Abstract
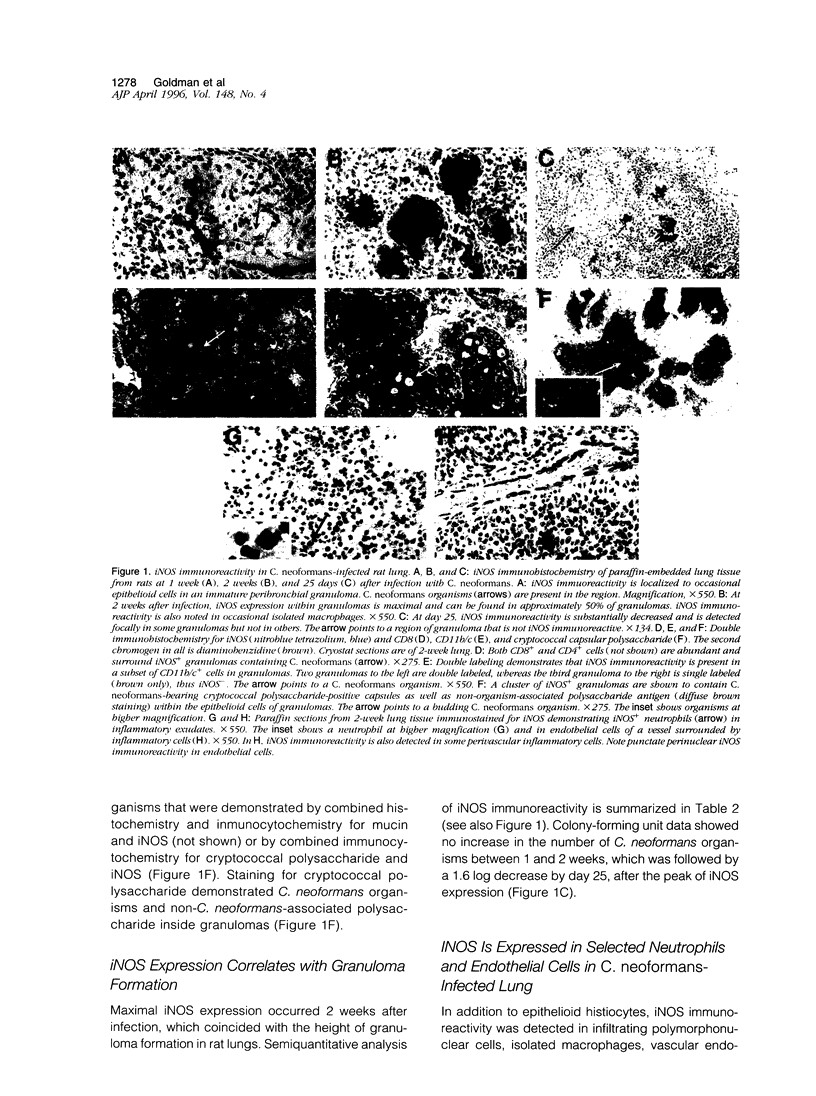
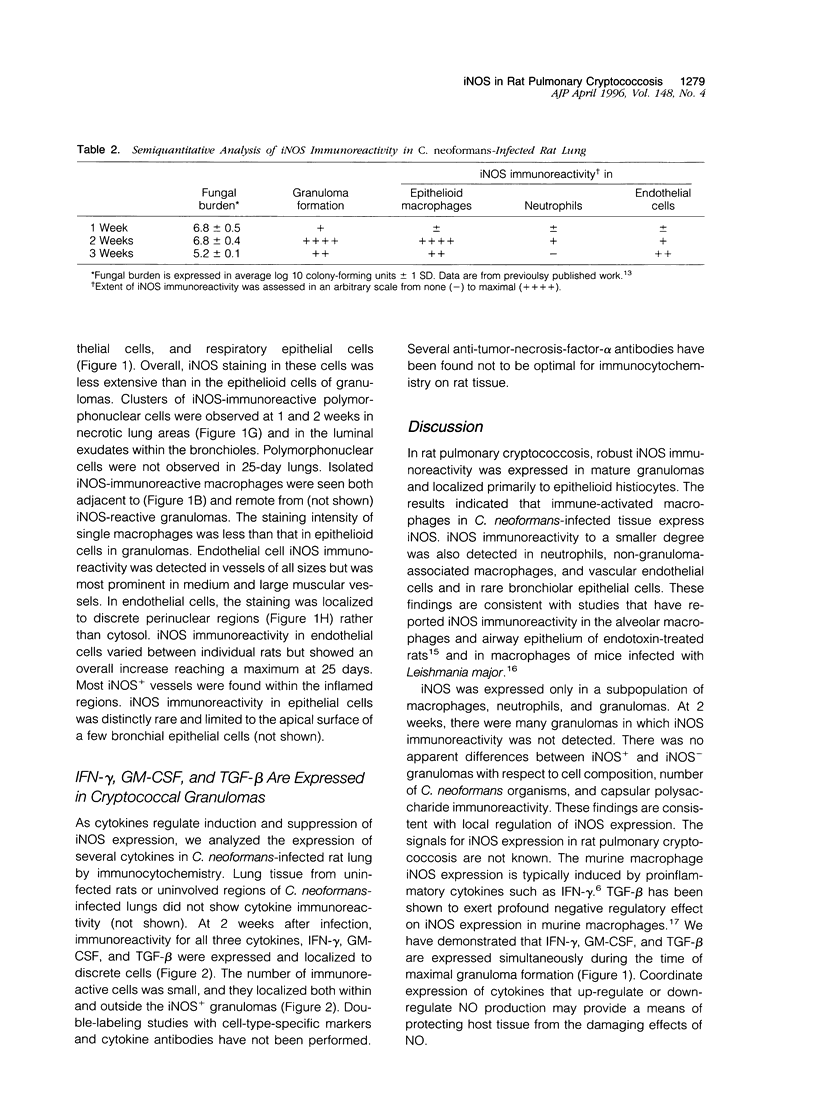
Rats, like humans, have extremely effective immune mechanisms for controlling pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection. The mechanism(s) responsible for efficient immunity in rat experimental infection is unknown. Recently, induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and nitric oxide (NO) have been implicated as an important microbicidal mechanism by which activated macrophages effect cytotoxicity against microbes. In this report, we investigated the expression of iNOS in rat pulmonary cryptococcosis. Localization and regulation of NO production was studied by immunohistochemistry for iNOS in conjunction with immunohistochemistry for cell markers, cytokines, and cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide. iNOS immunoreactivity was detected in macrophages, neutrophils, vascular endothelium, and respiratory epithelium. Double-immunolabeling studies revealed that the most prominent iNOS immunoreactivity was localized to epithelioid macrophages (CD11b/c+) within granulomas; CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were numerous around granulomas but did not express iNOS. iNOS immunoreactivity was detected in a selective population of epithelioid macrophages within some granulomas but not others. iNOS- granulomas were identical to iNOS+ granulomas with respect to morphology and immunohistochemical profiles. Macrophage iNOS immunoreactivity was detected 1 week after infection in one out of four rats and was strongly expressed in all rats at 2 weeks (in up to 50 percent of the granulomas) but declined considerably by 25 days. iNOS expression coincided with granuloma formation and preceded a decrease in lung fungal burden, suggesting an anticryptococcal role for NO. By double labeling, cytokines that have been shown to promote (interferon-gamma, granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor) and inhibit (transforming growth factor-beta) macrophage iNOS expression were detected around iNOS+ granuloma. iNOS immunoreactivity was expressed in selected neutrophils (1 and 2 weeks) and endothelial cells (1 and 2 weeks and 25 days) in the inflamed lung. Airway iNOS immunoreactivity was limited to the luminal border of rare bronchiolar epithelial cells. iNOS immunoreactivity was not detected in uninfected rats. The present study provides the first evidence for association of iNOS expression with protective cellular responses to cryptococcal infection in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albina J. E., Abate J. A., Henry W. L., Jr Nitric oxide production is required for murine resident peritoneal macrophages to suppress mitogen-stimulated T cell proliferation. Role of IFN-gamma in the induction of the nitric oxide-synthesizing pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):144–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alspaugh J. A., Granger D. L. Inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans replication by nitrogen oxides supports the role of these molecules as effectors of macrophage-mediated cytostasis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2291–2296. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2291-2296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi E., Barluzzi R., Mazzolla R., Tancini B., Saleppico S., Puliti M., Pitzurra L., Bistoni F. Role of nitric oxide and melanogenesis in the accomplishment of anticryptococcal activity by the BV-2 microglial cell line. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Apr;58(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(95)00016-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boockvar K. S., Granger D. L., Poston R. M., Maybodi M., Washington M. K., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Kurlander R. L. Nitric oxide produced during murine listeriosis is protective. Infect Immun. 1994 Mar;62(3):1089–1100. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.3.1089-1100.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttery L. D., Evans T. J., Springall D. R., Carpenter A., Cohen J., Polak J. M. Immunochemical localization of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin-treated rats. Lab Invest. 1994 Nov;71(5):755–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron M. L., Granger D. L., Weinberg J. B., Kozumbo W. J., Koren H. S. Human alveolar and peritoneal macrophages mediate fungistasis independently of L-arginine oxidation to nitrite or nitrate. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1313–1319. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Xing Y., Magliozzo R. S., Bloom B. R. Killing of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis by reactive nitrogen intermediates produced by activated murine macrophages. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1111–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas E. C., Bateman A. C., Wilkins B. S., Johnson P. A., Williams J. H., Lee A. H., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Microwave antigen retrieval in immunocytochemistry: a study of 80 antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;47(5):448–452. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Human monocytes/macrophages: NO or no NO? J Leukoc Biol. 1994 May;55(5):682–684. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Lee S. C., Casadevall A. Pathogenesis of pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection in the rat. Infect Immun. 1994 Nov;62(11):4755–4761. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.11.4755-4761.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Scheller L. F., Marletta M. A., Seguin M. C., Klotz F. W., Slayter M., Nelson B. J., Nacy C. A. Nitric oxide: cytokine-regulation of nitric oxide in host resistance to intracellular pathogens. Immunol Lett. 1994 Dec;43(1-2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)00158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. O., Harmsen A. G. Intrapulmonary growth and dissemination of an avirulent strain of Cryptococcus neoformans in mice depleted of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):755–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffnagle G. B., Yates J. L., Lipscomb M. F. Immunity to a pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection requires both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):793–800. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Dickson D. W., Brosnan C. F., Casadevall A. Human astrocytes inhibit Cryptococcus neoformans growth by a nitric oxide-mediated mechanism. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):365–369. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovchik J. A., Lyons C. R., Lipscomb M. F. A role for gamma interferon-induced nitric oxide in pulmonary clearance of Cryptococcus neoformans. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995 Jul;13(1):116–124. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.13.1.7598935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMicking J. D., Nathan C., Hom G., Chartrain N., Fletcher D. S., Trumbauer M., Stevens K., Xie Q. W., Sokol K., Hutchinson N. Altered responses to bacterial infection and endotoxic shock in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):641–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. D. Molecular basis of "suppressor" macrophages. Arginine metabolism via the nitric oxide synthetase pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2719–2723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian N., Berman J. W., Casadevall A. Immune complexes increase nitric oxide production by interferon-gamma- stimulated murine macrophage-like J774.16 cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Apr;57(4):657–662. doi: 10.1002/jlb.57.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee J., Casadevall A., Scharff M. D. Molecular characterization of the humoral responses to Cryptococcus neoformans infection and glucuronoxylomannan-tetanus toxoid conjugate immunization. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1105–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naslund P. K., Miller W. C., Granger D. L. Cryptococcus neoformans fails to induce nitric oxide synthase in primed murine macrophage-like cells. Infect Immun. 1995 Apr;63(4):1298–1304. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.4.1298-1304.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seguin M. C., Klotz F. W., Schneider I., Weir J. P., Goodbary M., Slayter M., Raney J. J., Aniagolu J. U., Green S. J. Induction of nitric oxide synthase protects against malaria in mice exposed to irradiated Plasmodium berghei infected mosquitoes: involvement of interferon gamma and CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):353–358. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger S., Thüring H., Röllinghoff M., Bogdan C. Tissue expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase is closely associated with resistance to Leishmania major. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):783–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodovotz Y., Bogdan C., Paik J., Xie Q. W., Nathan C. Mechanisms of suppression of macrophage nitric oxide release by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):605–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuger A., Louie E., Holzman R. S., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J. Cryptococcal disease in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Diagnostic features and outcome of treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Feb;104(2):234–240. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-2-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]