Abstract
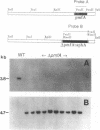
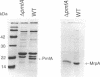
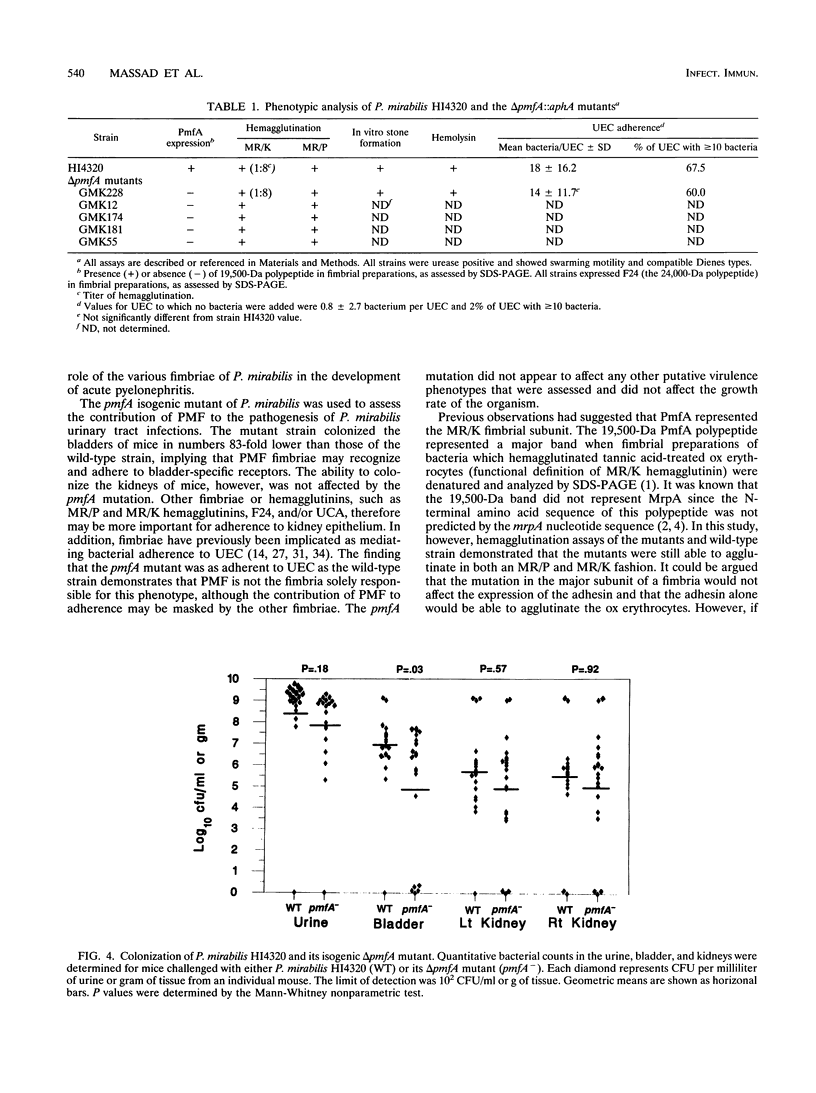
Proteus mirabilis, a cause of urinary tract infection and acute pyelonephritis, produces a number of different fimbriae. An isogenic fimbrial mutant of P. mirabilis HI4320 was constructed by marker exchange with delta pmfA::aphA to determine the role of the P. mirabilis fimbriae (PMF) in hemagglutination and in virulence in the CBA mouse model of ascending urinary tract infection. The pmfA mutant, which did not express the 19,500-Da major subunit of PMF, colonized the bladders of transurethrally challenged CBA mice (n = 20 in each group) in numbers 83-fold lower than those of the wild-type strain (mutant, log10 4.87 CFU/g; wild-type strain, log10 6.79 CFU/g; P = 0.023). However, the mutant colonized the kidneys in numbers similar to those of the wild-type strain. Hemagglutination patterns of the mutant ruled out the involvement of PMF in both mannose-resistant, Proteus-like and mannose-resistant, Klebsiella-like hemagglutination. Similarly, PMF does not appear to be involved in adherence to uroepithelial cells (UEC), since the mutant was as adherent as the wild-type strain (mutant, 14.1 +/- 11.7 mean bacteria per UEC, 60% of UEC with > or = 10 bacteria; wild-type strain, 18.1 +/- 16.2 mean bacteria per UEC, 68% of UEC with > or = 10 bacteria; not significantly different). These data suggest a role for PMF in colonization of the bladder but not in colonization of kidney tissue. PMF appear not to be responsible for mannose-resistant, Proteus-like or mannose-resistant, Klebsiella-like hemagglutination.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahrani F. K., Cook S., Hull R. A., Massad G., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis fimbriae: N-terminal amino acid sequence of a major fimbrial subunit and nucleotide sequences of the genes from two strains. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):884–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.884-891.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahrani F. K., Johnson D. E., Robbins D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis flagella and MR/P fimbriae: isolation, purification, N-terminal analysis, and serum antibody response following experimental urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3574–3580. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3574-3580.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahrani F. K., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis MR/P fimbriae: molecular cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of the major fimbrial subunit gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):457–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.457-464.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Larsson P., Lomberg H. Attachment of Proteus mirabilis to human urinary sediment epithelial cells in vitro is different from that of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):804–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.804-807.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairley K. F., Bond A. G., Brown R. B., Habersberger P. Simple test to determine the site of urinary-tract infection. Lancet. 1967 Aug 26;2(7513):427–428. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90849-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Engberg I., Freter R., Lam J., Olling S., Svanborg Edén C. Ascending, unobstructed urinary tract infection in mice caused by pyelonephritogenic Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.273-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Russell R. G., Lockatell C. V., Zulty J. C., Warren J. W., Mobley H. L. Contribution of Proteus mirabilis urease to persistence, urolithiasis, and acute pyelonephritis in a mouse model of ascending urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2748–2754. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2748-2754.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):80–128. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomberg H., Larsson P., Leffler H., Svanborg-Edén C. Different binding specificities of P. mirabilis compared to E. coli. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;33:37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R. Hemagglutinin, urease, and hemolysin production by Proteus mirabilis from clinical sources. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):525–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R., Tenney J. H., Warren J. W. Adherence to uroepithelial cells of Providencia stuartii isolated from the catheterized urinary tract. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Oct;132(10):2863–2872. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-10-2863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Penner J. L. Urease activity of Proteus penneri. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2302–2305. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2302-2305.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Warren J. W. Urease-positive bacteriuria and obstruction of long-term urinary catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2216–2217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2216-2217.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C., Adegbola R. A. Haemagglutinins and fimbriae of Morganella, Proteus and Providencia. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):551–564. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sareneva T., Holthöfer H., Korhonen T. K. Tissue-binding affinity of Proteus mirabilis fimbriae in the human urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3330–3336. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3330-3336.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setia U., Serventi I., Lorenz P. Bacteremia in a long-term care facility. Spectrum and mortality. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Aug;144(8):1633–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Ofek I. Influence of pili on the virulence of Proteus mirabilis in experimental hematogenous pyelonephritis. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):664–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets F., Gower P. E. The site of infection in 133 patients with bacteriuria. Clin Nephrol. 1973 Sep-Oct;1(5):290–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. W., Tenney J. H., Hoopes J. M., Muncie H. L., Anthony W. C. A prospective microbiologic study of bacteriuria in patients with chronic indwelling urethral catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):719–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Hull S. I., Cook R. G., Barrish J., Hull R. A. Identification and characterization of a uroepithelial cell adhesin from a uropathogenic isolate of Proteus mirabilis. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.43-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Die I., Zuidweg E., Hoekstra W., Bergmans H. The role of fimbriae of uropathogenic Escherichia coli as carriers of the adhesin involved in mannose-resistant hemagglutination. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]