Abstract
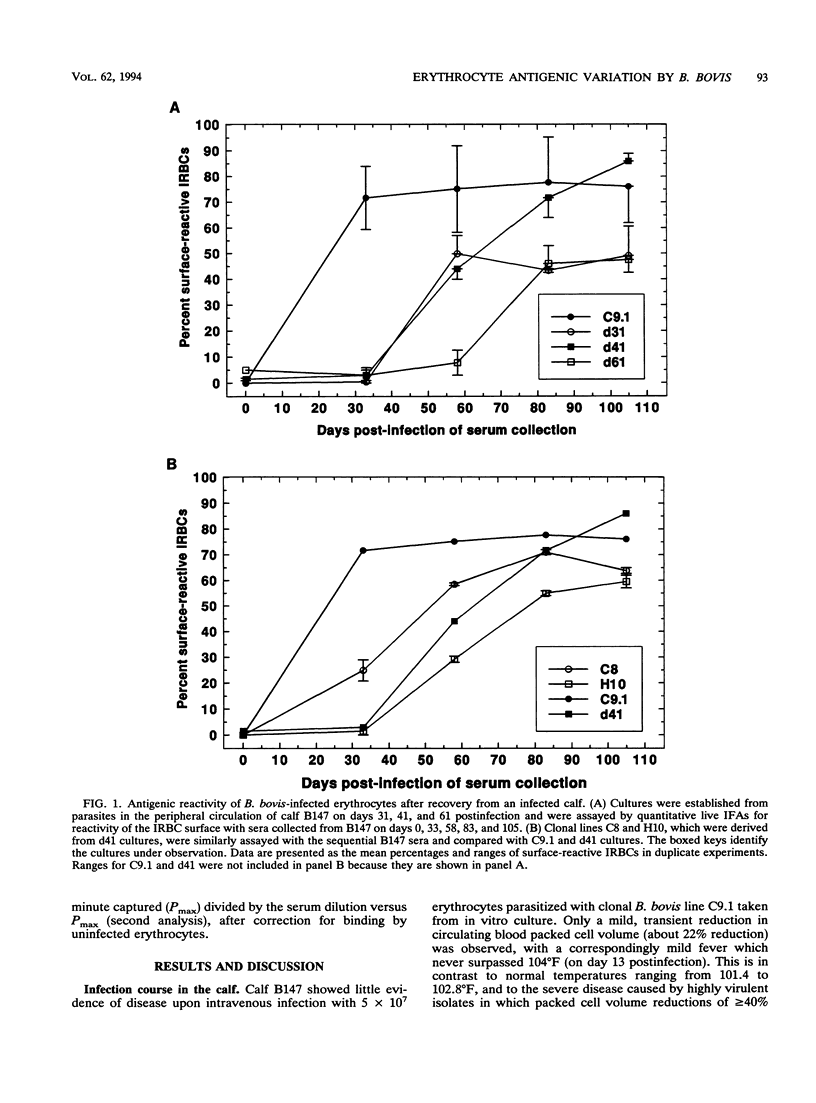
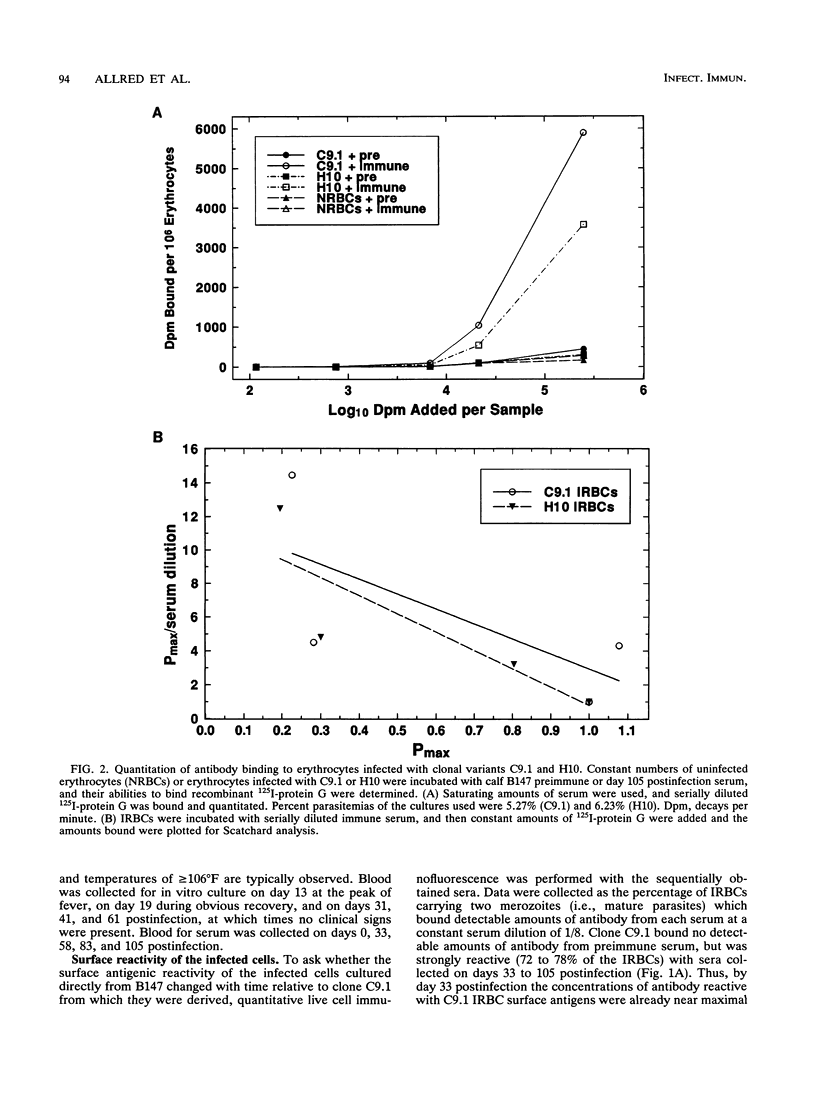
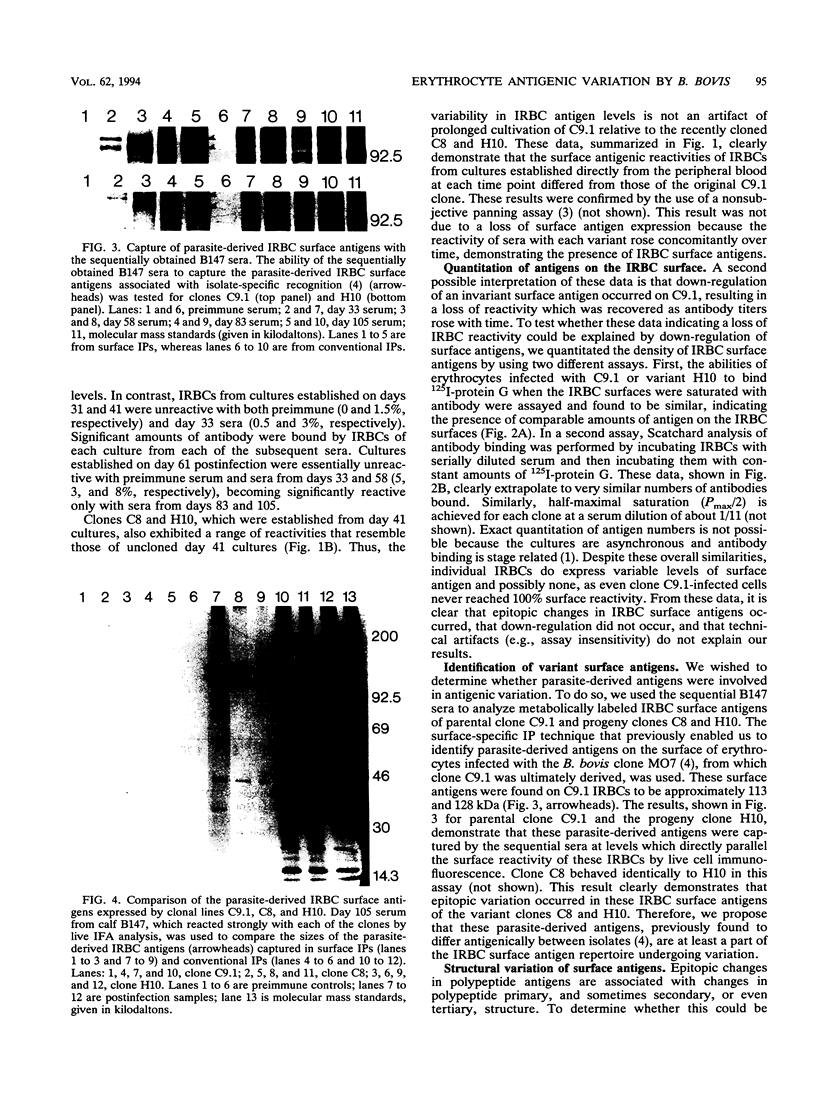
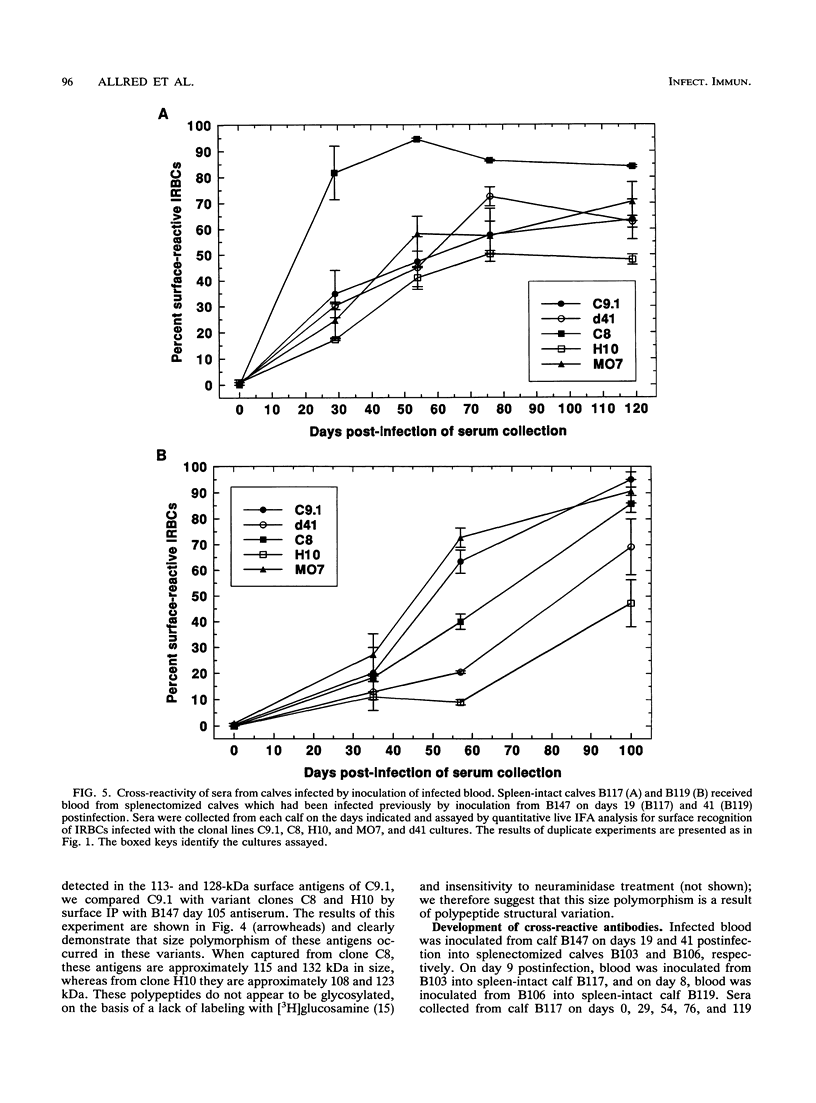
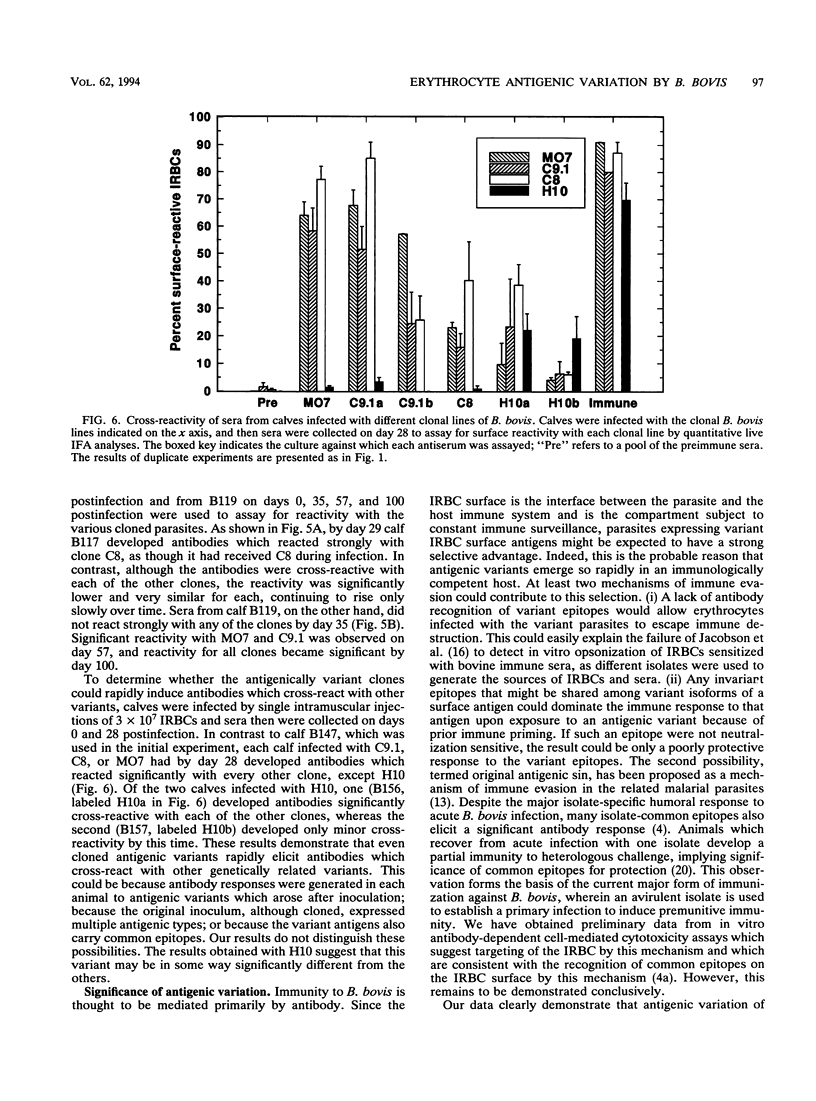
The hemoparasite Babesia bovis antigenically alters the bovine erythrocyte membrane surface by expression of isolate-specific, parasite-derived polypeptides. To determine whether antigenic variation also occurred on the infected erythrocyte surface, a calf was infected once with parasitized erythrocytes carrying the C9.1 clonal line of B. bovis. In vitro cultures then were established periodically from the peripheral blood and analyzed with sequentially collected sera from the same animal. The surface reactivity of infected erythrocytes cultured from the infected animal varied over time, on the basis of reactivity in live cell immunofluorescence, surface immunoprecipitation, and panning assays. Subclones C8 and H10, established from day 41 cultures, were analyzed immunochemically. A loss of immunoreactivity was observed in antigens corresponding to the 113- and 128-kDa parasite-derived antigens of clone C9.1, demonstrating epitopic variation in these antigens; the immunochemical recognition of these antigens paralleled the results of live cell immunofluorescence and panning assays. Concomitant size polymorphism suggested polypeptide structural variation of these antigens as well. Calves infected by inoculation of infected blood or by injection of cloned parasites from in vitro cultures rapidly developed antibodies which cross-reacted among the clonal variant lines, suggesting the presence of common as well as unique epitopes. These results demonstrate that antigenic variation occurs on the surface of B. bovis-infected erythrocytes and that the parasite-derived antigens of 113 and 128 kDa compose at least a part of the antigens undergoing variation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrens K. P., Allred D. R. Polypeptides reactive with antibodies eluted from the surface of Babesia bovis-infected erythrocytes. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1992;87 (Suppl 3):21–26. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761992000700002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M., Rabbege J., Uni S., Ristic M., Miller L. H. Structural alteration of the membrane of erythrocytes infected with Babesia bovis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Jan;34(1):45–49. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allred D. R., Ahrens K. P. A nonsubjective assay for antigenic modifications of the Babesia bovis-parasitized erythrocyte surface. J Parasitol. 1993 Apr;79(2):274–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allred D. R., Hines S. A., Ahrens K. P. Isolate-specific parasite antigens of the Babesia bovis-infected erythrocyte surface. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jul;60(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90035-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arese P., Turrini F., Ginsburg H. Erythrophagocytosis in malaria: Host defence or menace to the macrophage? Parasitol Today. 1991 Jan;7(1):25–28. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90082-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Anders R. F., Dillon H. E., Davern K. M., Martin M., Petersen C., Brown G. V. Adherence of infected erythrocytes to venular endothelium selects for antigenic variants of Plasmodium falciparum. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Cruchaud A., Perrin L. H. Assessment of immune phagocytosis of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells by human monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A method for visualizing infected red blood cells ingested by phagocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 14;63(2):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90430-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnow J. A. In vitro agglutination of bovine erythrocytes infected with Babesia argentina. Nature. 1968 Jan 20;217(5125):267–268. doi: 10.1038/217267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnow J. A. Studies on antigenic changes and strain differences in Babesia argentina infections. Aust Vet J. 1973 Jun;49(6):279–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1973.tb06806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff W. L., Wagner G. G., Craig T. M. Increased activity of bovine ADCC effector cells during acute Babesia bovis infection. Vet Parasitol. 1984 Oct;16(1-2):5–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(84)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff W. L., Wagner G. G., Craig T. M., Long R. F. The role of specific immunoglobulins in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity assays during Babesia bovis infection. Vet Parasitol. 1984 Mar;14(2):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(84)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff W. L., Yunker C. E. Effects of PH, buffers and medium-storage on the growth of Babesia bovis in vitro. Int J Parasitol. 1988 Sep;18(6):775–778. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(88)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Zevering Y., Currier J., Bilsborough J. 'Original antigenic sin', T cell memory, and malaria sporozoite immunity: an hypothesis for immune evasion. Parasite Immunol. 1993 Apr;15(4):187–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1993.tb00599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves P. M., Carter R., Keystone J. S., Seeley D. C., Jr Drug sensitivity and isoenzyme type in cloned lines of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Mar;33(2):212–219. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines S. A., McElwain T. F., Buening G. M., Palmer G. H. Molecular characterization of Babesia bovis merozoite surface proteins bearing epitopes immunodominant in protected cattle. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Nov;37(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson R. H., Parrodi F., Wright I. G., Fitzgerald C. J., Dobson C. Babesia bovis: in vitro phagocytosis promoted by immune serum and by antibodies produced against protective antigens. Parasitol Res. 1993;79(3):221–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00931896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. G., Ristic M. Babesia bovis: continuous cultivation in a microaerophilous stationary phase culture. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1218–1220. doi: 10.1126/science.7355284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F., Kerr J. D., Goodger B. V., Wright I. G. The immune response of cattle to Babesia bovis (syn. B. argentina). Studies on the nature and specificity of protection. Int J Parasitol. 1979 Aug;9(4):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(79)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney D. F., Wright I. G., Goodger B. V. Immunity in cattle to Babesia bovis after single infections with parasites of various origin. Aust Vet J. 1979 Jan;55(1):10–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1979.tb09535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrodi F., Jacobson R. H., Wright I. G., Fitzgerald C. J., Dobson C. The effect of immune serum and complement on the in vitro phagocytosis of Babesia rodhaini. Parasite Immunol. 1991 Sep;13(5):457–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1991.tb00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez S. D., Buening G. M., Green T. J., Carson C. A. Cloning of Babesia bovis by in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):15–18. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.15-18.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. J. Serum opsonins and the passive transfer of protection in Babesia rodhaini infections of rats. Int J Parasitol. 1974 Apr;4(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(74)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear H. L., Nussenzweig R. S., Bianco C. Immune phagocytosis in murine malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1288–1298. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega C. A., Buening G. M., Green T. J., Carson C. A. In vitro cultivation of Babesia bigemina. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Feb;46(2):416–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright I. G. An electron microscopic study of intravascular agglutination in the cerebral cortex due to Babesia argentina infection. Int J Parasitol. 1972 Jun;2(2):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(72)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright I. G. Ultrastructural changes in Babesia argentina-infected erythrocytes in kidney capillaries. J Parasitol. 1973 Aug;59(4):735–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]