Abstract
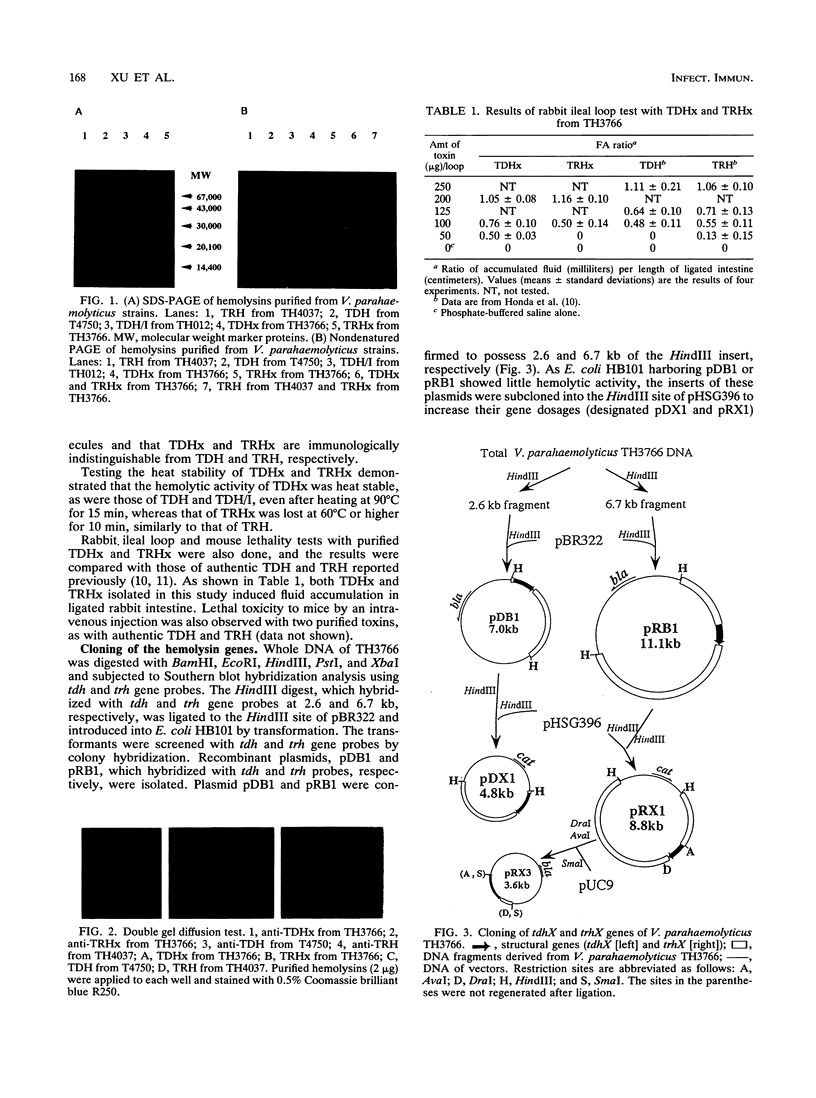
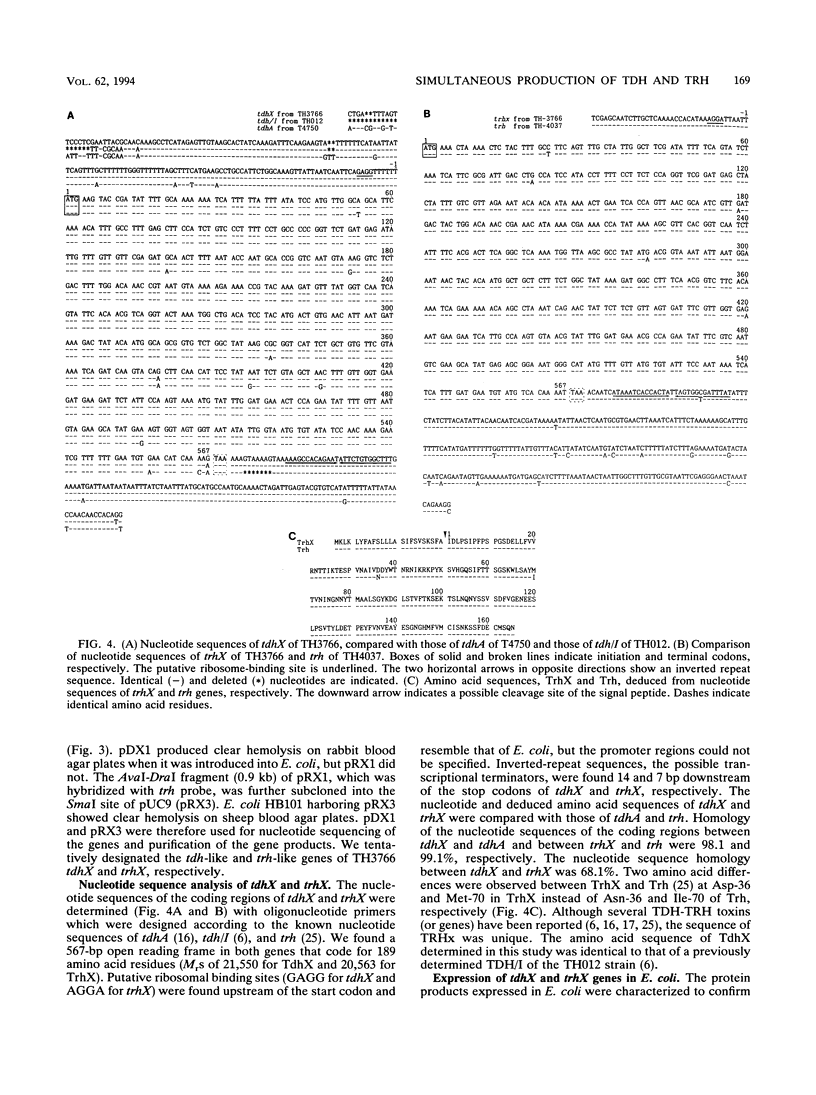
Simultaneous production of a thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH)-like toxin (TDHx) and a TDH-related hemolysin (TRH)-like toxin (TRHx) by a clinical isolate (strain TH3766) of Kanagawa phenomenon-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus was demonstrated and characterized. The two hemolysins were differentially purified by column chromatography on hydroxyapatite and immunoaffinity columns. The molecular weight of the two hemolysins were estimated to be 23,000 by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The purified TDHx was indistinguishable from the previously reported TDH/I (from strain TH012) but was different from the authentic TDH of a Kanagawa phenomenon-positive strain (T4750) physicochemically. The mobility of TRHx in nondenaturing PAGE differed from all the known TDHs and TRHs. The genes (tdhX and trhX) coding for TDHx and TRHx were cloned and sequenced. Homologies of nucleotide sequences of the coding regions between tdhX and tdhA (a gene for the authentic TDH) and between trhX and trh (a gene for the authentic TRH) were 98.1 and 99.1%, respectively, and homology between tdhX and trhX was 68.1%. At the amino acid level, TdhX was completely identical to TDH/I, although two base differences were found in the nucleotide sequences between tdhX and tdh/I. Two amino acid differences were observed between TrhX and Trh. Thus, these findings suggest that the TH3766 strain produces two types of hemolysins simultaneously. This is the first evidence that a strain of V. parahaemolyticus produces two types of toxins of the TDH-TRH family at the same time.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba K., Shirai H., Terai A., Takeda Y., Nishibuchi M. Analysis of the tdh gene cloned from a tdh gene- and trh gene-positive strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(3):253–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda S., Goto I., Minematsu I., Ikeda N., Asano N., Ishibashi M., Kinoshita Y., Nishibuchi M., Ohnda T., Miwatani T. [Vibrio parahaemolyticus infectious disease caused by Kanagawa phenomenon-negative O3:K6 originated from Maldives]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1987 Sep;61(9):1070–1078. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.61.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Abad-Lapuebla M. A., Ni Y. X., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Characterization of a new thermostable direct haemolysin produced by a Kanagawa-phenomenon-negative clinical isolate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Feb;137(2):253–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Goshima K., Takeda Y., Sugino Y., Miwatani T. Demonstration of the cardiotoxicity of the thermostable direct hemolysin (lethal toxin) produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):163–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.163-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Honda S., Ni Y. X., Miwatani T. [Development and application of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibody against a hemolysin (Vp-TRH) of Vibrio paraheamolyticus--evidence that Vp-TRH producing-Kanagawa phenomenon-negative V. parahaemolyticus is a human pathogen]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1990 Jul;64(7):767–773. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.64.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y. X., Hata A., Yoh M., Miwatani T., Okamoto T., Goshima K., Takakura H., Tsunasawa S., Sakiyama F. Properties of a hemolysin related to the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by a Kanagawa phenomenon negative, clinical isolate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Jun;36(6):395–399. doi: 10.1139/m90-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y. X., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of a hemolysin produced by a clinical isolate of Kanagawa phenomenon-negative Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related to the thermostable direct hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):961–965. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.961-965.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y., Miwatani T. Purification of a TDH-related hemolysin produced by a Kanagawa phenomenon-negative clinical isolate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus 06: K46. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Ni Y., Yoh M., Miwatani T. Production of monoclonal antibodies against thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and application of the antibodies for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(5):245–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00191059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda T., Hasibuan M. A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Identification of lethal toxin with the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and some physicochemical properties of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.133-139.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida T., Yamamoto K. Cloning and expression of two genes encoding highly homologous hemolysins from a Kanagawa phenomenon-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus T4750 strain. Gene. 1990 Sep 1;93(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90129-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishishita M., Matsuoka N., Kumagai K., Yamasaki S., Takeda Y., Nishibuchi M. Sequence variation in the thermostable direct hemolysin-related hemolysin (trh) gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2449–2457. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2449-2457.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Obara Y., Nikkawa T., Yamai S., Kato T., Yamada Y., Ohashi M. Simplified purification and biophysicochemical characteristics of Kanagawa phenomenon-associated hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):567–576. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.567-576.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Fasano A., Russell R. G., Kaper J. B. Enterotoxigenicity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus with and without genes encoding thermostable direct hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3539–3545. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3539-3545.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Kaper J. B. Duplication and variation of the thermostable direct haemolysin (tdh) gene in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):87–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Kumagai K., Kaper J. B. Contribution of the tdh1 gene of Kanagawa phenomenon-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus to production of extracellular thermostable direct hemolysin. Microb Pathog. 1991 Dec;11(6):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Taniguchi T., Misawa T., Khaeomanee-Iam V., Honda T., Miwatani T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene (trh) encoding the hemolysin related to the thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2691–2697. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2691-2697.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Kato T., Obara Y., Yamai S. Studies on the enteropathogenic, facultatively halophilic bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus. 3. Enteropathogenicity. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):325–331. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S., Sato M., Toba M., Masahashi W., Hashimoto-Gotoh T. High-copy-number and low-copy-number plasmid vectors for lacZ alpha-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene. 1987;61(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twedt R. M., Peeler J. T., Spaulding P. L. Effective ileal loop dose of Kanagawa-positive Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):1012–1016. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.1012-1016.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Honda T., Miwatani T., Tamatsukuri S., Shibata S. Enzyme-labeled oligonucleotide probes for detection of the genes for thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and TDH-related hemolysin (TRH) of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Can J Microbiol. 1992 May;38(5):410–416. doi: 10.1139/m92-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




