Abstract
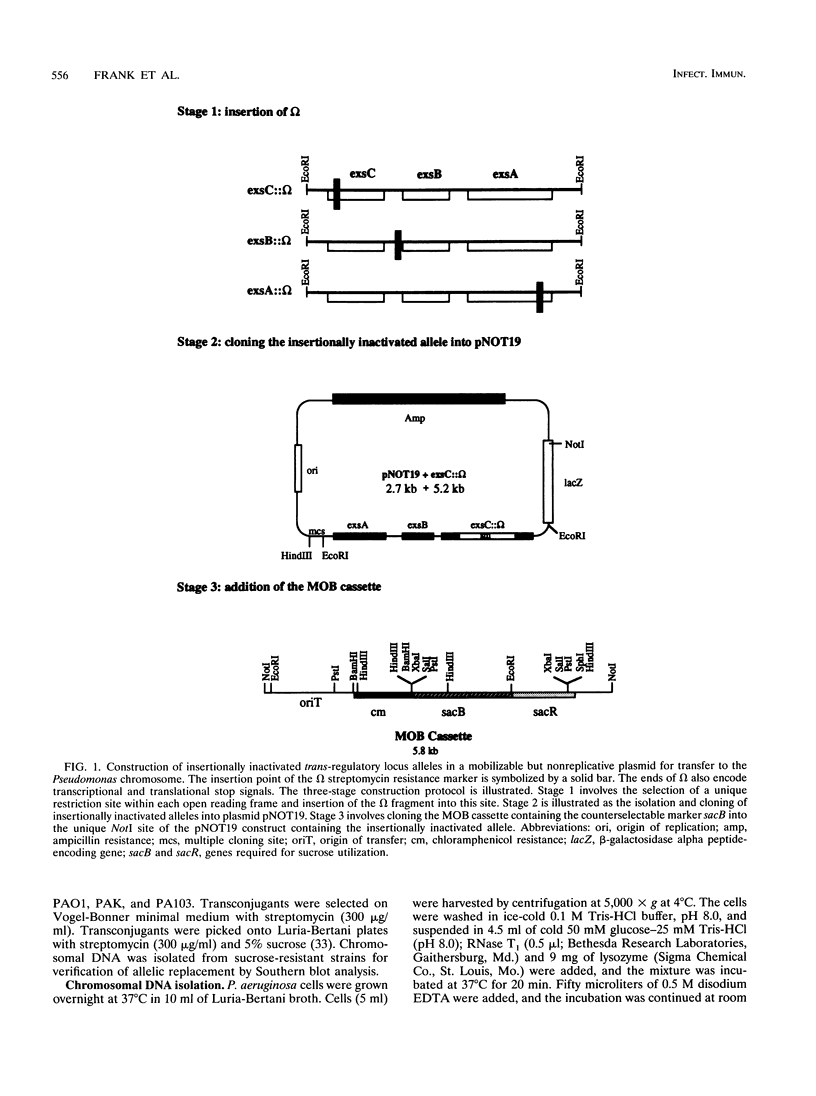
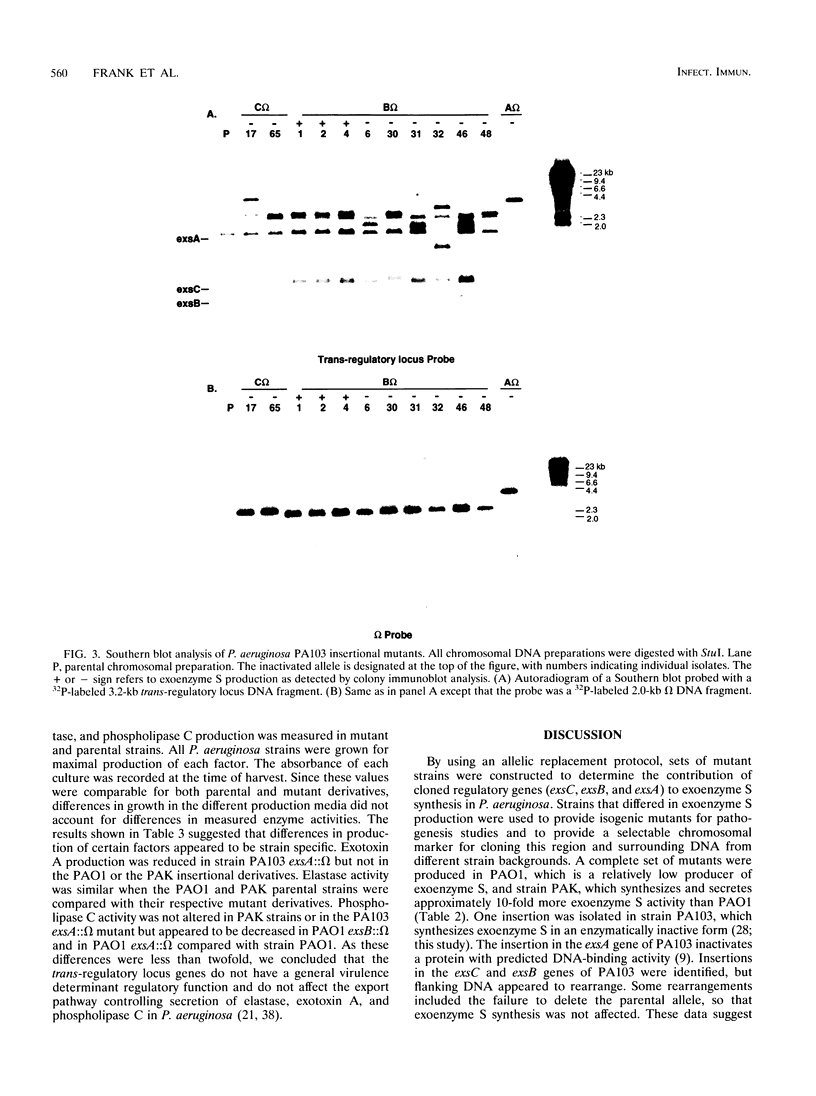
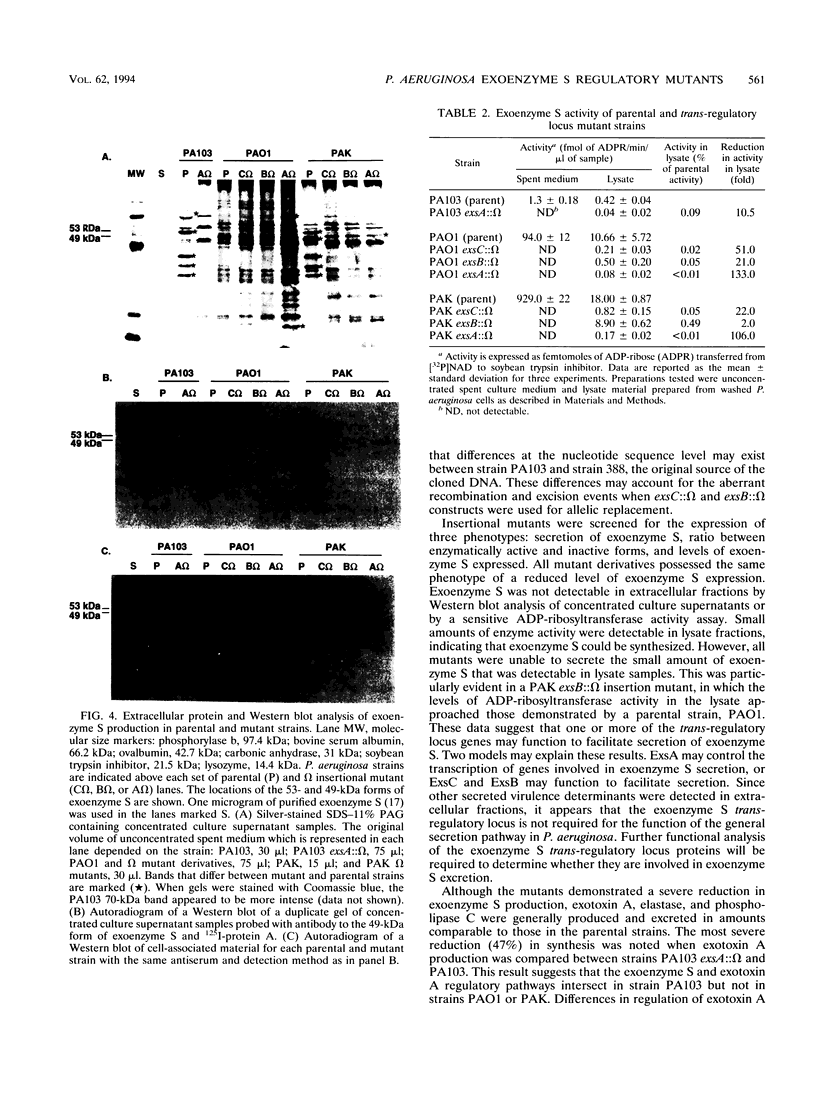
Exoenzyme S is an ADP-ribosyltransferase produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Synthesis of exoenzyme S depends on an intact trans-regulatory locus encoding three protein products, ExsC, ExsB, and ExsA. To identify the phenotype of ExsC, -B, and -A mutants in exoenzyme S production, specific insertional mutations with the streptomycin resistance-encoding omega interposon were introduced into cloned DNA and returned to the chromosomes of P. aeruginosa PA103, PAO1, and PAK. Southern blot analysis was used to confirm insertion of omega and resolution of vector sequences. Exoenzyme S expression was measured in parental and mutant derivatives by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis and ADP-ribosyltransferase activity measurement. A complete set of mutations were obtained in strains PAK and PAO1, but in strain PA103, only an insertion in the exsA coding region was identified. Southern blot analysis demonstrated that extensive duplication and rearrangement of the PA103 chromosomal trans-regulatory locus occurred when exsC::omega or exsB::omega recombination events were attempted. Exoenzyme S antigen was not detectable in the supernatant or lysate fractions of mutant strains by Western blot analysis. ADP-ribosyltransferase activity was detected in the lysate but not in the supernatant fractions of mutant derivatives. The general secretion pathway appeared to function normally in mutant strains, as elastase, exotoxin A, and phospholipase C were measured in the supernatants of parental and mutant strains. Several differences were noted when the extracellular protein profiles of parental strains were compared with similar samples from the insertional mutant strains. Some of these differences appeared to be unrelated to exoenzyme S. These data suggest that insertional inactivation of the exoenzyme S trans-regulatory locus may affect a subset of other extracellular proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorn M. J., Pavlovskis O. R., Thompson M. R., Iglewski B. H. Production of exoenzyme S during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections of burned mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):837–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.837-842.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Bolivar R., Fainstein V., Jadeja L. Infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):279–313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J., Dillon S. T., Iglewski B. H., Gill D. M. Exoenzyme S of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ADP-ribosylates the intermediate filament protein vimentin. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):996–998. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.996-998.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;175:133–143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76966-5_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J., Wyatt R. T., Iglewski B. H., Gill D. M. Several GTP-binding proteins, including p21c-H-ras, are preferred substrates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9004–9008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Sluiters C., de Rouvroit C. L., Michiels T. Homology between virF, the transcriptional activator of the Yersinia virulence regulon, and AraC, the Escherichia coli arabinose operon regulator. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.254-262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Cloning and sequence analysis of a trans-regulatory locus required for exoenzyme S synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6460–6468. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6460-6468.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Kinetics of toxA and regA mRNA accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4477–4483. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4477-4483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Storey D. G., Hindahl M. S., Iglewski B. H. Differential regulation by iron of regA and toxA transcript accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5304–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5304-5313.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambello M. J., Kaye S., Iglewski B. H. LasR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a transcriptional activator of the alkaline protease gene (apr) and an enhancer of exotoxin A expression. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1180-1184.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimwood K., To M., Rabin H. R., Woods D. E. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme expression by subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J., Bjorn M. J., Maxwell E. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S: an adenosine diphosphate ribosyltransferase distinct from toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3211–3215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulich S. M., Frank D. W., Barbieri J. T. Purification and characterization of exoenzyme S from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 388. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):307–313. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.307-313.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S. Determinants of extracellular protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3423–3428. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3423-3428.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S., Tai P. C. Characterization of the phospholipase C gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cloned in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Bradley J., Lochner J. E., Iglewski B. H. The role of exoenzyme S in infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):716–721. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. Contribution of exoenzyme S to the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:40–48. doi: 10.1159/000410470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of transposon-induced mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa deficient in production of exoenzyme S. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):470–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.470-474.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. The contribution of exoproducts to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Apr;31(4):387–392. doi: 10.1139/m85-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Cryz S. J., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):836–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.836-842.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff R. M., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Molecular comparison of a nonhemolytic and a hemolytic phospholipase C from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5915–5923. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5915-5923.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. W., Storey D. G., Vasil A. I., Vasil M. L. Regulation of toxA and regA by the Escherichia coli fur gene and identification of a Fur homologue in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103 and PA01. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2823–2831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer H. P. Allelic exchange in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using novel ColE1-type vectors and a family of cassettes containing a portable oriT and the counter-selectable Bacillus subtilis sacB marker. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1195–1204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Dennis J. J., MacDougall P. C., Sexton M., Woods D. E. Cloning and expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S toxin gene. Microb Pathog. 1990 Apr;8(4):243–257. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90051-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. G., Frank D. W., Farinha M. A., Kropinski A. M., Iglewski B. H. Multiple promoters control the regulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa regA gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):499–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. G., Raivio T. L., Frank D. W., Wick M. J., Kaye S., Iglewski B. H. Effect of regB on expression from the P1 and P2 promoters of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa regAB operon. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6088–6094. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6088-6094.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom M. S., Nunn D., Lory S. Multiple roles of the pilus biogenesis protein pilD: involvement of pilD in excretion of enzymes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1175–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1175-1180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. J., Frank D. W., Storey D. G., Iglewski B. H. Identification of regB, a gene required for optimal exotoxin A yields in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Que J. U. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):579–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.579-586.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]