Abstract
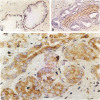
The clinical course of prostate cancer is highly variable and cannot satisfactorily be predicted by histological criteria alone. To study the prognostic significance of Bcl-2 and p53 overexpression in prostate cancer, 137 consecutive radical prostatectomy specimens were examined by immunohistochemistry. Both Bcl-2 and p53 were associated with malignant phenotype. Bcl-2 expression was more frequent in pT3 tumors (31% positive) than in pT2 tumors (5% positive, P = 0.001). p53 overexpression (found in 8%) was associated with high Gleason score (P = 0.03) and increased tumor growth fraction (Ki67 labeling index (LI); P = 0.017). Survival analysis showed that Bcl-2 expression (P = 0.03), high Ki67 LI (P = 0.018), high grade (P = 0.0037), advanced local stage (P = 0.0005), and positive lymph nodes (P = 0.026) were predictors of progression. The combined analysis of Ki67 LI and Bcl-2 allowed the distinction of three groups with different clinical outcome. Prognosis was best in Bcl-2-negative tumors with low Ki67 LI, worst in Bcl-2-positive tumors with high Ki67 LI, and intermediate in the remaining tumors (P = 0.03). These data suggest that altered expression of both Bcl-2 and p53 play a role in prostate cancer progression. Combined analysis of factors regulating both apoptosis and cell proliferation may be relevant in prostate cancer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aprikian A. G., Sarkis A. S., Fair W. R., Zhang Z. F., Fuks Z., Cordon-Cardo C. Immunohistochemical determination of p53 protein nuclear accumulation in prostatic adenocarcinoma. J Urol. 1994 May;151(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J. J., Sesterhenn I. A., Mostofi K. F., McLeod D. G., Srivastava S., Moul J. W. p53 nuclear protein expression is an independent prognostic marker in clinically localized prostate cancer patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Nov;1(11):1295–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava V., Kell D. L., van de Rijn M., Warnke R. A. Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinoma correlates with hormone receptor positivity. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):535–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boise L. H., González-García M., Postema C. E., Ding L., Lindsten T., Turka L. A., Mao X., Nuñez G., Thompson C. B. bcl-x, a bcl-2-related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90508-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., MacGrogan D., Hilsenbeck S. G., Sharkey F., Allred D. C. p53 is mutated in a subset of advanced-stage prostate cancers. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 15;53(14):3369–3373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosari S., Moneghini L., Graziani D., Lee A. K., Murray J. J., Coggi G., Viale G. bcl-2 oncoprotein in colorectal hyperplastic polyps, adenomas, and adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 1995 May;26(5):534–540. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner M. P., Culin C., Reed J. C., Furth E. E. The bcl-2 proto-oncogene and the gastrointestinal epithelial tumor progression model. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jan;146(1):20–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle V. P., Heidelberger K. P., Bromberg J., Ou X., Dole M., Nuñez G. Expression of the apoptosis-suppressing protein bcl-2, in neuroblastoma is associated with unfavorable histology and N-myc amplification. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1543–1550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D., el-Naggar A. K., Brisbay S., Redline R. W., McDonnell T. J. Apoptosis and expression of the bcl-2 proto-oncogene in the fetal and adult human kidney: evidence for the contribution of bcl-2 expression to renal carcinogenesis. Hum Pathol. 1994 Aug;25(8):789–796. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombel M., Symmans F., Gil S., O'Toole K. M., Chopin D., Benson M., Olsson C. A., Korsmeyer S., Buttyan R. Detection of the apoptosis-suppressing oncoprotein bc1-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):390–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalquen P., Sauter G., Torhorst J., Schultheiss E., Jordan P., Lehmann S., Solèr M., Stulz P., Mihatsch M. J., Gudat F. Nuclear p53 overexpression is an independent prognostic parameter in node-negative non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Pathol. 1996 Jan;178(1):53–58. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199601)178:1<53::AID-PATH415>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. I., Pizov G., Walsh P. C. Correlation of pathologic findings with progression after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Cancer. 1993 Jun 1;71(11):3582–3593. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930601)71:11<3582::aid-cncr2820711120>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esrig D., Elmajian D., Groshen S., Freeman J. A., Stein J. P., Chen S. C., Nichols P. W., Skinner D. G., Jones P. A., Cote R. J. Accumulation of nuclear p53 and tumor progression in bladder cancer. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 10;331(19):1259–1264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411103311903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G., Barbareschi M., Doglioni C., Palma P. D., Mauri F. A., Boracchi P., Bevilacqua P., Caffo O., Morelli L., Verderio P. Expression of bcl-2 protein predicts efficacy of adjuvant treatments in operable node-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Feb;1(2):189–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Glynne-Jones E., Goddard L., Wilson D. W., Matenhelia S. S., Conn I. G., Peeling W. B., Griffiths K. Relationship of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in prostatic carcinomas to various clinical parameters. Prostate. 1992;20(3):243–253. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990200309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. A., Walther P. J. Adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Part II: Tissue prognosticators. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993 Sep;100(3):256–269. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/100.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joensuu H., Pylkkänen L., Toikkanen S. Bcl-2 protein expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1994 Nov;145(5):1191–1198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallakury B. V., Figge J., Ross J. S., Fisher H. A., Figge H. L., Jennings T. A. Association of p53 immunoreactivity with high gleason tumor grade in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1994 Jan;25(1):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Winterford C. M., Harmon B. V. Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer. 1994 Apr 15;73(8):2013–2026. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940415)73:8<2013::aid-cncr2820730802>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange P. H., Ercole C. J., Lightner D. J., Fraley E. E., Vessella R. The value of serum prostate specific antigen determinations before and after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 1989 Apr;141(4):873–879. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)41037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Yoon A., Kalapurakal S. K., Ro J. Y., Lee J. J., Tu N., Hittelman W. N., Hong W. K. Expression of p53 oncoprotein in non-small-cell lung cancer: a favorable prognostic factor. J Clin Oncol. 1995 Aug;13(8):1893–1903. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.8.1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone L. R., White A., Sprouse J., Livanos E., Jacks T., Tlsty T. D. Altered cell cycle arrest and gene amplification potential accompany loss of wild-type p53. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):923–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapara M. Y., Bargou R., Zugck C., Döhner H., Ustaoglu F., Jonker R. R., Krammer P. H., Dörken B. APO-1 mediated apoptosis or proliferation in human chronic B lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with bcl-2 oncogene expression. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(3):702–708. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell T. J., Troncoso P., Brisbay S. M., Logothetis C., Chung L. W., Hsieh J. T., Tu S. M., Campbell M. L. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6940–6944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Wang H. G., Lin H. K., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moch H., Sauter G., Mihatsch M. J., Gudat F., Epper R., Waldman F. M. p53 but not erbB-2 expression is associated with rapid tumor proliferation in urinary bladder cancer. Hum Pathol. 1994 Dec;25(12):1346–1351. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir C. S., Nectoux J., Staszewski J. The epidemiology of prostatic cancer. Geographical distribution and time-trends. Acta Oncol. 1991;30(2):133–140. doi: 10.3109/02841869109092336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. B., Oelschlager D., Srivastava S., Grizzle W. E. Accumulation of the p53 protein occurs more frequently in metastatic than in localized prostatic adenocarcinomas. Prostate. 1994 Nov;25(5):243–248. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990250504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone N. M., Troncoso P., Pisters L. L., Goodrow T. L., Palmer J. L., Nichols W. W., von Eschenbach A. C., Conti C. J. p53 protein accumulation and gene mutation in the progression of human prostate carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Oct 20;85(20):1657–1669. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.20.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohori M., Wheeler T. M., Scardino P. T. The New American Joint Committee on Cancer and International Union Against Cancer TNM classification of prostate cancer. Clinicopathologic correlations. Cancer. 1994 Jul 1;74(1):104–114. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940701)74:1<104::aid-cncr2820740119>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltvai Z. N., Milliman C. L., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Radinsky R., Kruzel E., Berry K., Yonehara S. Anti-Fas on nonhematopoietic tumors: levels of Fas/APO-1 and bcl-2 are not predictive of biological responsiveness. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 15;54(6):1580–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin A. W., Pound C. R., Clemens J. Q., Epstein J. I., Walsh P. C. Serum PSA after anatomic radical prostatectomy. The Johns Hopkins experience after 10 years. Urol Clin North Am. 1993 Nov;20(4):713–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Turley H., Kuzu I., Tungekar M. F., Dunnill M. S., Pierce C. B., Harris A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 2;329(10):690–694. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309023291003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffo A. J., Perlman H., Chen M. W., Day M. L., Streitman J. S., Buttyan R. Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 1;55(19):4438–4445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinker-Schaeffer C. W., Partin A. W., Isaacs W. B., Coffey D. S., Isaacs J. T. Molecular and cellular changes associated with the acquisition of metastatic ability by prostatic cancer cells. Prostate. 1994 Nov;25(5):249–265. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990250505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen P. P., Lesser M. L., Arroyo C. D., Cranor M., Borgen P., Norton L. p53 in node-negative breast carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study of epidemiologic risk factors, histologic features, and prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 1995 Apr;13(4):821–830. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter G., Deng G., Moch H., Kerschmann R., Matsumura K., De Vries S., George T., Fuentes J., Carroll P., Mihatsch M. J. Physical deletion of the p53 gene in bladder cancer. Detection by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):756–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal N. H., Cohen R. J., Haffejee Z., Savage N. BCL-2 proto-oncogene expression in prostate cancer and its relationship to the prostatic neuroendocrine cell. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994 Jun;118(6):616–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurbaji M. S., Kalbfleisch J. H., Thurmond T. S. Immunohistochemical detection of p53 protein as a prognostic indicator in prostate cancer. Hum Pathol. 1995 Jan;26(1):106–109. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., Sato T., Krajewski S., Kochel K., Irie S., Millan J. A., Reed J. C. Cloning and functional analysis of BAG-1: a novel Bcl-2-binding protein with anti-cell death activity. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90410-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. J., Robinson M., King P., Hasan T., Charlton R., Martin J., Carr T. W., Neal D. E. p53 expression and clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Br J Urol. 1993 Nov;72(5 Pt 2):778–781. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1993.tb16267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. J., Mellon K., Charlton R. G., Marsh C., Robinson M., Neal D. E. P53 and Ki-67 immunoreactivity in human prostate cancer and benign hyperplasia. Br J Urol. 1992 Jun;69(6):609–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1992.tb15632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor A. D., Yandell D. W. Prognostic significance of p53 overexpression in node-negative breast carcinoma: preliminary studies support cautious optimism. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Feb 3;85(3):176–177. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.3.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesalainen S. L., Lipponen P. K., Talja M. T., Alhava E. M., Syrjänen K. J. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and p53 expression as prognostic factors in T1-2M0 prostatic adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jul 15;58(2):303–308. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viale G., Roncalli M., Grimelius L., Graziani D., Wilander E., Johansson H., Bergholm U., Coggi G. Prognostic value of bcl-2 immunoreactivity in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1995 Sep;26(9):945–950. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visakorpi T., Kallioniemi O. P., Heikkinen A., Koivula T., Isola J. Small subgroup of aggressive, highly proliferative prostatic carcinomas defined by p53 accumulation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):883–887. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visakorpi T. Proliferative activity determined by DNA flow cytometry and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunohistochemistry as a prognostic factor in prostatic carcinoma. J Pathol. 1992 Sep;168(1):7–13. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Szekely L., Okan I., Klein G., Wiman K. G. Wild-type p53-triggered apoptosis is inhibited by bcl-2 in a v-myc-induced T-cell lymphoma line. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3427–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin P., Stattin P., Damber J. E., Bergh A. Castration therapy rapidly induces apoptosis in a minority and decreases cell proliferation in a majority of human prostatic tumors. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jun;146(6):1368–1375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]