Abstract
The present studies examined production of the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), and IL-6 by human monocyte-derived macrophages exposed to Pneumocystis carinii in vitro and the impact of concurrent macrophage infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) on these cytokine responses. Macrophages were infected with the HIV-1 BaL monocytotropic strain for 10 to 14 days and then exposed to P. carinii. At various times following P. carinii treatment, culture supernatants were harvested to assess the cytokine profile. Addition of P. carinii to HIV-uninfected macrophages resulted in augmented production of IL-6, TNF-alpha, and IL-1 beta protein. By contrast, in HIV-infected macrophages exposed to P. carinii, only the release of IL-6 was increased compared with that for HIV-uninfected macrophages, while the levels of TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta decreased. This altered response was confirmed at the molecular level for TNF-alpha mRNA. Preventing physical contact between P. carinii and macrophages by a membrane filter inhibited all cytokine release. Substituting P. carinii with a preparation of P. carinii 95- to 115-kDa major membrane glycoprotein A yielded a response similar to that obtained by addition of intact P. carinii. These results suggest that HIV-1 infection of human macrophages modulates cytokine responses to P. carinii.
Full text
PDF

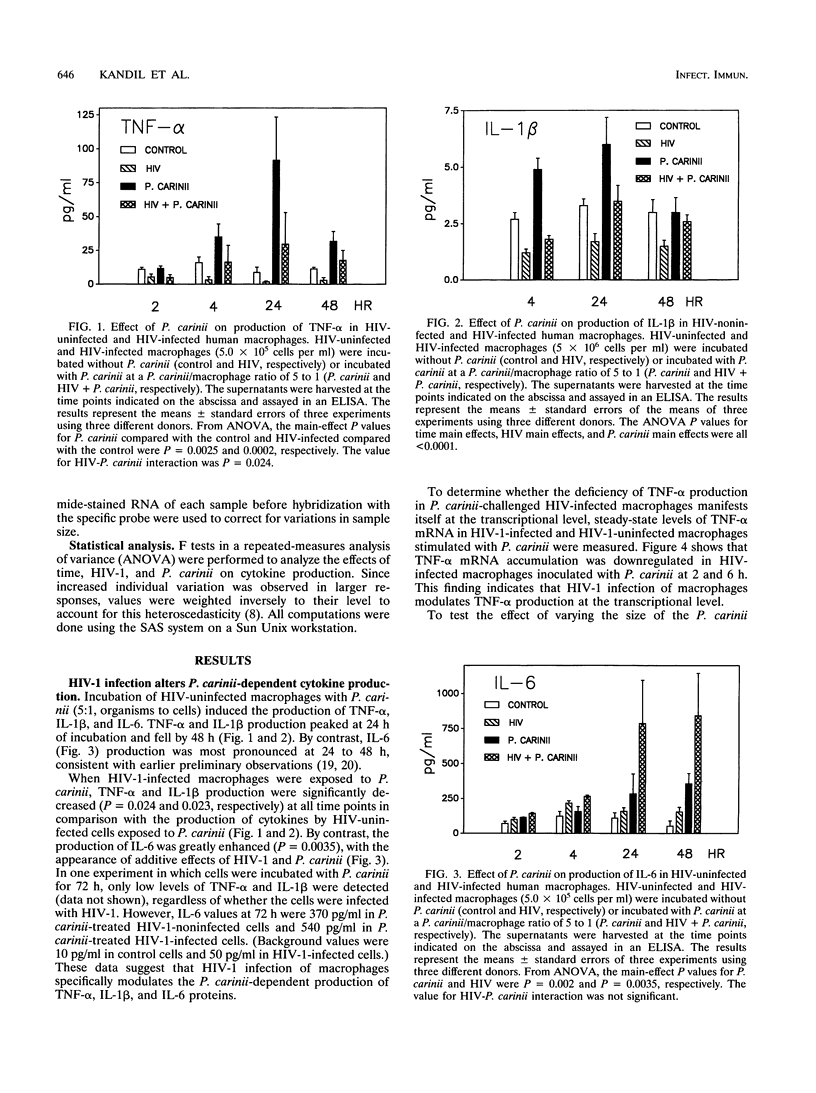
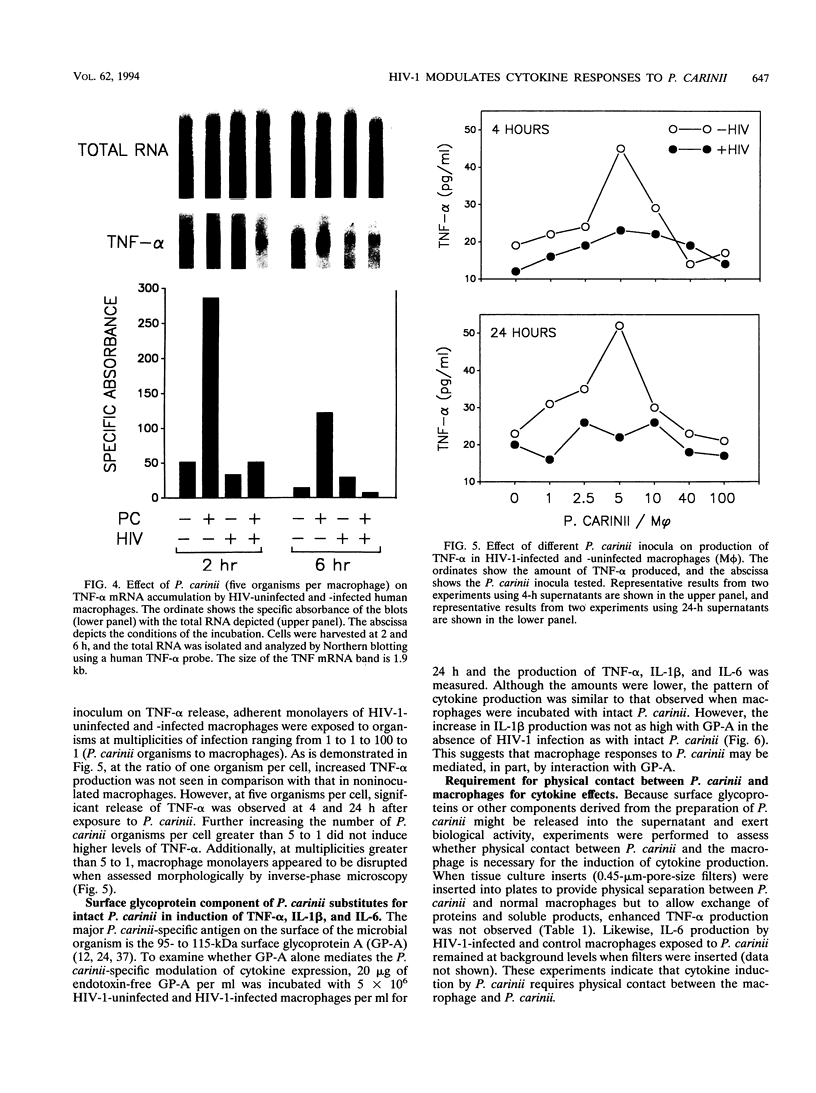
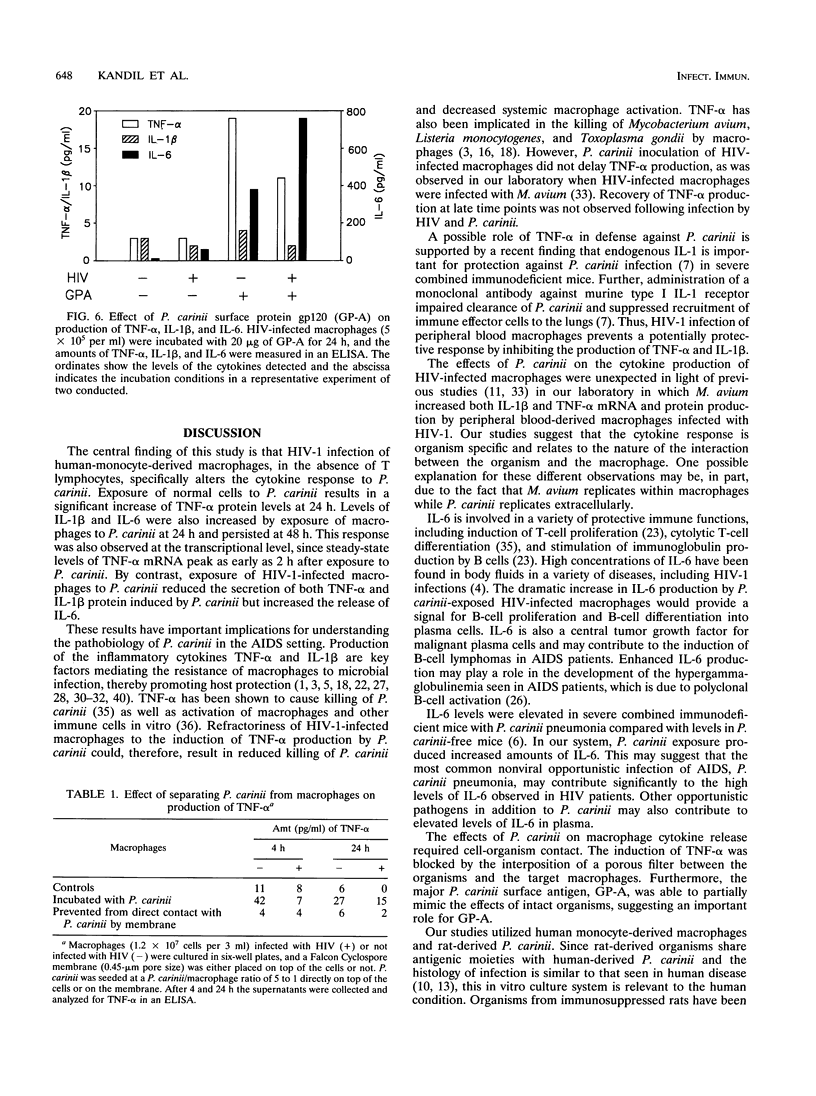


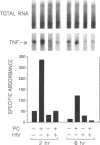
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiri P., Locksley R. M., Parslow T. G., Sadick M., Rector E., Ritter D., McKerrow J. H. Tumour necrosis factor alpha restores granulomas and induces parasite egg-laying in schistosome-infected SCID mice. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):604–607. doi: 10.1038/356604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. New rat model of Pneumocystis carinii infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1100-1102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen E. C., Rezai A. R., Nakajima K., Beall G. N., Mitsuyasu R. T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Martinez-Maza O. Infection with HIV is associated with elevated IL-6 levels and production. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):480–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. R., Grau G. E., Pechère J. C. Role of TNF and IL-1 in infections with Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):33–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Havell E. A., Gigliotti F., Harmsen A. G. Interleukin-6 production in a murine model of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: relation to resistance and inflammatory response. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.97-102.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Havell E. A., Moldawer L. L., McIntyre K. W., Chizzonite R. A., Harmsen A. G. Interleukin 1: an important mediator of host resistance against Pneumocystis carinii. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):713–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J. A., Strauss H. W., Fischman A. J., Nedelman M., Callahan R., Khaw B. A., Rubin R. H. Imaging of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with 111In-labelled non-specific polyclonal IgG: an experimental study in rats. Nucl Med Commun. 1991 Mar;12(3):175–187. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199103000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan H. X., Ruef C., Hall B. F., Tobin E., Remold H. G., Mellors J. W. Interleukin-6 expression in primary macrophages infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Aug;7(8):671–679. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F. Host species-specific antigenic variation of a mannosylated surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):329–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C. Immunological studies of Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1989 Jan-Feb;36(1):60–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb02700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler D. N., Deepe G. S., Pogue C. L., Walzer P. D. Blastogenic responses to Pneumocystis carinii among patients with human immunodeficiency (HIV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Oct;74(1):7–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen A. G., Stankiewicz M. Requirement for CD4+ cells in resistance to Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):937–945. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Evidence that tumor necrosis factor has an important role in antibacterial resistance. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. R., Pappas M. G., Hansen B. D. Fluorogenic substrate detection of viable intracellular and extracellular pathogenic protozoa. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):435–438. doi: 10.1126/science.2578226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. L. A protective role for endogenous tumor necrosis factor in Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1979–1983. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1979-1983.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Byrn R., Groopman J., Baltimore D. Temporal aspects of DNA and RNA synthesis during human immunodeficiency virus infection: evidence for differential gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3708–3713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3708-3713.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Taga T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):593–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1411569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koziel H., Williams D. J., Armstrong M. Y., Richards F. F., Fishman J. A., Ezekowitz R. A., Warner A., Fuglestad J., Rose R. M. New rapid method for the study of Pneumocystis carinii interaction with alveolar macrophages. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):173S–174S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan V. L., Meager A., Mitchell D. M., Pinching A. J. Alveolar macrophages in AIDS patients: increased spontaneous tumour necrosis factor-alpha production in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):156–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Immunologic abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:477–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastroeni P., Arena A., Costa G. B., Liberto M. C., Bonina L., Hormaeche C. E. Serum TNF alpha in mouse typhoid and enhancement of a Salmonella infection by anti-TNF alpha antibodies. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jul;11(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90091-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Jones T. C. The interaction in vitro of Pneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirovsky P., Fishman J. A. An improved method for the prolonged maintenance of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1470–1473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Numata A., Minagawa T. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, and gamma interferon levels during Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):523–528. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.523-528.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. W., Kelley T. G., Gan H., Kandil O., Newman M. J., Pinkston P., Rose R. M., Remold H. G. Concurrent infection of human macrophages with HIV-1 and Mycobacterium avium results in decreased cell viability, increased M. avium multiplication and altered cytokine production. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2261–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky T. J., Roslansky P. F., Siber G. R., Warren H. S. Turbidimetric method for quantifying serum inhibition of Limulus amoebocyte lysate. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):211–216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.211-216.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Kitahara M., Kishimoto S., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. IL-6/BSF-2 functions as a killer helper factor in the in vitro induction of cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1543–1549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L. Interaction of cytokines and alveolar cells with Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):611–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding J. A., Armstrong M. Y., Ullu E., Richards F. F. Identification and isolation of a major cell surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2149–2157. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2149-2157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan W. Inactivation of hepatitis viruses and HIV in plasma and plasma derivatives by treatment with beta-propiolactone/UV irradiation. Curr Stud Hematol Blood Transfus. 1989;(56):122–127. doi: 10.1159/000416562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Dougan G., Chatfield S. N. The involvement of tumor necrosis factor in immunity to Salmonella infection. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3161–3164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Behren L. A., Pesanti E. L. Uptake and degradation of Pneumocystis carinii by macrophages in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Dec;118(6):1051–1059. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to type I alveolar cells studied by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):812–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.812-815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]