Abstract
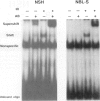
Mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene are rarely found in neuroblastoma. Though typically a nuclear protein, a number of tumor cell types have recently been reported to exhibit cytoplasmic p53 immunostaining, and it has been suggested that altered cellular localization is another mechanism of inhibiting p53 function. We examined p53 protein expression, localization, and function in neuroblastoma cell lines with wild-type p53 genes. Basal p53 levels were largely confined to the cytoplasmic compartment in these cells. However, after irradiation, p53 protein levels increased predominately in the nucleus. Transcriptional activity of p53 was intact in these cells because "downstream" proteins, p21WAF1 and MDM2, were induced by irradiation. In contrast to a neuroblastoma cell line harboring a mutant p53 gene, the neuroblastoma cells with wild-type protein were associated with an intact G1 arrest after DNA damage. The induced nuclear protein in these neuroblastoma cells also appeared functional as measured by its capacity to bind to a DNA oligomer containing a p53-consensus sequence. We have concluded that although p53 expression in neuroblastoma cells is primarily localized to the cytosol, ionizing radiation induces a functional p53 protein in the nucleus and that this cytoplasmic sequestration of p53 in human neuroblastoma is not a mechanism of inactivating p53 function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canman C. E., Wolff A. C., Chen C. Y., Fornace A. J., Jr, Kastan M. B. The p53-dependent G1 cell cycle checkpoint pathway and ataxia-telangiectasia. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 1;54(19):5054–5058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castresana J. S., Bello M. J., Rey J. A., Nebreda P., Queizán A., García-Miguel P., Pestaña A. No TP53 mutations in neuroblastomas detected by PCR-SSCP analysis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1994 Jun;10(2):136–138. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870100209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. W., Buchan H. L., Civin C. I., Kastan M. B. Altered cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution of the c-myc protein in differentiating ML-1 human myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 May;4(5):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi G., Hara J., Okamura T., Osugi Y., Ishihara S., Fukuzawa M., Okada A., Okada S., Tawa A. Low frequency of the p53 gene mutations in neuroblastoma. Cancer. 1994 Jun 15;73(12):3087–3093. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940615)73:12<3087::aid-cncr2820731230>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Canman C. E., Leonard C. J. P53, cell cycle control and apoptosis: implications for cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995 Mar;14(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00690207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Radin A. I., Kuerbitz S. J., Onyekwere O., Wolkow C. A., Civin C. I., Stone K. D., Woo T., Ravindranath Y., Craig R. W. Levels of p53 protein increase with maturation in human hematopoietic cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 15;51(16):4279–4286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro H., Hayashi Y., Kawamura M., Hayashi K., Kaneko Y., Kamoshita S., Hanada R., Yamamoto K., Hongo T., Yamada M. Mutations of the p53 gene are involved in Ewing's sarcomas but not in neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5284–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll U. M., LaQuaglia M., Bénard J., Riou G. Wild-type p53 protein undergoes cytoplasmic sequestration in undifferentiated neuroblastomas but not in differentiated tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4407–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll U. M., Riou G., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms alter p53 in breast cancer: mutation and nuclear exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7262–7266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Beach D. Cyclin G is a transcriptional target of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4816–4822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds H., Krall L., Remington L., Saenz-Robles M., Lowe S., Jacks T., Van Dyke T. p53-dependent apoptosis suppresses tumor growth and progression in vivo. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogan K., Bernstein M., Leclerc J. M., Brisson L., Brossard J., Brodeur G. M., Pelletier J., Gros P. Absence of p53 gene mutations in primary neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5269–5273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]