Abstract
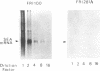
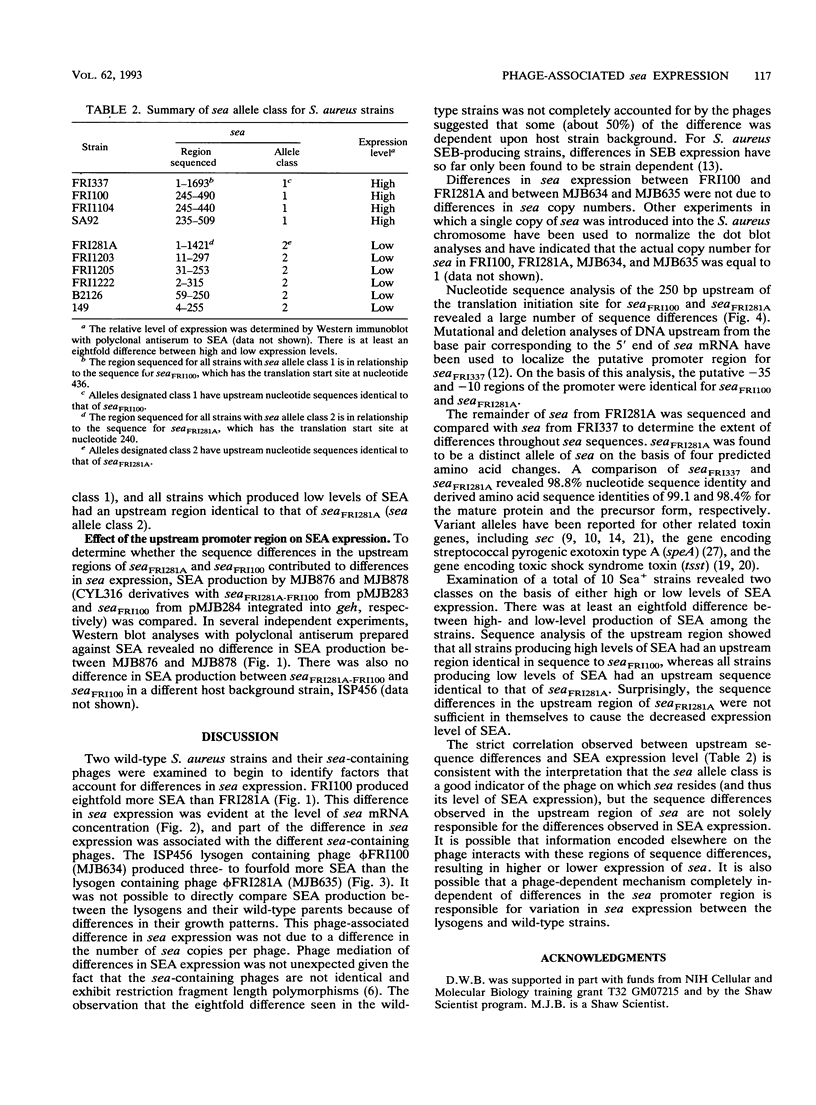
Staphylococcus aureus strains which produced either high or low levels of staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) with a minimal eightfold difference between the two groups were identified. For FRI100 and FRI281A (prototypes for each group), strain differences in the expression of the SEA-encoding gene (sea) were found to occur at the level of sea mRNA concentration, and part of the difference in expression was associated with the sea-containing phages. Southern blot analysis revealed that this phage-associated difference was not due to differences in the copy number of sea. Nucleotide sequence analysis of sea from FRI281A revealed a new allele of sea, with the majority of the sequence differences occurring in the upstream promoter region. Although a strict correlation was observed between the level of SEA production and sea allele class for several strains, the sequence differences observed in the upstream region were not sufficient in themselves to alter the expression level of sea.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayles K. W., Iandolo J. J. Genetic and molecular analyses of the gene encoding staphylococcal enterotoxin D. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4799–4806. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4799-4806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Borst D. W., Regassa L. B. Staphylococcal enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin and streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins: a comparative study of their molecular biology. Chem Immunol. 1992;55:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type A staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.34-41.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Mekalanos J. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A is encoded by phage. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.3160112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Schlievert P. M. Conservation of the biologically active portions of staphylococcal enterotoxins C1 and C2. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2249–2252. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2249-2252.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 gene and relatedness to other pyrogenic toxins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00329830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst D. W., Betley M. J. Mutations in the promoter spacer region and early transcribed region increase expression of staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5421–5425. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5421-5425.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compagnone-Post P., Malyankar U., Khan S. A. Role of host factors in the regulation of the enterotoxin B gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1827–1830. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1827-1830.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Betley M. J. Nucleotide sequence of the type C3 staphylococcal enterotoxin gene suggests that intergenic recombination causes antigenic variation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4507–4510. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4507-4510.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch J. L., Soltis M. T., Betley M. J. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type E staphylococcal enterotoxin gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2954–2960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2954-2960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., Bergdoll M. S. Staphylococcal enterotoxin synthesis during the exponential, transitional, and stationary growth phases. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):229–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.229-235.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill M. E., Khan S. A. Regulation of the enterotoxin B gene in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6276–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho G., Campbell W. H., Bergdoll M. S., Carlson E. Production of a toxic shock syndrome toxin variant by Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with sheep, goats, and cows. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1946–1948. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1946-1948.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho G., Campbell W. H., Carlson E. Ovine-associated Staphylococcus aureus protein with immunochemical similarity to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):210–212. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.210-212.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovde C. J., Hackett S. P., Bohach G. A. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C3 gene: sequence comparison of all three type C staphylococcal enterotoxins. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):329–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00260504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagle W. O., Tremaine M. T., Betley M. J. The carboxyl-terminal region of staphylococcal enterotoxin type A is required for a fully active molecule. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2126-2134.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Buranen S. L., Ye Z. H. Construction of single-copy integration vectors for Staphylococcus aureus. Gene. 1991 Jul 15;103(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90399-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallonee D. H., Glatz B. A., Pattee P. A. Chromosomal mapping of a gene affecting enterotoxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.397-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill R. J., Fanning G. R., Delahoz F., Wolff R., Gemski P. Oligonucleotide probes for detection and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus strains containing genes for enterotoxins A, B, and C and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1514–1518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1514-1518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Schlievert P. M., Selander R. K., Musser J. M. Characterization and clonal distribution of four alleles of the speA gene encoding pyrogenic exotoxin A (scarlet fever toxin) in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1271–1274. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Brodsky R. Studies on plasmid replication. I. Plasmid incompatibility and establishment in Staphylococcus aureus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):285–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otero A., García M. L., García M. C., Moreno B., Bergdoll M. S. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxins C1 and C2 and thermonuclease throughout the growth cycle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):555–559. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.555-559.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Glatz B. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of enterotoxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.186-193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Neveln D. S. Transformation analysis of three linkage groups in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):201–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.201-211.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. L., Novick R. P., Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Schlievert P. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of an accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4365–4372. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4365-4372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regassa L. B., Couch J. L., Betley M. J. Steady-state staphylococcal enterotoxin type C mRNA is affected by a product of the accessory gene regulator (agr) and by glucose. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):955–962. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.955-962.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler P., Weisblum B. Erythromycin-induced stabilization of ermA messenger RNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltis M. T., Mekalanos J. J., Betley M. J. Identification of a bacteriophage containing a silent staphylococcal variant enterotoxin gene (sezA+). Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1614–1619. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1614-1619.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobberingh E. E., Winkler K. C. Restriction-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):359–367. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremaine M. T., Brockman D. K., Betley M. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A gene (sea) expression is not affected by the accessory gene regulator (agr). Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):356–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.356-359.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]