Abstract
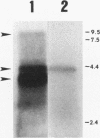
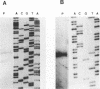
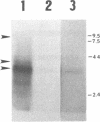
The leukotoxin of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans has been implicated as a virulence determinant in various human infections and is encoded by a multigene operon consisting of four known genes, designated ltxC, ltxA, ltxB, and ltxD. The ltx operon appears to be present in all A. actinomycetemcomitans strains, but levels of toxin expression vary greatly among strains. Thus, to gain a better understanding of the expression and regulation of the ltx operon, we have analyzed the ltx promoters of a highly toxic (JP2) and a minimally toxic (652) strain of A. actinomycetemcomitans. The nucleotide sequence of the JP2 ltx promoter contains -10 and -35 elements situated 350 bases upstream of ltxC, and primer extension of JP2 RNA confirmed that they are functional in vivo. However, a second primer extension product of 40 bases was present, and analysis of a series of truncated JP2 promoters fused to lacZ suggested that the region immediately upstream of ltxC also promotes transcription in Escherichia coli. These results suggest that two promoters may direct ltx expression in JP2. In addition, a small open reading frame capable of encoding a peptide of 78 amino acids was identified upstream of ltxC. Northern blots showed that this open reading frame is transcribed as part of a 4.2-kb mRNA, a transcript not previously identified as being derived from the ltx operon. In contrast, strain 652 expresses low steady-state levels of ltx mRNA, and its intact ltx promoter was inefficient in transcribing lacZ in E. coli. The nucleotide sequence of the 652 promoter is similar to that of the JP2 promoter but contains a region of 530 bp that is not present in JP2. Of 15 additional strains of A. actinomycetemcomitans that were analyzed, 13 contained promoters resembling the 652 sequence and 2 possessed JP2-like promoters. Both strains possessing the JP2-like promoter expressed 10- to 20-fold-higher levels of leukotoxin than did the strains possessing promoters resembling the 652 promoter. These results suggest that high levels of leukotoxin expression may correlate with the presence of the JP2-like promoter.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehni P. C., Tsai C. C., McArthur W. P., Hammond B. F., Shenker B. J., Taichman N. S. Leukotoxic activity in different strains of the bacterium Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans isolated from juvenile periodontitis in man. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(8):671–676. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Schmid A., Wagner W., Goebel W. Pore formation by the Escherichia coli hemolysin: evidence for an association-dissociation equilibrium of the pore-forming aggregates. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):887–895. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.887-895.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block P. J., Yoran C., Fox A. C., Kaltman A. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans endocarditis: report of a case and review of the literature. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Nov;266(5):387–392. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Welch R. A. Alterations of amino acid repeats in the Escherichia coli hemolysin affect cytolytic activity and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie K. R., Issartel J. P., Koronakis E., Hughes C., Koronakis V. In vitro activation of Escherichia coli prohaemolysin to the mature membrane-targeted toxin requires HlyC and a low molecular-weight cytosolic polypeptide. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1669–1679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issartel J. P., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Activation of Escherichia coli prohaemolysin to the mature toxin by acyl carrier protein-dependent fatty acylation. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):759–761. doi: 10.1038/351759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwase M., Lally E. T., Berthold P., Korchak H. M., Taichman N. S. Effects of cations and osmotic protectants on cytolytic activity of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1782–1788. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1782-1788.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Hughes C. Identification of the promoters directing in vivo expression of hemolysin genes in Proteus vulgaris and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):99–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00333404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Koronakis E., Hughes C. Comparison of the haemolysin secretion protein HlyB from Proteus vulgaris and Escherichia coli; site-directed mutagenesis causing impairment of export function. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):551–555. doi: 10.1007/BF00339631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Dailey T., Kolodrubetz D. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: homology to the alpha-hemolysin/leukotoxin gene family. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.920-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lally E. T., Golub E. E., Kieba I. R., Taichman N. S., Decker S., Berthold P., Gibson C. W., Demuth D. R., Rosenbloom J. Structure and function of the B and D genes of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin complex. Microb Pathog. 1991 Aug;11(2):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90004-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lally E. T., Golub E. E., Kieba I. R., Taichman N. S., Rosenbloom J., Rosenbloom J. C., Gibson C. W., Demuth D. R. Analysis of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin gene. Delineation of unique features and comparison to homologous toxins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15451–15456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lally E. T., Kieba I. R., Demuth D. R., Rosenbloom J., Golub E. E., Taichman N. S., Gibson C. W. Identification and expression of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde G., McDonald T. V., Gardner P., O'Hanley P. D. Identification of a hemolysin from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and characterization of its channel properties in planar phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13559–13564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Jarchau T., Benz R., Goebel W. The repeat domain of Escherichia coli haemolysin (HlyA) is responsible for its Ca2+-dependent binding to erythrocytes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):553–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00330494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Vogel M., Goebel W. Mutations affecting activity and transport of haemolysin in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):238–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00333579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S., Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi: the specific secretion functions are analogous to those of Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. I., King E. O. Infection due to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Haemophilus aphrophilus. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jul 28;275(4):181–188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196607282750403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann M. D., Stauffer L. T., Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. Complete nucleotide sequence of the E. coli glyA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2065–2075. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. J., Webb R., Sherman L. A. Bacterial RNA isolation with one hour centrifugation in a table-top ultracentrifuge. Biotechniques. 1990 Mar;8(3):250–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J., Jr, Kraig E., Kolodrubetz D. Regulation of leukotoxin in leukotoxic and nonleukotoxic strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1394–1401. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1394-1401.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Regulation of expression of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5955–5962. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5955-5962.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Dean R. T., Sanderson C. J. Biochemical and morphological characterization of the killing of human monocytes by a leukotoxin derived from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):258–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.258-268.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Shenker B. J., Tsai C. C., Glickman L. T., Baehni P. C., Stevens R., Hammond B. F. Cytopathic effects of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans on monkey blood leukocytes. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Mar;19(2):133–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taichman N. S., Simpson D. L., Sakurada S., Cranfield M., DiRienzo J., Slots J. Comparative studies on the biology of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin in primates. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1987 Sep;2(3):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Delepelaire P. TolC, an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein required for hemolysin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Pellett S. Transcriptional organization of the Escherichia coli hemolysin genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1622–1630. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1622-1630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A. Pore-forming cytolysins of gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):521–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1985 Jan;12(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1985.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Slots J., Genco R. J. Serology of oral Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and serotype distribution in human periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):19–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.19-27.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]