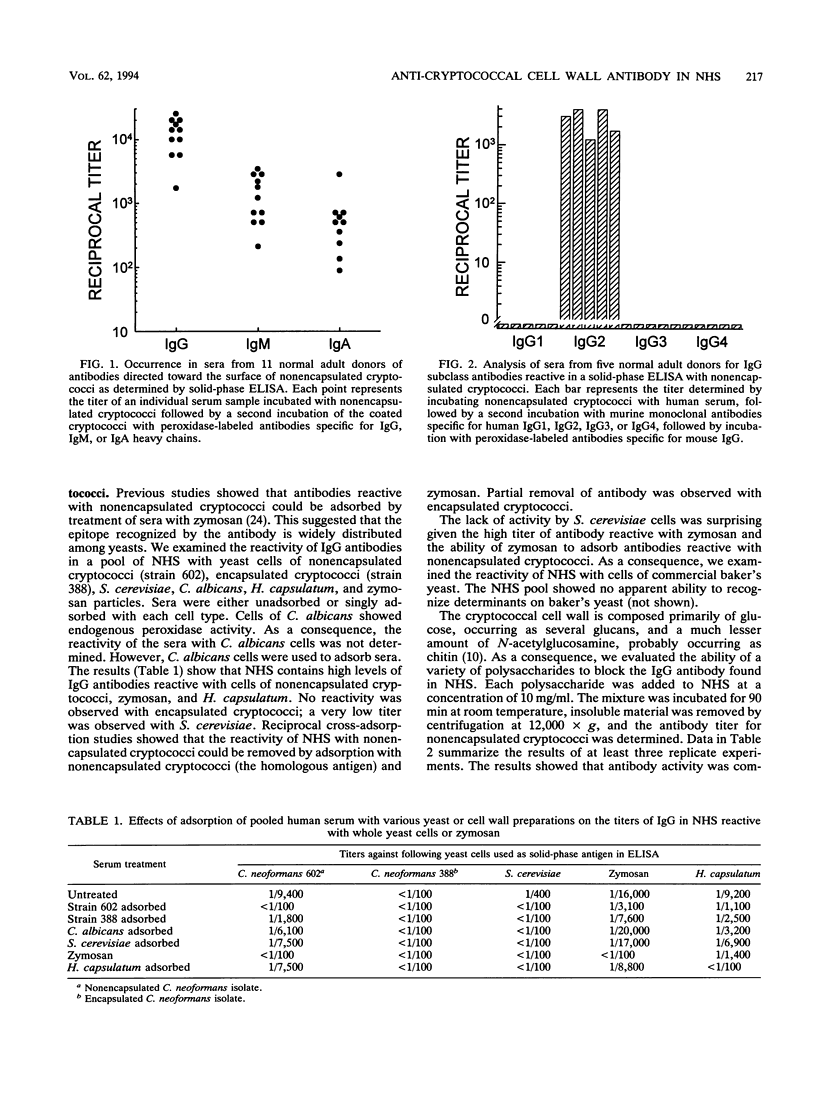
Abstract
Previous studies found that normal human serum (NHS) contains an immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody that mediates initiation of the classical complement pathway by nonencapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. The present study used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with whole nonencapsulated yeast cells as solid-phase antigens to demonstrate the presence of high levels of IgG antibody in each of 11 sera from normal adult donors. The IgG antibodies were of the IgG2 subclass. The antibody activity was blocked completely by treatment of serum with isolated yeast glucan. Treatment of serum with mannan or chitin had no effect on antibody levels. Antibody activity was adsorbed completely by treatment of serum with zymosan particles. Adsorption with intact cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Candida albicans had no effect, suggesting that the glucan on S. cerevisiae or C. albicans is not surface exposed. Assessment of the opsonic requirements for phagocytosis of nonencapsulated cryptococci by monocyte-derived human macrophages (MO-M phi) showed that high levels of phagocytosis occurred when yeast cells were opsonized with NHS. Removal of anti-glucan antibody by adsorption with whole nonencapsulated cryptococci did not diminish opsonic activity. Heat-inactivated serum or anti-glucan antibody affinity purified from NHS lacked opsonic activity. Taken together, these results indicate that phagocytosis of nonencapsulated cryptococci by monocyte-derived human macrophages has an obligatory requirement for opsonic ligands of the complement system, with no contribution by the anti-glucan IgG that is found in NHS.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUM L. EVIDENCE FOR IMMUNOLOGICAL SPECIFICITY OF THE PROPERDIN SYSTEM; DEMONSTRATION, ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF A SERUM FACTOR WHICH INTERACTS WITH ZYMOSAN AND OTHER POLYSACCHARIDES AT 0 DEGREES CENTIGRADE. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:61–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon J. S., Farmer V. C., Jones D., Taylor I. F. The glucan components of the cell wall of baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) considered in relation to its ultrastructure. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):557–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1140557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barras D. R., Stone B. A. Beta-1,3-glucan hydrolases from Euglena gracilis. II. Purification and properties of the beta-1,3-glucan exo-hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 4;191(2):342–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett D. J., Ayoub E. M. IgG2 subclass restriction of antibody to pneumococcal polysaccharides. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jan;63(1):127–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Bowers B., Sburlati A., Silverman S. J. Fungal cell wall synthesis: the construction of a biological structure. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Dec;5(12):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI CARLO F. J., FIORE J. V. On the composition of zymosan. Science. 1958 Apr 4;127(3301):756–757. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3301.756-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M., Vonlanthen M. Location of mannan and chitin on thin sections of budding yeasts with gold markers. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Oct 24;115(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00427837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Douglas S. D., Nusbacher J., Kochwa S., Rosenfield R. E. IgG subclass specificity of human monocyte receptor sites. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):419–420. doi: 10.1038/229419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P. G., Cherniak R., Jones R. G., Stortz C. A., Reiss E. Cell-wall glucans of Cryptococcus neoformans Cap 67. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Apr 2;198(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84273-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Highison B., Stratton C. J. Localization on encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans of serum components opsonic for phagocytosis by macrophages and neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.574-579.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Guerlain A. S., Highison B. A., Highison G. J. Role of the capsule in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S436–S439. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Murphy J. W. Early events in initiation of alternative complement pathway activation by the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3101–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3101-3110.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J. Differential stimulation of murine resident peritoneal cells by selectively opsonized encapsulated and acapsular Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2544–2551. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2544-2551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Tabuni A. Binding of Cryptococcus neoformans by human cultured macrophages. Requirements for multiple complement receptors and actin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):528–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI115027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manners D. J., Masson A. J., Patterson J. C. The structure of a beta-(1 leads to 3)-D-glucan from yeast cell walls. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):19–30. doi: 10.1042/bj1350019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D., Tronchin G., Dubremetz J. F., Biguet J. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Candida albicans blastospores: study of its constitutive layers by the use of a cytochemical technique revealing polysaccharides. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Feb-Mar;129(2):141–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein H. A., Ruddy S. The role of immunoglobulins in alternative complement pathway activation by zymosan. I. Human IgG with specificity for Zymosan enhances alternative pathway activation by zymosan. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein H. A., Ruddy S. The role of immunoglobulins in alternative pathway activation by zymosan. II. The effect of IgG on the kinetics of the alternative pathway. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stengelin S., Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Isolation of cDNAs for two distinct human Fc receptors by ligand affinity cloning. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. A., Kozel T. R. Contribution of antibody in normal human serum to early deposition of C3 onto encapsulated and nonencapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):754–761. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.754-761.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. J., Kozel T. R. Effects of strain variation, serotype, and structural modification on kinetics for activation and binding of C3 to Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2966–2972. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2966-2972.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



