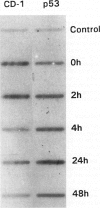
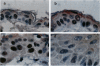
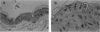
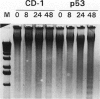
Abstract
p53 tumor suppressor plays a vital role in the cellular responses to genotoxic stress. It is believed that p53 regulates the cell cycle by activating the G1 checkpoint after exposure to agents like ionizing radiation, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, or genotoxic chemicals. Recently, it is conjectured that p53 may have additional functions in DNA repair and apoptosis. Previously, we demonstrated that p53-transgenic mice that carry mutant alleles of a p53 gene developed twice as many skin tumors as control mice after UV exposure. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutant p53 in skin cancers, we studied DNA repair efficiency and the rate of apoptosis in murine keratinocytes after UV irradiation. In this report, we show that mutant p53-transgenic mouse skin has reduced repair of UV-induced DNA damage in both in vivo and in vitro radioimmunoassays. In control mice, DNA repair is associated with increased amounts of wild-type P53 protein. Unexpectedly, mutant p53-transgenic mice had slightly increased apoptosis after UV irradiation, suggesting that the wild-type p53 protein in the cells still functions in inducing apoptosis, or that this cell death results from p53-independent mechanisms. These results suggest that mutant p53 interferes with wild-type p53 in the repair of UV-induced DNA damage but not in apoptosis.
Full text
PDF



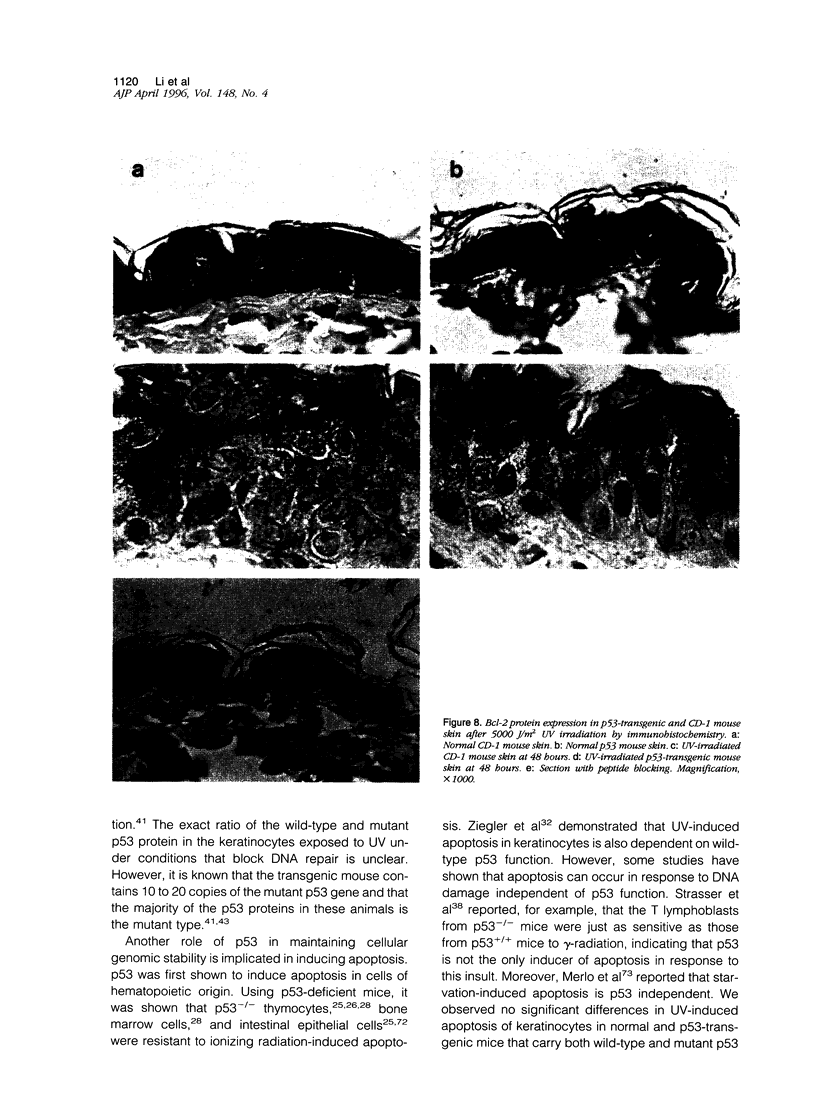



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borner M. M., Myers C. E., Sartor O., Sei Y., Toko T., Trepel J. B., Schneider E. Drug-induced apoptosis is not necessarily dependent on macromolecular synthesis or proliferation in the p53-negative human prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Cancer Res. 1995 May 15;55(10):2122–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Rudolph J. A., Simon J. A., Lin A., McKenna G. J., Baden H. P., Halperin A. J., Pontén J. A role for sunlight in skin cancer: UV-induced p53 mutations in squamous cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10124–10128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. E., Baird M. C., Clark L. J., Burns P. A., Edington K., Chapman C., Mitchell R., Robertson G., Soutar D., Parkinson E. K. Gene mutations and increased levels of p53 protein in human squamous cell carcinomas and their cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1993 Jun;67(6):1274–1284. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelles C., Helmberg A., Karin M. p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of transcriptional activation of p53-target genes. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):220–223. doi: 10.1038/370220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey G., Lo-Hsueh M., Lopez M. E., Vogelstein B., Stanbridge E. J. Growth suppression of human breast cancer cells by the introduction of a wild-type p53 gene. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1791–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou S. K., Rao L., White E. Bcl-2 blocks p53-dependent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2556–2563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillardon F., Eschenfelder C., Uhlmann E., Hartschuh W., Zimmermann M. Differential regulation of c-fos, fosB, c-jun, junB, bcl-2 and bax expression in rat skin following single or chronic ultraviolet irradiation and in vivo modulation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotide superfusion. Oncogene. 1994 Nov;9(11):3219–3225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb E., Haffner R., von Rüden T., Wagner E. F., Oren M. Down-regulation of wild-type p53 activity interferes with apoptosis of IL-3-dependent hematopoietic cells following IL-3 withdrawal. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1368–1374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gujuluva C. N., Baek J. H., Shin K. H., Cherrick H. M., Park N. H. Effect of UV-irradiation on cell cycle, viability and the expression of p53, gadd153 and gadd45 genes in normal and HPV-immortalized human oral keratinocytes. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):1819–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner R., Oren M. Biochemical properties and biological effects of p53. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Feb;5(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(95)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar S., Negrini M., Monne M., Sabbioni S., Croce C. M. Down-regulation of bcl-2 by p53 in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2095–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Different tumor-derived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological activities. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):113–116. doi: 10.1126/science.2218501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., McKee P. H., Menage H. D., Dover R., Lane D. P. High levels of p53 protein in UV-irradiated normal human skin. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
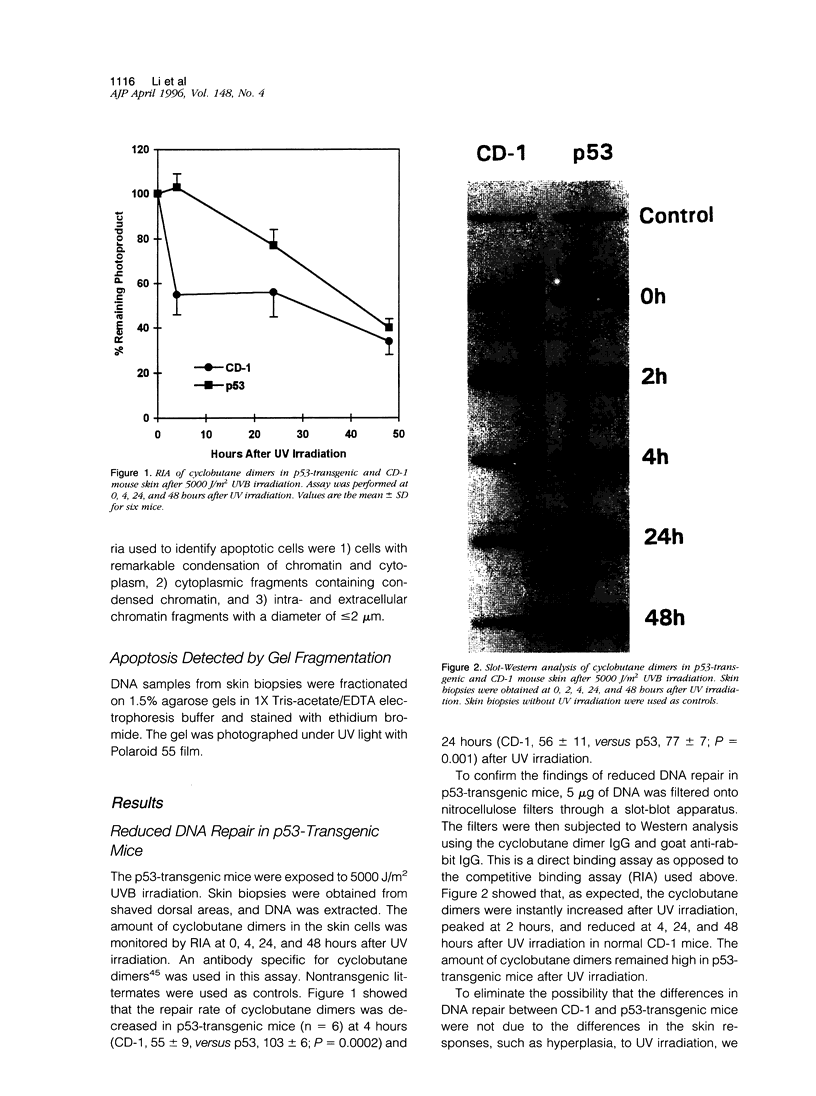
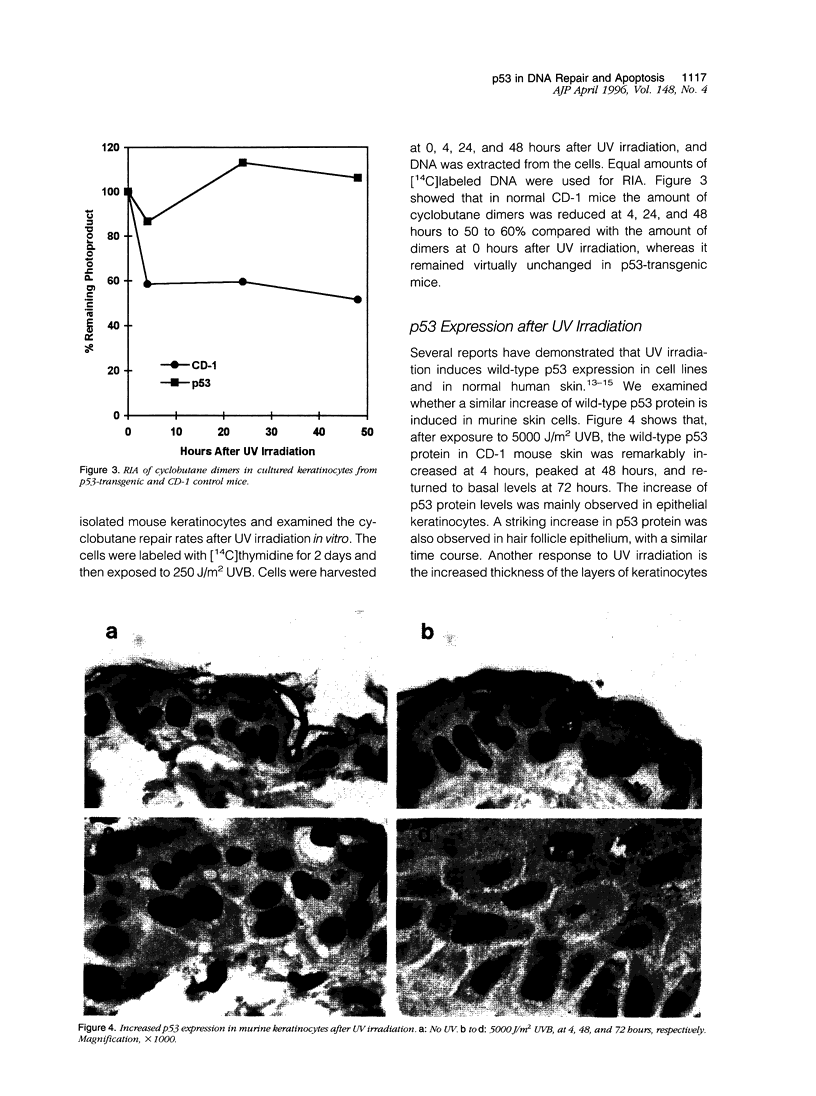
- Ishizaki K., Ejima Y., Matsunaga T., Hara R., Sakamoto A., Ikenaga M., Ikawa Y., Aizawa S. Increased UV-induced SCEs but normal repair of DNA damage in p53-deficient mouse cells. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jul 15;58(2):254–257. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman J., Prives C. Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by short single strands of DNA requires the p53 C-terminus. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessis T. D., Slebos R. J., Nelson W. G., Kastan M. B., Plunkett B. S., Han S. M., Lorincz A. T., Hedrick L., Cho K. R. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 expression disrupts the p53-mediated cellular response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Bodrug S., Gascoyne R., Berean K., Krajewska M., Reed J. C. Immunohistochemical analysis of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 proteins in normal and neoplastic lymph nodes. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):515–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress S., Sutter C., Strickland P. T., Mukhtar H., Schweizer J., Schwarz M. Carcinogen-specific mutational pattern in the p53 gene in ultraviolet B radiation-induced squamous cell carcinomas of mouse skin. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6400–6403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Lu X., Hupp T., Hall P. A. The role of the p53 protein in the apoptotic response. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 Aug 30;345(1313):277–280. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., Maltby V., Mock D., Rossant J., Pawson T., Bernstein A. High incidence of lung, bone, and lymphoid tumors in transgenic mice overexpressing mutant alleles of the p53 oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3982–3991. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Abrahamson J. L., Bernstein A. DNA damage, oncogenesis and the p53 tumour-suppressor gene. Mutat Res. 1994 Jun 1;307(2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Bernstein A. p53 mutations increase resistance to ionizing radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5742–5746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Elenbaas B., Levine A., Griffith J. p53 and its 14 kDa C-terminal domain recognize primary DNA damage in the form of insertion/deletion mismatches. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1013–1020. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Ho V. C., Berean K., Tron V. A. Ultraviolet radiation induction of squamous cell carcinomas in p53 transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1995 May 15;55(10):2070–2074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipponen P. K., Aaltomaa S. Apoptosis in bladder cancer as related to standard prognostic factors and prognosis. J Pathol. 1994 Aug;173(4):333–339. doi: 10.1002/path.1711730408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Hematopoietic cells from mice deficient in wild-type p53 are more resistant to induction of apoptosis by some agents. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Lane D. P. Differential induction of transcriptionally active p53 following UV or ionizing radiation: defects in chromosome instability syndromes? Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):765–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90496-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlo G. R., Basolo F., Fiore L., Duboc L., Hynes N. E. p53-dependent and p53-independent activation of apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells reveals a survival function of EGF and insulin. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1185–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt A. J., Potten C. S., Kemp C. J., Hickman J. A., Balmain A., Lane D. P., Hall P. A. The role of p53 in spontaneous and radiation-induced apoptosis in the gastrointestinal tract of normal and p53-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):614–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Clarkson J. M., Chao C. C., Rosenstein B. S. Repair of cyclobutane dimers and (6-4) photoproducts in ICR 2A frog cells. Photochem Photobiol. 1986 May;43(5):595–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1986.tb09539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Cleaver J. E., Epstein J. H. Repair of pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts in mouse skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jul;95(1):55–59. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12873312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Humphrey R. M., Adair G. M., Thompson L. H., Clarkson J. M. Repair of (6-4)photoproducts correlates with split-dose recovery in UV-irradiated normal and hypersensitive rodent cells. Mutat Res. 1988 Jan;193(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Rosenstein B. S. The use of specific radioimmunoassay to determine action spectra for the photolysis of (6-4) photoproducts. Photochem Photobiol. 1987 Jun;45(6):781–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1987.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Vaughan J. E., Nairn R. S. Inhibition of transient gene expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells by cyclobutane dimers and (6-4) photoproducts in transfected ultraviolet-irradiated plasmid DNA. Plasmid. 1989 Jan;21(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Wang H. G., Lin H. K., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat M., Cheng A., Kimura N., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Rearrangements of the cellular p53 gene in erythroleukaemic cells transformed by Friend virus. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):633–636. doi: 10.1038/314633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. Relationship of p53 to the control of apoptotic cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Jun;5(3):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. p53: the ultimate tumor suppressor gene? FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3169–3176. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Morrison H., Jones M., Gatter K. C., Lane D., Harris A. L., Mason D. Y. Immunohistochemical detection of p53 and bcl-2 proteins in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology. 1993 Jan;22(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1993.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rady P., Scinicariello F., Wagner R. F., Jr, Tyring S. K. p53 mutations in basal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3804–3806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumaran M., Lin H. K., Miyashita T., Wang H. G., Krajewski S., Reed J. C., Hoffman B., Liebermann D. Immediate early up-regulation of bax expression by p53 but not TGF beta 1: a paradigm for distinct apoptotic pathways. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1791–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivji K. K., Kenny M. K., Wood R. D. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for DNA excision repair. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90416-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Chen I. T., Zhan Q., Bae I., Chen C. Y., Gilmer T. M., Kastan M. B., O'Connor P. M., Fornace A. J., Jr Interaction of the p53-regulated protein Gadd45 with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1376–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.7973727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Chen I. T., Zhan Q., O'Connor P. M., Fornace A. J., Jr Involvement of the p53 tumor suppressor in repair of u.v.-type DNA damage. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 16;10(6):1053–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Jacks T., Cory S. DNA damage can induce apoptosis in proliferating lymphoid cells via p53-independent mechanisms inhibitable by Bcl-2. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Dong Z., Nakamura K., Colburn N. H. Dosage-dependent dominance over wild-type p53 of a mutant p53 isolated from nasopharyngeal carcinoma. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):944–950. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds H., Krall L., Remington L., Saenz-Robles M., Lowe S., Jacks T., Van Dyke T. p53-dependent apoptosis suppresses tumor growth and progression in vivo. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Carbone D., Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Hida T., Linnoila I., Ueda R., Minna J. D. Wild-type but not mutant p53 suppresses the growth of human lung cancer cells bearing multiple genetic lesions. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 15;52(8):2340–2343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):574–578. doi: 10.1038/369574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. W., Forrester K., Yeh H., Feitelson M. A., Gu J. R., Harris C. C. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits p53 sequence-specific DNA binding, transcriptional activity, and association with transcription factor ERCC3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. W., Yeh H., Schaeffer L., Roy R., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Wang Z., Freidberg E. C., Evans M. K., Taffe B. G. p53 modulation of TFIIH-associated nucleotide excision repair activity. Nat Genet. 1995 Jun;10(2):188–195. doi: 10.1038/ng0695-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Szekely L., Okan I., Klein G., Wiman K. G. Wild-type p53-triggered apoptosis is inhibited by bcl-2 in a v-myc-induced T-cell lymphoma line. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3427–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. S., Tron V. A. Analysis of HMB-45 immunoreactivity in common and cellular blue nevi. J Cutan Pathol. 1991 Aug;18(4):261–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1991.tb01233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Carrier F., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction of cellular p53 activity by DNA-damaging agents and growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4242–4250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Fan S., Bae I., Guillouf C., Liebermann D. A., O'Connor P. M., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction of bax by genotoxic stress in human cells correlates with normal p53 status and apoptosis. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3743–3751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Lord K. A., Alamo I., Jr, Hollander M. C., Carrier F., Ron D., Kohn K. W., Hoffman B., Liebermann D. A., Fornace A. J., Jr The gadd and MyD genes define a novel set of mammalian genes encoding acidic proteins that synergistically suppress cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2361–2371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y. M., Bradbury D. A., Russell N. H. Wild-type p53 is required for apoptosis induced by growth factor deprivation in factor-dependent leukaemic cells. Br J Cancer. 1994 Mar;69(3):468–472. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A., Jonason A. S., Leffell D. J., Simon J. A., Sharma H. W., Kimmelman J., Remington L., Jacks T., Brash D. E. Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):773–776. doi: 10.1038/372773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]