Abstract
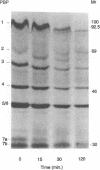
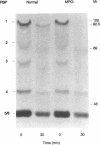
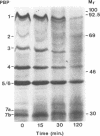
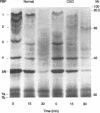
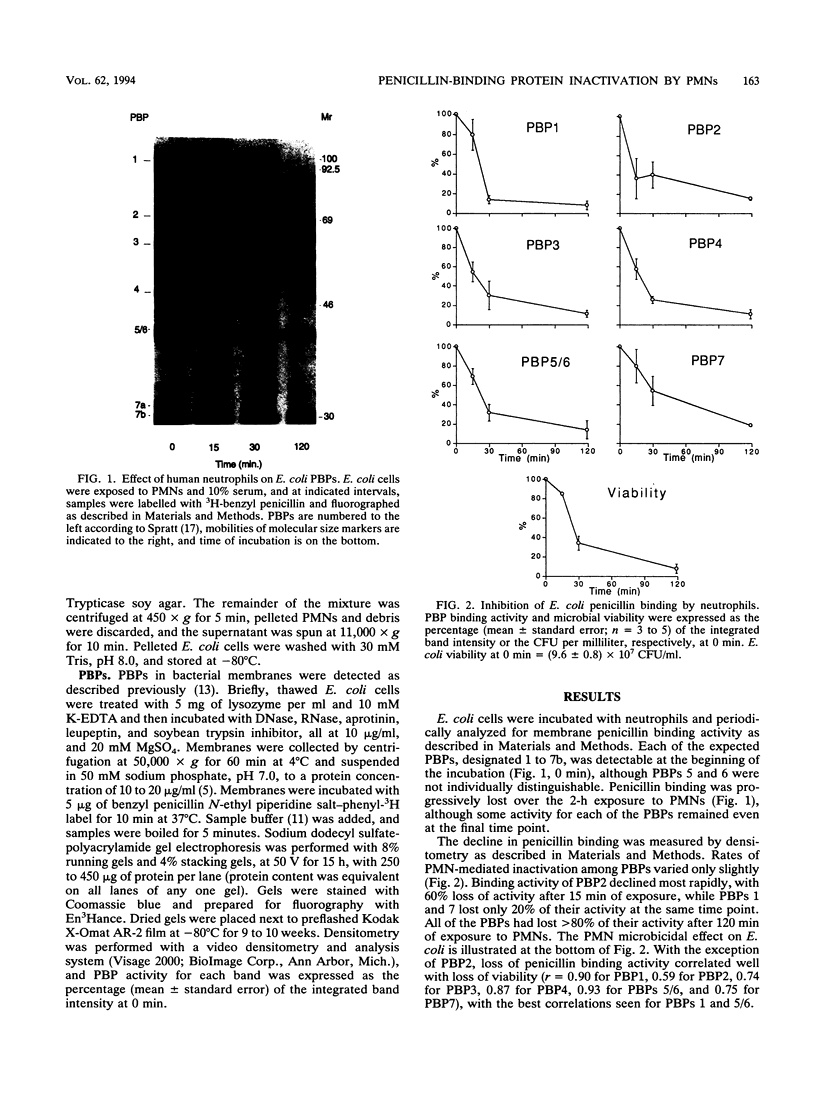
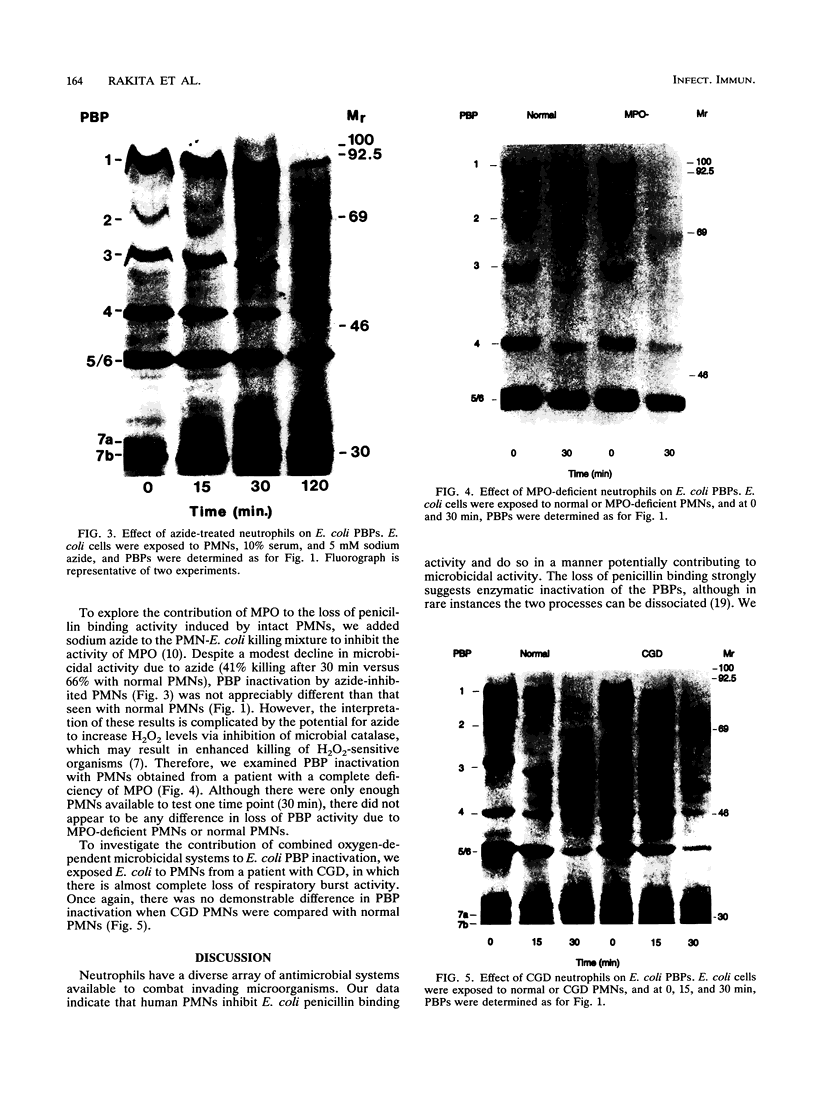
Neutrophils use a variety of microbicidal mechanisms in their role as one of the primary arms of the human host defense system. We have previously observed that a cell-free system containing myeloperoxidase (MPO), one of the major components of the neutrophil's oxidative antimicrobial systems, inactivated microbial penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), which mediate the formation of the peptidoglycan layer of eubacterial cell walls. This is a potentially important mechanism of MPO-mediated bacterial toxicity. Since numerous other microbicidal systems, both oxidative and nonoxidative, are used by whole neutrophils, we investigated the effect of intact neutrophils on Escherichia coli PBPs. Penicillin binding activity was progressively reduced by neutrophil exposure for all PBPs. Loss of penicillin binding activity correlated well with loss of microbial viability for almost all PBPs. Azide-treated neutrophils, MPO-deficient neutrophils, and chronic granulomatous disease neutrophils inactivated E. coli PBPs in a manner similar to that of normal neutrophils, suggesting that MPO-independent, and even oxygen-independent, microbicidal systems are also involved in inactivation of PBPs. PBP inactivation, an antimicrobial strategy used by beta-lactam-producing molds (and now by physicians), may be an important microbicidal mechanism used by human neutrophils.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belding M. E., Klebanoff S. J., Ray C. G. Peroxidase-mediated virucidal systems. Science. 1970 Jan 9;167(3915):195–196. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3915.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Clark R. A., Haudenschild C. C. Damage to Candida albicans hyphae and pseudohyphae by the myeloperoxidase system and oxidative products of neutrophil metabolism in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):908–917. doi: 10.1172/JCI109958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Curnutte J. T., Rosen H., Orkin S. H. A missense mutation in the neutrophil cytochrome b heavy chain in cytochrome-positive X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2012–2016. doi: 10.1172/JCI114393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frère J. M., Joris B. Penicillin-sensitive enzymes in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;11(4):299–396. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson D. L., Webber R. J. Miniaturization of the BCA protein assay. Biotechniques. 1988 Jan;6(1):14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Coombs R. W. Viricidal effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on human immunodeficiency virus type 1: possible role in heterosexual transmission. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):289–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Hamon C. B. Role of myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial systems in intact leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):170–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase-halide-hydrogen peroxide antibacterial system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2131–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2131-2138.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Malawista S. E., Roberts R. L., Rosen H., Ochs H. D., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Phosphorylation of the oxidase-related 48K phosphoprotein family in the unusual autosomal cytochrome-negative and X-linked cytochrome-positive types of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):811–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakita R. M., Rosen H. Penicillin-binding protein inactivation by human neutrophil myeloperoxidase. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):750–754. doi: 10.1172/JCI115372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Chemiluminescence and superoxide production by myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):50–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI108458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Michel B. R., Chait A. Phagocytosis of opsonized oil droplets by neutrophils. Adaptation to a microtiter plate format. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 5;144(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90237-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Onunka V. C., Jannoun M., Huthwaite L. W. Molecular mechanism for the antigonococcal action of lysosomal cathepsin G. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1269–1277. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Cromie K. D. Penicillin-binding proteins of gram-negative bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins and the antibacterial effectiveness of beta-lactam antibiotics. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 (Suppl 3):S260–S278. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]