Abstract
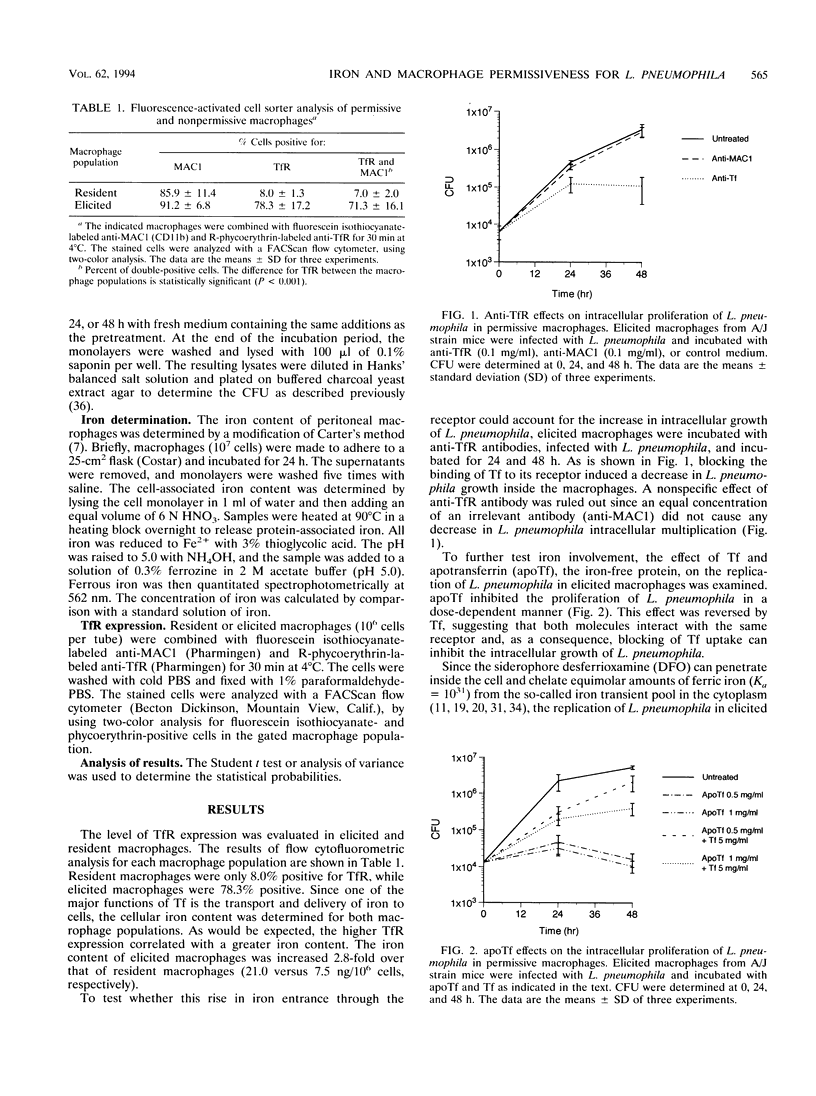
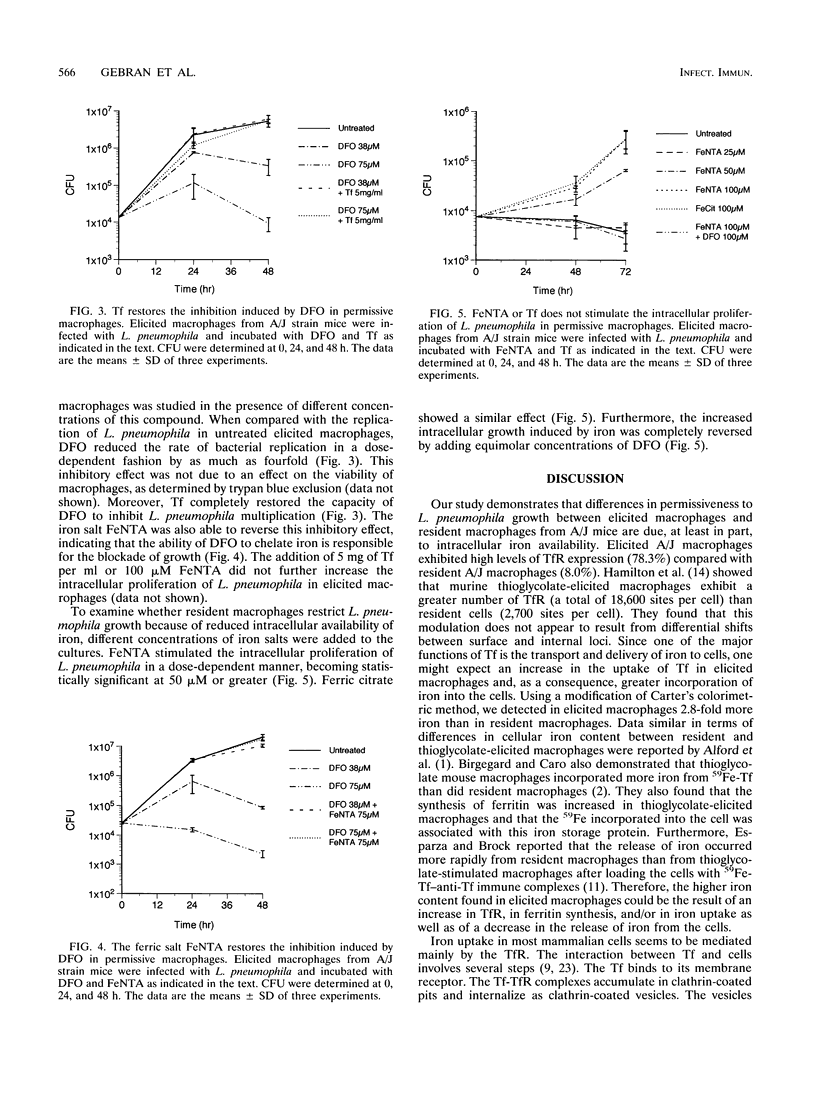
We have investigated the modulation of iron in two populations of macrophages which differ in susceptibility to Legionella pneumophila intracellular proliferation. Previously, we reported that thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages obtained from the inbred A/J mouse strain readily support the intracellular growth of L. pneumophila, while resident macrophages from the same strain do not. In this study, we show that A/J elicited macrophages exhibit markedly higher expression of transferrin receptor and intracellular iron content than A/J resident macrophages. Furthermore, apotransferrin and desferrioxamine inhibited the intracellular proliferation of L. pneumophila in elicited macrophages, and this suppression was reversed by the additions of Fe-transferrin or ferric nitrilotriacetate. Fe-transferrin and ferric nitrilotriacetate did not further increase the intracellular proliferation of L. pneumophila in thioglycolate-elicited macrophages. However, ferric citrate and ferric nitrilotriacetate stimulated in a dose-dependent manner the growth of L. pneumophila in resident macrophages. Furthermore, equimolar concentrations of desferrioxamine reversed the stimulatory effect of iron in these resident cells. These data provide evidence supporting the hypothesis that differences in susceptibility to L. pneumophila growth between permissive elicited macrophages and nonpermissive resident macrophages from the A/J mouse strain are due to intracellular availability of iron.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alford C. E., King T. E., Jr, Campbell P. A. Role of transferrin, transferrin receptors, and iron in macrophage listericidal activity. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):459–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgegård G., Caro J. Increased ferritin synthesis and iron uptake in inflammatory mouse macrophages. Scand J Haematol. 1984 Jul;33(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortner C. A., Miller R. D., Arnold R. R. Bactericidal effect of lactoferrin on Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):373–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.373-377.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd T. F., Horwitz M. A. Interferon gamma-activated human monocytes downregulate transferrin receptors and inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila by limiting the availability of iron. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1457–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI114038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd T. F., Horwitz M. A. Lactoferrin inhibits or promotes Legionella pneumophila intracellular multiplication in nonactivated and interferon gamma-activated human monocytes depending upon its degree of iron saturation. Iron-lactoferrin and nonphysiologic iron chelates reverse monocyte activation against Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1103–1112. doi: 10.1172/JCI115409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd T. F., Horwitz M. A. Regulation of transferrin receptor expression and ferritin content in human mononuclear phagocytes. Coordinate upregulation by iron transferrin and downregulation by interferon gamma. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):969–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI116318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. Spectrophotometric determination of serum iron at the submicrogram level with a new reagent (ferrozine). Anal Biochem. 1971 Apr;40(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Brock J. H. Release of iron by resident and stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages following ingestion and degradation of transferrin-antitransferrin immune complexes. Br J Haematol. 1981 Dec;49(4):603–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb07270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldoni P., Visca P., Pastoris M. C., Valenti P., Orsi N. Growth of Legionella spp. under conditions of iron restriction. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Feb;34(2):113–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-2-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Weiel J. E., Adams D. O. Expression of the transferrin receptor in murine peritoneal macrophages is modulated in the different stages of activation. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2285–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1618–1635. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Varner L., Poch M. Acquisition of iron by Legionella pneumophila: role of iron reductase. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2376–2381. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2376-2381.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T., Spencer R., Walsh C. Mechanism and kinetics of iron release from ferritin by dihydroflavins and dihydroflavin analogues. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4011–4017. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleber E. E., Torrance J. D., Bothwell T. H., Simon M. O., Charlton R. W. Mobilisation of iron from peritoneal rat macrophages by desferrioxamine. Scand J Haematol. 1981 Sep;27(3):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1981.tb00474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz D. A., Dugard J., Simon M. O., Bothwell T. H., Charlton R. W. The site of action of desferrioxamine. Br J Haematol. 1971 Apr;20(4):395–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. A., MacSween R. N., Pechet G. S. Iron metabolism by reticuloendothelial cells in vitro. Physical and chemical conditions, lipotrope deficiency, and acute inflammation. Lab Invest. 1969 Sep;21(3):236–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Núez M. T., Gaete V., Watkins J. A., Glass J. Mobilization of iron from endocytic vesicles. The effects of acidification and reduction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6688–6692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S., Aisen P., Lasky F. D., Vanderhoff G. Chelate mediated transfer of iron from transferrin to desferrioxamine. Br J Haematol. 1976 Oct;34(2):231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Hutner S. H., George J. R., Harrell W. K. Metal requirements of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.688-695.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Neilands J. B., Balows A. Absence of siderophore activity in Legionella species grown in iron-deficient media. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):324–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.324-329.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D., Baker E. The uptake of inorganic iron complexes by human melanoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 7;1093(1):20–28. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90133-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Gowda S. Chemically defined medium for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.115-119.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S., Bomford A. Chelation of transferrin iron by desferrioxamine in K562 cells. The partition of iron between ferrioxamine and ferritin. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):869–875. doi: 10.1042/bj2540869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock A., Alexander J., Lamb J., Craven C. M., Kaplan J. Characterization of a transferrin-independent uptake system for iron in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3139–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topham R., Goger M., Pearce K., Schultz P. The mobilization of ferritin iron by liver cytosol. A comparison of xanthine and NADH as reducing substrates. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):137–143. doi: 10.1042/bj2610137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. P., Jacobs A. Iron uptake by Chang cells from transferrin, nitriloacetate and citrate complexes: the effects of iron-loading and chelation with desferrioxamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 3;543(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Klein T. W., Newton C. A., Widen R., Friedman H. Differential growth of Legionella pneumophila in guinea pig versus mouse macrophage cultures. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1369–1374. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1369-1374.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Klein T. W., Newton C. A., Widen R., Friedman H. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages from A/J mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):370–375. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.370-375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Mizuguchi Y. Multiplication of Legionella pneumophila Philadelphia-1 in cultured peritoneal macrophages and its correlation to susceptibility of animals. Can J Microbiol. 1986 May;32(5):438–442. doi: 10.1139/m86-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



