Abstract
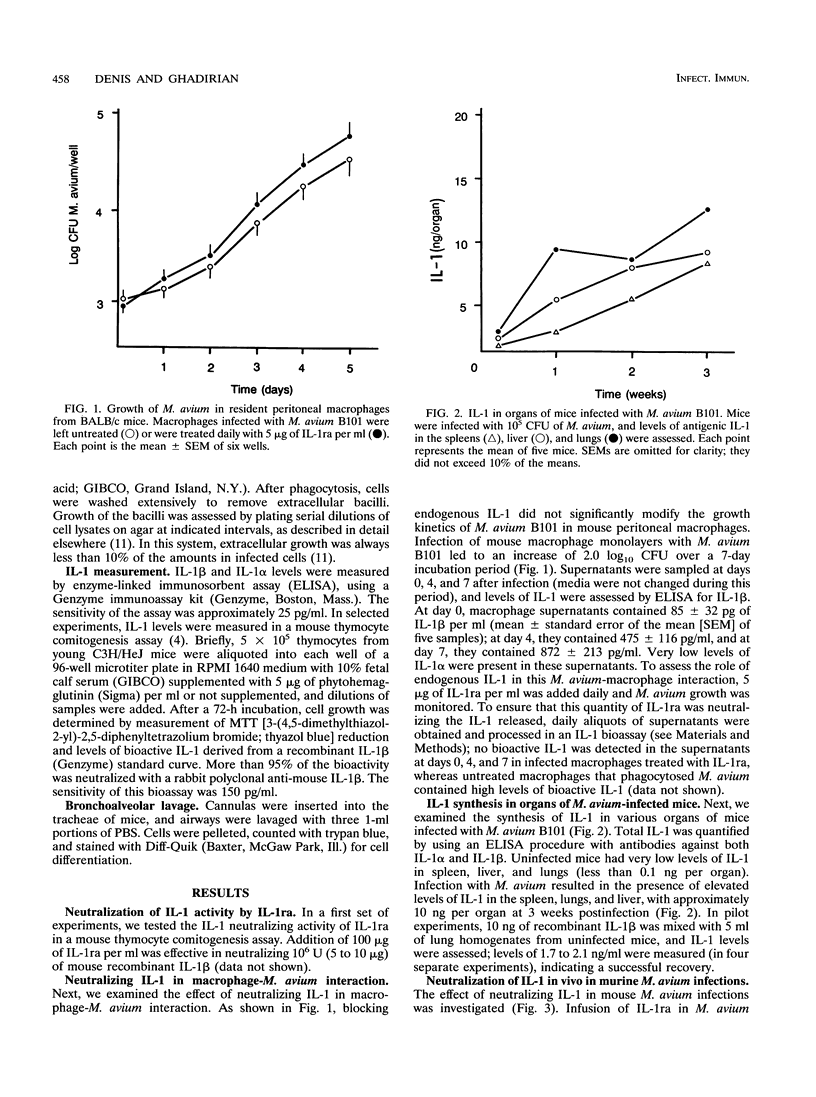
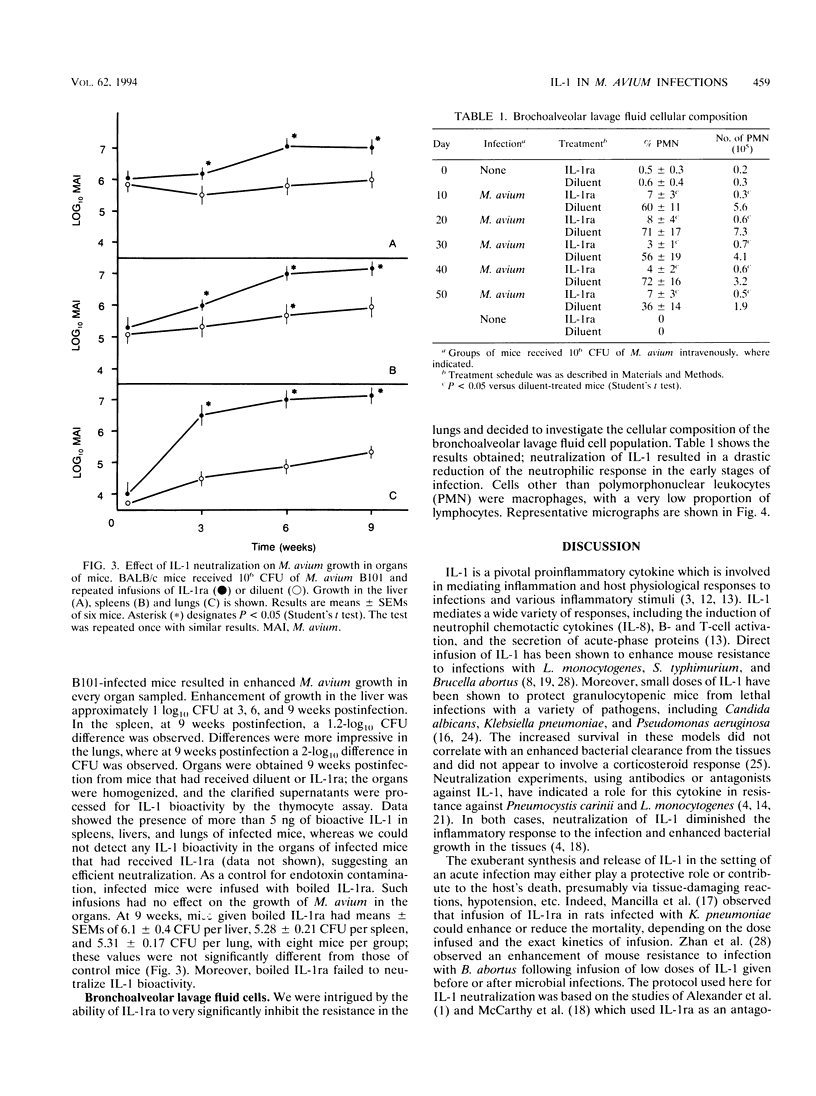
In this study, we examined the contribution of the monokine interleukin-1 (IL-1) in mouse resistance to the intracellular pathogen Mycobacterium avium. The effect of neutralizing endogenous IL-1 in mouse macrophage resistance to M. avium infection was investigated. Infection of mouse peritoneal macrophages with M. avium B101 was shown to result in significant IL-1 beta release by cells at 4 and 7 days postinfection. Addition of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) at doses of 5 micrograms daily, which neutralized endogenous IL-1, failed to significantly modify the intracellular growth of M. avium. Mice were injected with M. avium B101 by the intravenous route, and the growth of the mycobacteria was monitored in the organs of intact mice and in those of mice that received repeated high doses of IL-1ra. The infection with M. avium elicited the production of large amounts of IL-1 in the lungs, livers, and spleens. Repeated injections of IL-1ra into M. avium-infected mice resulted in moderately enhanced growth of the bacilli in the livers and spleens but in much enhanced growth in the lungs. The enhanced growth of M. avium in the lungs correlated with a diminished inflammatory influx of cells (particularly neutrophils) in the bronchoalveolar space. These data argue for a role for IL-1 in host resistance to M. avium infections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander H. R., Doherty G. M., Buresh C. M., Venzon D. J., Norton J. A. A recombinant human receptor antagonist to interleukin 1 improves survival after lethal endotoxemia in mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Welgus H. G., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Biological properties of recombinant human monocyte-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1694–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI114622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Villa L., Volpini G., Bossù P., Censini S., Ghiara P., Scapigliat G., Nencioni L., Bartalini M., Matteucci G. Differential activity of interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta in the stimulation of the immune response in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):317–321. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Havell E. A., Moldawer L. L., McIntyre K. W., Chizzonite R. A., Harmsen A. G. Interleukin 1: an important mediator of host resistance against Pneumocystis carinii. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):713–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., North R. J. Early pathogenesis of infection in the liver with the facultative intracellular bacteria Listeria monocytogenes, Francisella tularensis, and Salmonella typhimurium involves lysis of infected hepatocytes by leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5164–5171. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5164-5171.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Tsang A. Y., Vatter A. E., May M. H. Comparison of 15 laboratory and patient-derived strains of Mycobacterium avium for ability to infect and multiply in cultured human macrophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):812–821. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.812-821.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Young K. M., Cooley A. J., Kurtz R. S. Effects of murine recombinant interleukin 1 alpha on the host response to bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):962–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Tracey D. E., Kenney J. S., Remick D. G. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein inhibits interleukin-8 expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human whole blood. Am J Pathol. 1992 May;140(5):1045–1054. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gregg E. O. Modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in murine macrophages: reversal of unresponsiveness to interferon-gamma by indomethacin or interleukin-4. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Interleukin-6 is used as a growth factor by virulent Mycobacterium avium: presence of specific receptors. Cell Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;141(1):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90137-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Role of interleukin-1 in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:119–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Moldawer L. L., Helfgott D., Kilian P. L., Sehgal P. B. Type I IL-1 receptor blockade exacerbates murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1486–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullberg B. J., van 't Wout J. W., van Furth R. Role of granulocytes in increased host resistance to Candida albicans induced by recombinant interleukin-1. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3319–3324. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3319-3324.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancilla J., García P., Dinarello C. A. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist can either reduce or enhance the lethality of Klebsiella pneumoniae sepsis in newborn rats. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):926–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.926-932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy P. L., Jr, Abhyankar S., Neben S., Newman G., Sieff C., Thompson R. C., Burakoff S. J., Ferrara J. L. Inhibition of interleukin-1 by an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist prevents graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):1915–1918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. J., Charrier K. Interleukin-1 administration to C3H/HeJ mice after but not prior to infection increases resistance to Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4729–4731. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4729-4731.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Linzer B. A., Zuberi R. I., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I., Catanzaro A. Activity of defensins from human neutrophilic granulocytes against Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4720–4725. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4720-4725.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. W., Sheehan K. C., Brunt L. M., Dower S. K., Unanue E. R., Schreiber R. D. Interleukin 1 participates in the development of anti-Listeria responses in normal and SCID mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1011–1015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Barr R. M., Alexander J. Studies on the interaction of Mycobacterium microti and Mycobacterium lepraemurium with mouse polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):185–189. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima T., Collins F. M. T-cell-mediated immunity in persistent Mycobacterium intracellulare infections in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2782–2787. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2782-2787.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels M. T., Sweep C. G., Hermus A. R., van der Meer J. W. Interleukin-1-induced nonspecific resistance to bacterial infection in mice is not mediated by glucocorticosteroids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2785–2789. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. S., Fujiwara H., Ellner J. J. Direct stimulation of monocyte release of interleukin 1 by mycobacterial protein antigens. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):193–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Y. F., Stanley E. R., Cheers C. Prophylaxis or treatment of experimental brucellosis with interleukin-1. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1790-1794.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
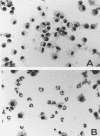
- van der Meer J. W., Barza M., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. A low dose of recombinant interleukin 1 protects granulocytopenic mice from lethal gram-negative infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1620–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]