Abstract
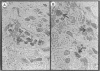
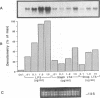
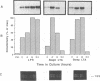
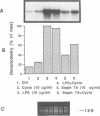
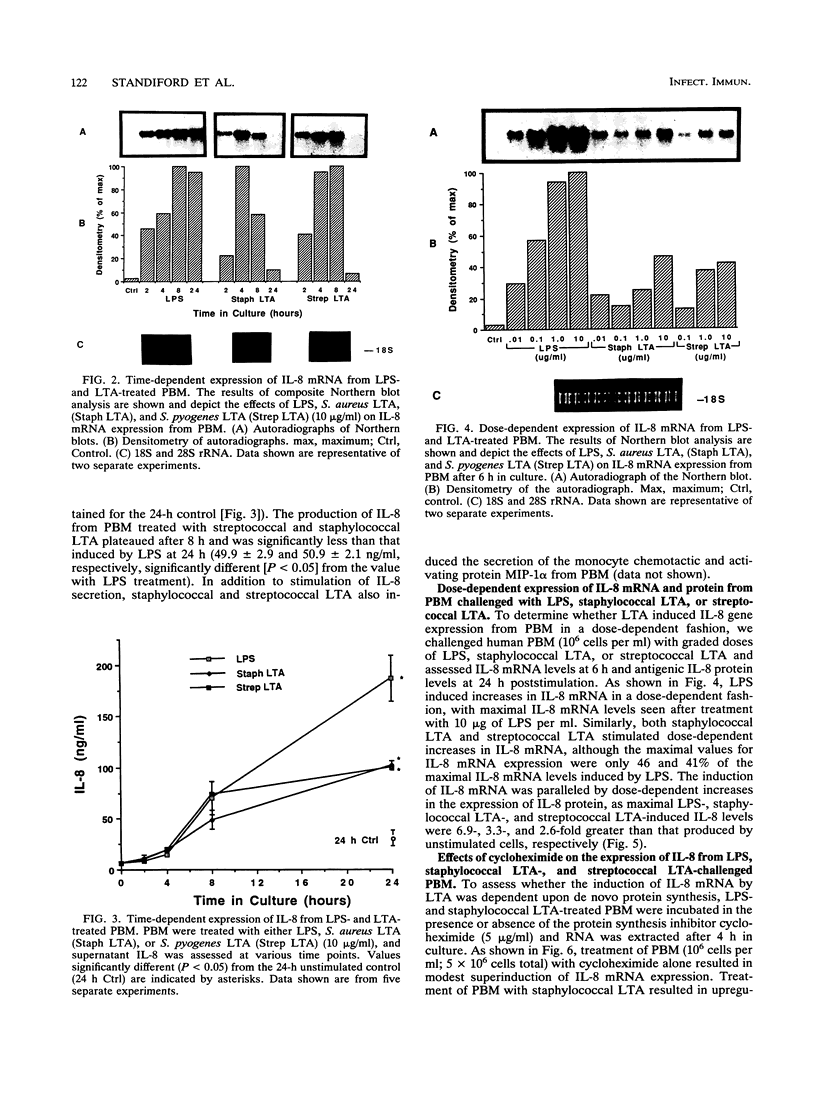
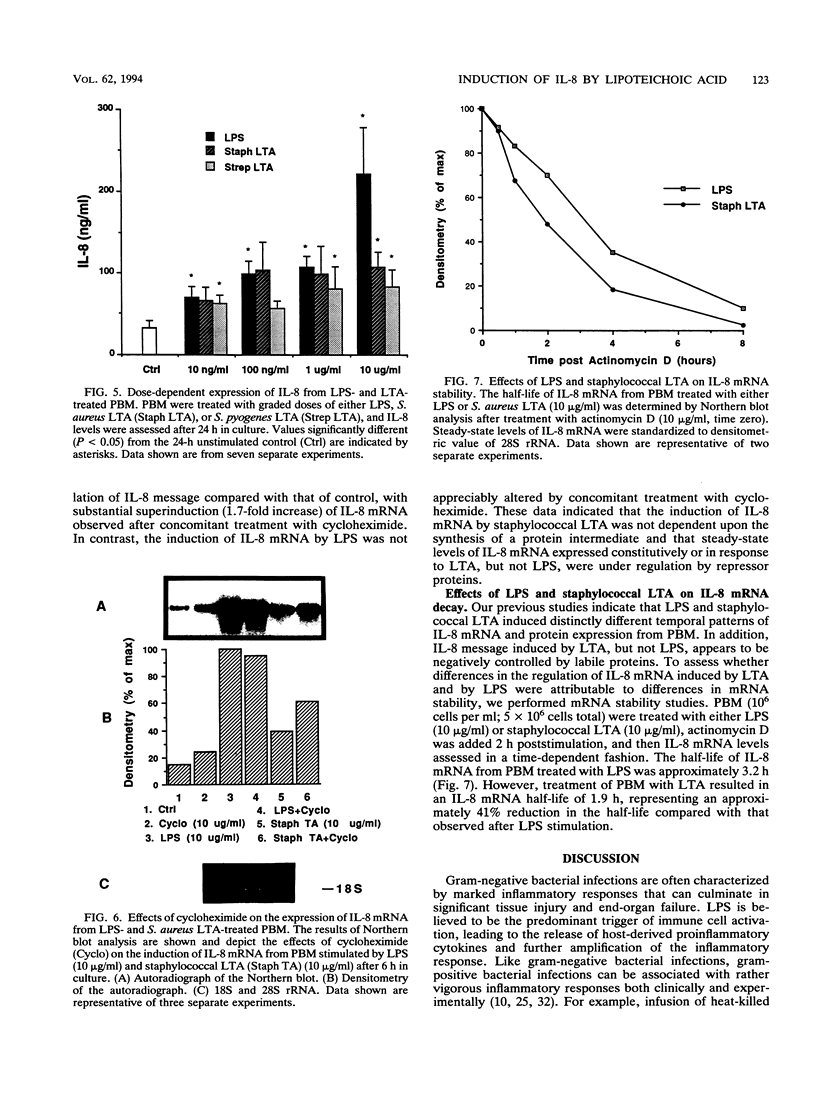
Invasion by gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial organisms is characterized immunopathologically by the activation of mononuclear phagocytic cells, leading to the elaboration of macrophage-derived regulatory and chemotactic factors, and the resultant influx of inflammatory leukocytes. Little is known regarding the mechanisms by which gram-positive organisms initiate macrophage activation and subsequent inflammation. In this investigation, we postulated that lipoteichoic acid (LTA) purified from two different gram-positive bacterial species was an important signal for the expression of chemotactic cytokines from human peripheral blood monocytes (PBM). In initial experiments, we demonstrated that cell-associated interleukin-8 (IL-8) was expressed by mononuclear phagocytes present in inflamed areas of endocardium in cases of acute Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. We next demonstrated that LTA purified from either Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes induced the time- and dose-dependent expression of IL-8 mRNA and protein from human PBM. The expression of IL-8 mRNA from LTA- but not lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated PBM was superinduced by concomitant treatment with cycloheximide, indicating that the expression of IL-8 mRNA from LTA-treated PBM was negatively controlled by repressor proteins. Furthermore, mRNA stability studies indicated that IL-8 mRNA was less stable in the presence of LTA than in the presence of LPS. Our findings indicate that LTA can induce the secretion of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor IL-8 and that LTA may be an important cellular mediator of inflammatory cell recruitment that characterizes immune responses to gram-positive bacterial infections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Klonisch T., Nuber P., Fischer W. Stimulation of monokine production by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4614–4620. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4614-4620.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi A. M., Jacoby D. B. Influenza virus A infection induces interleukin-8 gene expression in human airway epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Sep 14;309(3):327–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80799-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Shiotsuki K., Blanchard D. K. Functional activation of human neutrophils by recombinant monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor/IL-8. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2205–2210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Schreiber A. D., Gustilo K., Chien P., Rossman M. D., Lammie P. J., Daniele R. P. Differential interleukin 1 elaboration by unfractionated and density fractionated human alveolar macrophages and blood monocytes: relationship to cell maturity. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3198–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J. S., Remick D. G., Shattock R., Griffin G. E. Secretion of interleukin-8 following phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by human monocyte cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hart M., van Schijndel R. J., Eerenberg A. J., Nuijens J. H., Thijs L. G., Aarden L. A. Interleukin-8 in sepsis: relation to shock and inflammatory mediators. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2835–2842. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2835-2842.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas E., Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Epidermal keratin gene expressed in embryos of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Fischer W., Keist R., Bassetti S. Macrophage response to bacteria: induction of marked secretory and cellular activities by lipoteichoic acids. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3664–3672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3664-3672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. P., 3rd, Standiford T. J., Rolfe M. W., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M. Neutrophilic alveolitis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The role of interleukin-8. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jun;145(6):1433–1439. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S. Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2814487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 8 and MCAF: novel inflammatory cytokines inducible by IL 1 and TNF. Cytokine. 1989 Nov;1(1):2–13. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(89)91043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauciel C., Fleck J., Martin J. P., Mock M., Nguyen-Huy H. Adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycans on the production of delayed hypersensitivity and on antibody response. Eur J Immunol. 1974 May;4(5):352–356. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Zachariae C. O., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene "intercrine" cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:617–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Sylvester I., Smith S., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J. Macrophages cultured in vitro release leukotriene B4 and neutrophil attractant/activation protein (interleukin 8) sequentially in response to stimulation with lipopolysaccharide and zymosan. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1556–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI114875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. L., Miller C. G., DeForge L. E., Kelty L., Shanley C. J., Bartlett R. H., Remick D. G. Local production of interleukin-8 is associated with nosocomial pneumonia. J Trauma. 1992 Jul;33(1):74–82. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199207000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Weissmann C. Induction of mRNA for a serine protease and a beta-thromboglobulin-like protein in mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):250–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M. The monocyte-derived neutrophil activating peptide (NAP/interleukin 8) stimulates human neutrophil arachidonate-5-lipoxygenase, but not the release of cellular arachidonate. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):847–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N. Staphylococcus aureus. The persistent pathogen (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 May 31;310(22):1437–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405313102206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Westwick J., Kasahara K., Kunkel S. L. IL-4 inhibits the expression of IL-8 from stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1435–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart-Tull D. E. The immunological activities of bacterial peptidoglycans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:311–340. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckle M. Y. Post-transcriptional regulation of gro alpha, beta, gamma, and IL-8 mRNAs by IL-1 beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):917–920. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kasahara K., Allen R. M., Standiford T. J., Rolfe M. W., Becker F. S., Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L. Cytokine-induced neutrophil-derived interleukin-8. Am J Pathol. 1992 Aug;141(2):397–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Genord M., Raiford C., Spengler R., Kunkel S. L. Differential regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human alveolar macrophages and peripheral blood monocytes: a cellular and molecular analysis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;1(1):57–63. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usami H., Yamamoto A., Sugawara Y., Hamada S., Yamamoto T., Kato K., Kokeguchi S., Takada H., Kotani S. A nontoxic tumour necrosis factor induced by streptococcal lipoteichoic acids. Br J Cancer. 1987 Dec;56(6):797–799. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi G., Gelfand J. A., Jung W. K., Connolly R. J., Burke J. F., Dinarello C. A. Staphylococcus epidermidis induces complement activation, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1, a shock-like state and tissue injury in rabbits without endotoxemia. Comparison to Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1925–1935. doi: 10.1172/JCI115218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]