Abstract
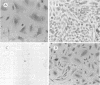
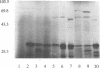
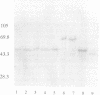
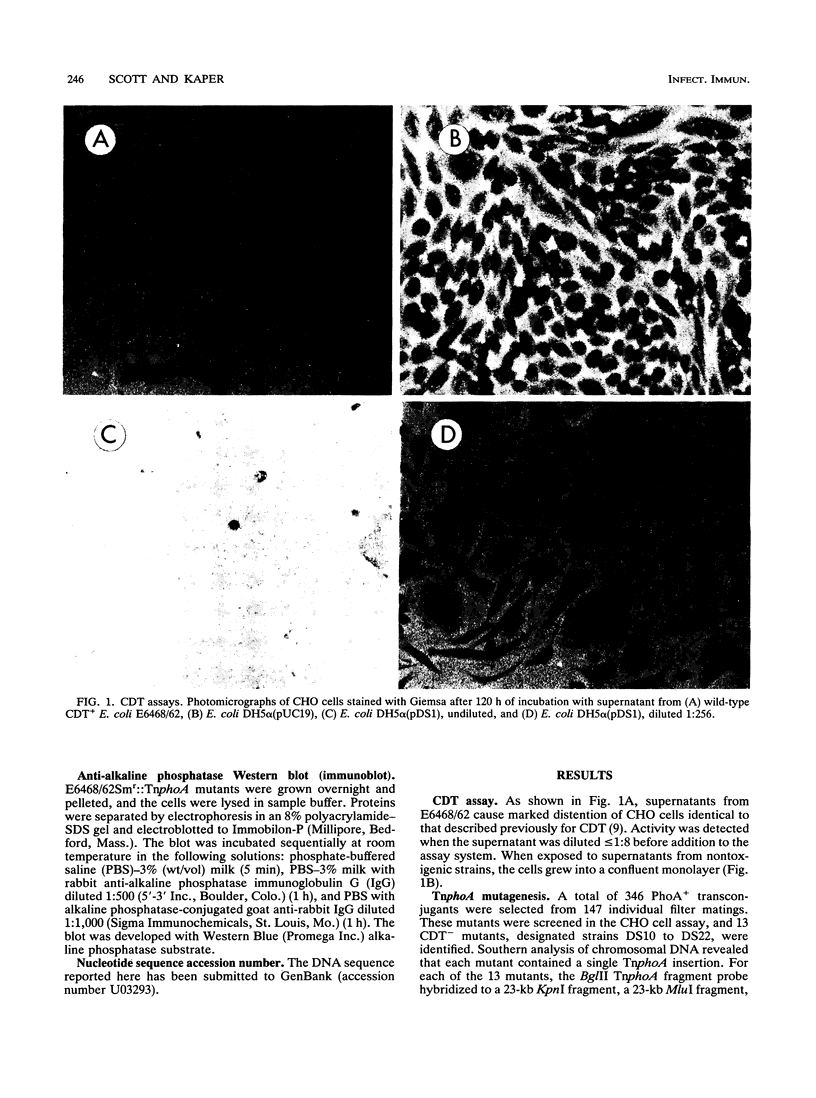
Escherichia coli strains expressing cytolethal distending toxin (CDT) cause elongation of CHO cells at 24 h, followed by progressive cellular distention and death for up to 120 h. Similar distention and cytotoxicity are seen in HeLa, HEp-2, and, to a lesser extent, Vero cells. The initial elongation in CHO cells is indistinguishable from that caused by E. coli heat-labile toxin (LT). In contrast to those from LT strains, supernatants from these strains have no effect on Y-1 adrenal cells. TnphoA was introduced into CDT-positive E. coli E6468/62 (O86:H34), isolated from a child with diarrhea, and 13 CDT-negative transconjugants were identified. DNA probes constructed from DNA flanking the TnphoA insertion sites of CDT-negative mutants were used to identify a CDT-positive clone from an E6468/62 genomic library with a 5.5-kb insert. Exonuclease deletions were created and assayed in CHO cells. In this manner, a 2.3-kb CDT-active region was defined, and the nucleotide sequence was determined. Sequence analysis identified three open reading frames (ORFs), designated cdtA, cdtB, and cdtC. These contain 711, 819, and 570 bp, respectively, and encode polypeptides with predicted molecular masses of 25.5, 29.8, and 20.3 kDa, respectively. Each ORF has a putative signal sequence, and there are 4-bp overlaps between cdtA and cdtB and between cdtB and cdtC. The nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences have no significant homology with those of any previously reported genes or proteins. By in vitro transcription-translation and an anti-alkaline phosphatase immunoblot, native proteins and/or fusion proteins corresponding to each ORF were identified.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., MacNab A. J., Gransden W. R., Damm S. M., Johnson W. M., Lior H. Gastroenteritis and encephalopathy associated with a strain of Escherichia coli 055:K59:H4 that produced a cytolethal distending toxin. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Dec;6(12):1135–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisicchia R., Ciammarughi R., Caprioli A., Falbo V., Ruggeri F. M. Toxin production and haemagglutination in strains of Escherichia coli from diarrhoea in Brescia, Italy. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):353–361. doi: 10.1017/s002217240006277x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzari S., Varghese A. Cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) production by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC). FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Sep 1;59(1-2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90055-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caprioli A., Falbo V., Ruggeri F. M., Baldassarri L., Bisicchia R., Ippolito G., Romoli E., Donelli G. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor production by hemolytic strains of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):146–149. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.146-149.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Further evaluation of the Biken test (modified Elek test) for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing heat-labile enterotoxin and application of the test to sampling of heat-stable enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):60–62. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.60-62.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. A new heat-labile cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) produced by Campylobacter spp. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. A new heat-labile cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) produced by Escherichia coli isolates from clinical material. Microb Pathog. 1988 Feb;4(2):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman H., Kaper J. B. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the A2 and B subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13722–13726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Merson M. H., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Martin W. T., Dewitt W. E., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Bessudo D. M. Laboratory investigation of diarrhea in travelers to Mexico: evaluation of methods for detecting enterotoxigenic Echerichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):486–495. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.486-495.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B., Robins-Browne R., Prado V., Vial P., Levine M. M. Patterns of adherence of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Sep;6(9):829–831. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198709000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Murphy J. R. Bacteriophage conversion of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):172–177. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.172-177.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Yokota T., Takano T. Overlapping genes in the heat-labile enterotoxin operon originating from Escherichia coli human strain. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):356–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00332701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Y. L. A simple and inexpensive method for drying high-percentage polyacrylamide gradient gels. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):381–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]