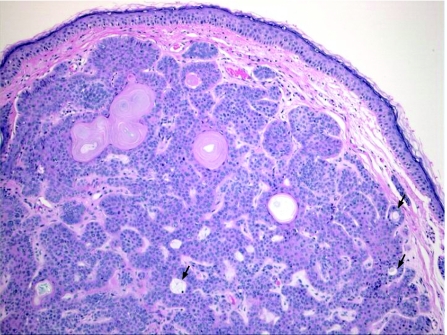
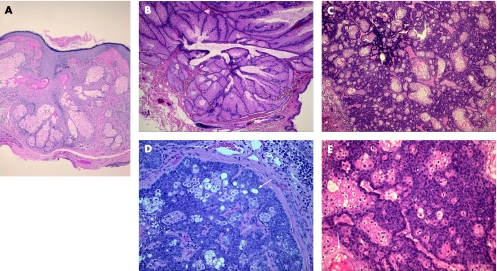
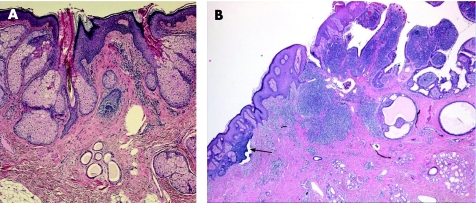
This is a benign congenital malformation, usually presenting at birth as solitary yellowish, waxy hairless plaques, or linear lesions, and as verrucous nodules in adults. It most commonly affects the head and neck region, with predilection to the scalp. NSJ, particularly if multiple, can be associated with epidermal nevus syndrome, epidermal hamartomas and extracutaneous abnormalities, principally involving the brain, eye and skeletal system.73 Histologically, NSJ is a hamartomatous lesion that represents mature elements of all lines of adnexal differentiation, and shows a wide range of morphological features, depending on the lesion's growth phase. Early lesions show multiple foci of lobules of mature sebaceous glands, and a small number of disorganised eccrine ducts and apocrine sweat glands. In adults, as the lesion progresses, the sebaceous lobules in the well‐developed lesions become prominent, and poorly formed follicular units caused by proliferation of basaloid follicular germinal epithelium can be seen. Characteristically, lobules of heterotropic/ectopic apocrine glands are identified in the reticular dermis. The overlying epidermis shows papillomatous/verrucous hyperplasia, and the sebaceous lobules are numerous, irregular and directly open into the epidermis (fig 13A). The term “organoid nevus” has been used to describe lesions which show overlapping features of NSJ and epidermal nevi. A variety of lesions have been described in association with NSJ; the incidence of these lesions increases with age, particularly after puberty. These include benign adnexal tumours such as trichoblastoma, SCAP (fig 13B), trichilemmoma, BEP (fig 2C), sebaceoma, nodular hidradenoma, hidrocystoma and eccrine poroma.41,42 Other lesions include seborrhoeic keratosis, leiomyoma, melanocytic nevi, and viral warts. Trichoblastoma and SCAP are the most common benign tumours encountered in NSJ. Malignant cutaneous neoplasms are less commonly seen, and include BCC, and, to a lesser extent, SCC,74 trichilemmal carcinoma,75 sebaceous carcinoma,76 porocarcinoma77 and apocrine carcinoma.78 In a recent study of 596 cases of NSJ, malignancies were encountered in <1% of cases, whereas benign tumours were identified in 13.6% of cases of NSJ.42 In many cases, different tumours coexist within an individual NSJ.74,75,79 Allelic deletions of the human homologue of the Drosophila‐patched gene are described in NSJ,80 and this may account for the development of aggressive malignant tumours within the lesions. In general, prophylactic and complete excision is advised in all cases of NSJ.
Figure 13 (A) Nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn revealing prominent sebaceous glands opening directly to the surface, with immature hair follicles and heterotopic apocrine glands; (B) syringocystadenoma papilliferum on the right side, with basaloid proliferations (arrow), arising in a nevus sebaceous.
Take‐home messages
Skin adnexal tumours are usually classified according to the predominant morphological component.
Most skin adnexal tumours are benign, but some of these tumours might be markers for syndromes associated with internal malignancies.
Morphological evaluation is very important in evaluating skin adnexal tumours, and special and/or immunohistochemical stains may occasionally serve as ancillary tools.
Follicular differentiation is characterised by the presence of proliferation of basaloid bulbar germinative cells, peripheral nuclear palisading and adjacent papillary mesenchymal cells. The presence of shadow (ghost) cells and tumour attachment to normal follicular structures are other features.
Sebaceous differentiation is indicated by the presence of cells with coarsely vacuolated cytoplasm and starry nuclei (mulberry cells), which are characteristically positive epithelial membrane antigens.
Abbreviations
BCC - basal cell carcinoma
BEPs - basaloid epidermal proliferations
BFH - basaloid follicular hamartoma
CEA - carcinoembryonic antigen
DTE - desmoplastic trichoepithelioma
EMA - epithelial membrane antigen
GCDEP‐15 - gross cystic disease fluid protein 15
HAS - hidroacanthoma simplex
H&E - haematoxylin and eosin
HMWK - high molecular weight keratin
IHC - immunohistochemical
LMWK - low‐molecular weight cytokeratin
MFT - multiple familial trichoepithelioma
NSJ - nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn
PAS - periodic acid Schiff
PTC - proliferating trichilemmal cyst
SAT - Skin adnexal tumours
SCAP - syringocystadenoma papilliferum
SMA - smooth muscle actin
Footnotes
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Rudolph P. Benign adnexal skin tumors. Pathologe 20022371–78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rodriguez‐Diaz E, Armio M. Mixed tumors with follicular differentiation: complex neoplasms of the primary epithelial germ. Int J Dermatol 199534782–785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sato K, Kang W H, Saga K.et al Biology of sweat glands and their disorders. I. Normal sweat gland function. J Am Acad Dermatol 198920537–563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van der Putte S C. Apoeccrine glands in nevus sebaceous. Am J Dermatopathol 19941623–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Klein W, Chan E, Seykora J T. Tumors of the epidermal appendages. In: Elder DE, Editor‐in‐Chief. Lever's histopathology of the skin. 9th edn. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilikins, 2005867–926.
- 6.Kamada A, Saga K, Jimbow K. Apoeccrine sweat duct obstruction as a cause for Fox‐Fordyce disease. J Am Acad Dermatol 200348453–455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wheeler C E, Jr, Carroll M A, Groben P A.et al Autosomal dominantly inherited generalized basaloid follicular hamartoma syndrome: report of a new disease in a North Carolina family. J Am Dermatol 200043189–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yoshida Y, Urabe K, Mashino T.et al Basal cell carcinomas in association with basaloid follicular hamartoma. Dermatology 200320757–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Akasaka T, Kon S, Mihm M C., Jr Multiple basaloid cell hamartoma with alopecia and autoimmune disease (systemic lupus erythematosus). J Dermatol 199623821–824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Morton S, Stevens A, Powell R J. Basaloid follicular hamartoma, total body hair loss and SLE. Lupus 19983207–209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mascaro J M, Jr, Ferrando J, Bombi J A.et al Congenital generalized follicular hamartoma associated with alopecia and cystic fibrosis in three siblings. Arch Dermatol 1995131454–458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jih D M, Shapiro M, James W D.et al Familial basaloid follicular hamartoma: lesional characterization and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol 200325130–137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stashower M E, Smith K, Corbett D.et al Basaloid/follicular hyperplasia overlying connective tissue/mesenchymal hamartomas simulating basal cell carcinomas. J Am Acad Dermatol 200145886–891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mehregan D R, Thomas L, Thomas J E. Epidermal basaloid proliferation in cutaneous myxomas. J Cutan Pathol 200330499–503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Han K H, Huh C H, Cho K H. Proliferation and differentiation of the keratinocytes in hyperplastic epidermis overlying dermatofibroma: immunohistochemical characterization. Am J Dermatopathol 20012390–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rossen K, Haersley T, Hou‐Jensen K.et al Metallothionein expression in basaloid proliferations overlying dermatofibromas and in basal cell carcinomas. Br J Dermatol 199713630–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rossen K, Haersley T, Hou‐Jensen K.et al Bcl‐2 overexpression in basaloid proliferations overlying dermatofibromas and basal cell carcinomas. APMIS 199710535–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Haersley T, Rossen K, Hou‐Jensen K.et al Immunohistochemical detection of p53 in epidermal proliferations overlying dermatofibromas. Acta Dermatol Venereol 199575187–189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mahmoodi M, Asad H, Salim S.et al Anti‐cytokeratyin 20 staining of Merkel cells helps differentiate basaloid proliferations overlying dermatofibromas from basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol 200532491–495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hartschuh W, Schulz T. Immunohistochemical investigation of the different developmental stages of trichofolliculoma with special reference to the Merkel cell. Am J Dermatopathol 1999218–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stern J B, Stout D A. Trichofolliculoma showing perineural invasion. Trichofolliculocarcinoma? Arch Dermatol 19791151003–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Plewig G. Sebaceous trichofolliculoma. J Cutan Pathol 19807394–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ramdial P K, Chrystal V, Madaree A. Folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma. Pathology 199830212–214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tanimura S, Arita K, Iwao F.et al Two cases of folliculosebaceous cystic hamartoma. Clin Exp Dermatol 20063168–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Welsch M J, Krunic A, Medenica M M. Birt‐Hogg‐Dube syndrome. Int J Dermatol 200544668–673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Harada H, Hashimoto K, Ko M S. The gene for multiple familial trichoepithelioma maps to chromosome 9p21. J Invest Dermatol 199610741–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang X J, Liang Y H, He P P.et al Identification of the cylindromatosis tumor‐suppressor gene responsible for multiple familial trichoepithelioma. J Invest Dermatol 2004122658–664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zheng G, Hu L, Huang W.et al CYLD mutation causes multiple familial trichoepithelioma in three Chinese families. Hum Mutat 200423400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kanitakis J, Bourchany D, Faure M.et al Expression of the hair stem cell‐specific keratin 15 in pilar tumours of skin. Eur J Dermatol 19999363–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yamamoto O, Asahi M. Cytokeratin expression in trichoblastic fibroma (small nodular type trichoblastoma), trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol 19991408–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Poniecka A W, Alexis J B. An immunohistochemical study of basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma. Am J Dermatopathol 199 21332–336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kirchmann T T, Prieto V G, Smoller B R. Use of CD34 in assessing the relationship between stroma and tumor in desmoplastic keratinocytic neoplasms. J Cutan Pathol 199522422–426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pham T T, Selim M A, Burchette J L., Jret al CD10 expression in trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol 200633123–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Abdelsayed R A, Guijarro‐Rojas M, Ibrahim N A.et al Immunohistochemical evaluation of basal cell carcinoma and trichoepithelioma using bcl‐2, Ki67, PCNA and p53. J Cutan Pathol 200027169–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hunt S J, Abell E. Malignant hair matrix tumor (“malignant trichoepithelioma”) arising in the setting of multiple hereditary trichoepithelioma. Am J Dermatopathol 199113275–281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Matsuki T, Hayashi N, Mizushima J.et al Two cases of desmoplastic trichoepithelioma. J Dermatol 200431824–827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Takei Y, Fukushiro S, Ackerman A B. Criteria for histologic differentiation of desmoplastic trichoepithelioma (sclerosing epithelial hamartoma) from morphea‐like basal‐cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol 19857207–221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kirchmann T T, Prieto V G, Smoller B R. CD34 staining pattern distinguishes basal cell carcinoma from trichoepithelioma. Arch Dermatol 1994130589–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thewes M, Worret W I, Engst R.et al Stromelysin‐3: a potent marker for histologic differentiation between desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and morphealike basal cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol 199820140–142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Abesamis‐Cubillan E, El‐Shabrawi‐Caelen L, LeBoit P E. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol 200022311–315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jaqueti G, Requena L, Sanchez Yus E. Trichoblastoma is the most common neoplasm develop in nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn: a clinicopathologic study of a series of 155 cases. Am J Dermatopathol 200022108–118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cribier B, Scrivener Y, Grosshans E. Tumors arising in nevus sebaceous: a study of 596 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol 200042263–268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Beguin L, Poulin J F, Chatelanin D.et al Plaque variant of trichoblastic fibroma. Ann Dermatol Venereol 200112835–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Altman D A, Mikhail G R, Johnson T M.et al Trichoblastic fibroma. A series of 10 cases with report of a new plaque variant. Arch Dermatol 1995131198–201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Regauer S, Beham‐Schmid C, Okuc M.et al Trichoblastic carcinoma (“malignant trichoblastoma”) with lymphatic and hematogenous metastases. Mod Pathol 200013673–678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schulz T, Proske S, Hartschuh W.et al High‐grade trichoblastic carcinoma arising in trichoblastoma: a rare adnexal neoplasm often showing metastatic spread. Am J Dermatopathol 2005279–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brownstein M H, Mehregan A H, Bikowski J B.et al The dermatopathology of Coweden's syndrome. Br J Dermatol 1979100667–673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hunt S J, Kilzer B, Santa Cruz D J. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma: histologic variant resembling invasive carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol 19901745–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tellechea O, Reis J P, Baptista A P. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma. Am J Derrmatopathol 199214107–114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Illueca C, Monteagudo C, Revert A.et al Diagnostic value of CD34 immunostaining in desmoplastic trichilemmoma. J Cutan Pathol 199825435–439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chan K O, Kim I J, Baladas H G.et al Multiple tumour presentation of trichilemmal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg 200329886–889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lai T F, Huilgol S C, James C L.et al Trichilemmal carcinoma of the upper eyelid. Acta Opthalmol Scand 200381536–538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Casas J G, Woscoff A. Giant pilar tumor of the scalp. Arch Dermatol 19801161395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bengoechea‐Beeby M P, Velasco‐Oses A, Casado‐Perez C. Multiple proliferating trichilemmal tumors and cysts involving the scalp: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 199452985–986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Folpe A L, Reisenauer A K, Mentzel T.et al Proliferating trichilemmal tumors: clinicopathologic evaluation is a guide to biologic behavior. J Cutan Pathol 200330492–498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lopez‐Rios F, Rodriguez‐Peralto J L, Aguilar A.et al Proliferating trichilemmal cyst with focal invasion: report of a case and a review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol 200022183–187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fernandez S H. Malignant proliferating trichilemmal tumour: a case report. Malays J Pathol 199921117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Amaral A L, Nascimento A G, Goellner J R. Proliferating pilar (trichilemmal) cyst. Report of two cases, one with carcinomatous transformation and one with distant metastases. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1984108808–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Geh J L, Moss A L. Multiple pilomatrixomata and myotonic dystrophy: a familial association. Br J Plast Surg 199952143–145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bayle P, Bazex J, Lamant L.et al Multiple perforating and non perforating pilomatricomas in a patient with Churg–Strauss syndrome and Rubinstein‐Taybi syndrome. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 200418607–610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Noguchi H, Kayashima K, Nishiyama S.et al Two cases of pilomatrixoma in Turner's syndrome. Dermatology 1999199338–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Xia J, Urabe K, Moroi Y.et al beta‐Catenin mutation and its nuclear localization are confirmed to be frequent causes of Wnt signaling pathway activation in pilomatricomas. J Dermatol Sci 20064167–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Falk S. EMH in pilomatricomas. Am J Dermatopathol 199618218–219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bremnes R M, Kvamme J M, Stalsberg H.et al Pilomatrix carcinoma with multiple metastases: report of a case and review of the literature. Eur J Cancer 199935433–437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bassarova A, Nesland J M, Sedloev T.et al Pilomatrix carcinoma with lymph node metastases. J Cutan Pathol 200431330–335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ponti G, Ponz de Leon M. Muir‐Torr syndrome. Lancet Oncol 20056980–987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Misago N, Suse T, Uemura T.et al Basal cell carcinoma with sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol 200426298–303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Misago N, Mihara I, Ansai S.et al Sebaceoma and related neoplasms with sebaceous differentiation: a clinicopathologic study of 30 cases. Am J Dermatopathol 200224294–304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pereira P R, Odashiro A N, Rodrigues‐Reyes A A.et al Histopathological review of sebaceous carcinoma of the eyelid. J Cutan Pathol 200532496–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ansai S, Mitsuhashi Y, Kondo S.et al Immunohistochemical differentiation of extra‐ocular sebaceous carcinoma from other skin cancers. J Dermatol 200431998–1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bayer‐Garner I B, Givens V, Smoller B. Immunohistochemical staining for androgen receptors: a sensitive marker of sebaceous differentiation. Am J Dermatopathol 199921426–431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Schirren C G, Jansen T, Lindner A.et al Diffuse sebaceous gland hyperplasia. A case report and an immunohistochemical study with cytokeratins. Am J Dermatopathol 199618296–301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Sugarman J L. Epidermal nevus syndromes. Semin Cutan Med Surg 200423145–157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ball F A, Hussain M, Moss A L. Squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma arising in a naevus sebaceous of Jadassohn: case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol 200530259–260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Misago N, Narisaway Y. Tricholemmal carcinoma in continuity with trichoblastoma within nevus sebaceus. Am J Dermatopathol 200224149–155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.de Giorgi V, Massi D, Brunasso G.et al Sebaceous carcinoma arising from nevus sebaceus: a case report. Dermatol Surg 200329105–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tarkhan I I, Domingo J. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma developing in a sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn. Report of a case. Arch Dermatol 1985121413–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Dalles S, Skowron F, Balme B.et al Apocrine carcinoma developed in nevus sebaceous of Jadassohn. Eur J Dermatol 200313487–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Miller C J, Ioffreda M D, Billingsley E M. Sebaceous carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, trichoadenoma, trichoblastoma, and syringocystadenoma papilliferum arising within a nevus sebaceus. Dermatol Surg 200430(Pt 2)1546–1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Xin H, Matt D, Qin J Z.et al The sebaceous nevus: a nevus with deletions of the PTCH gene. Cancer Res 1999591834–1836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]