Abstract
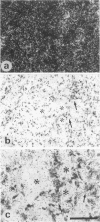
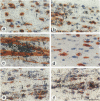
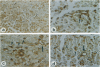
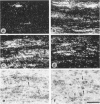
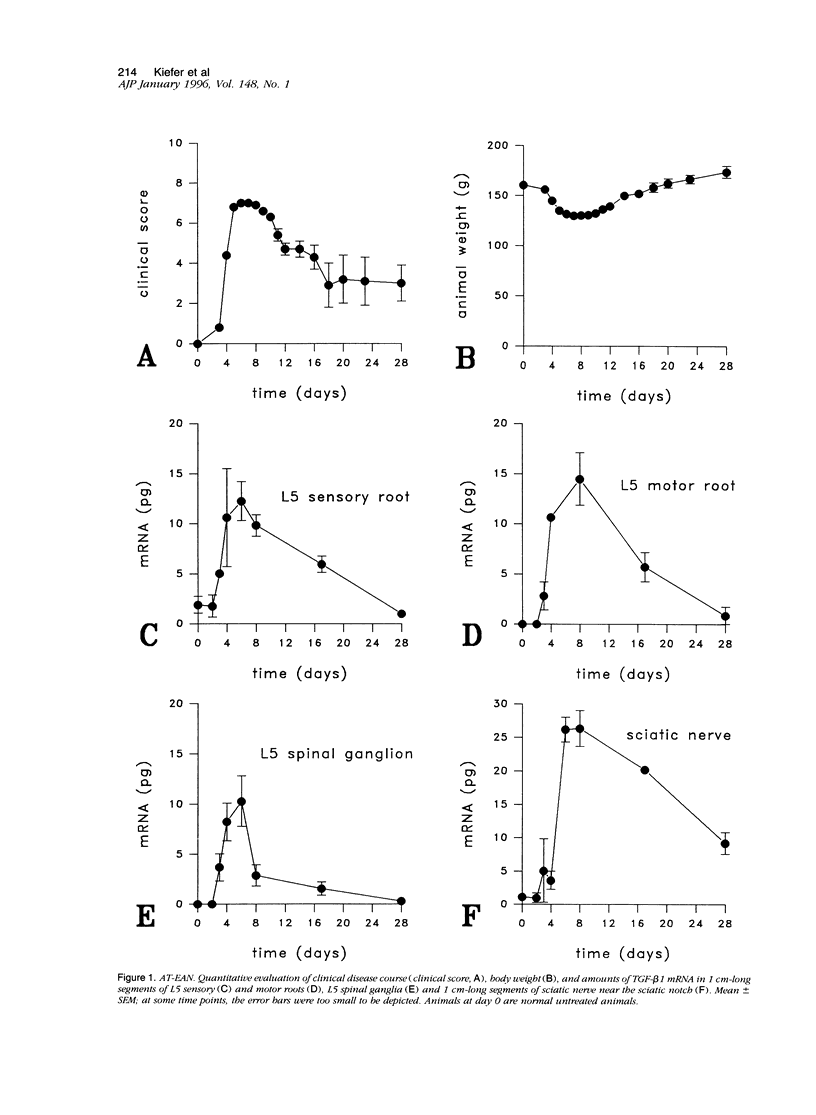
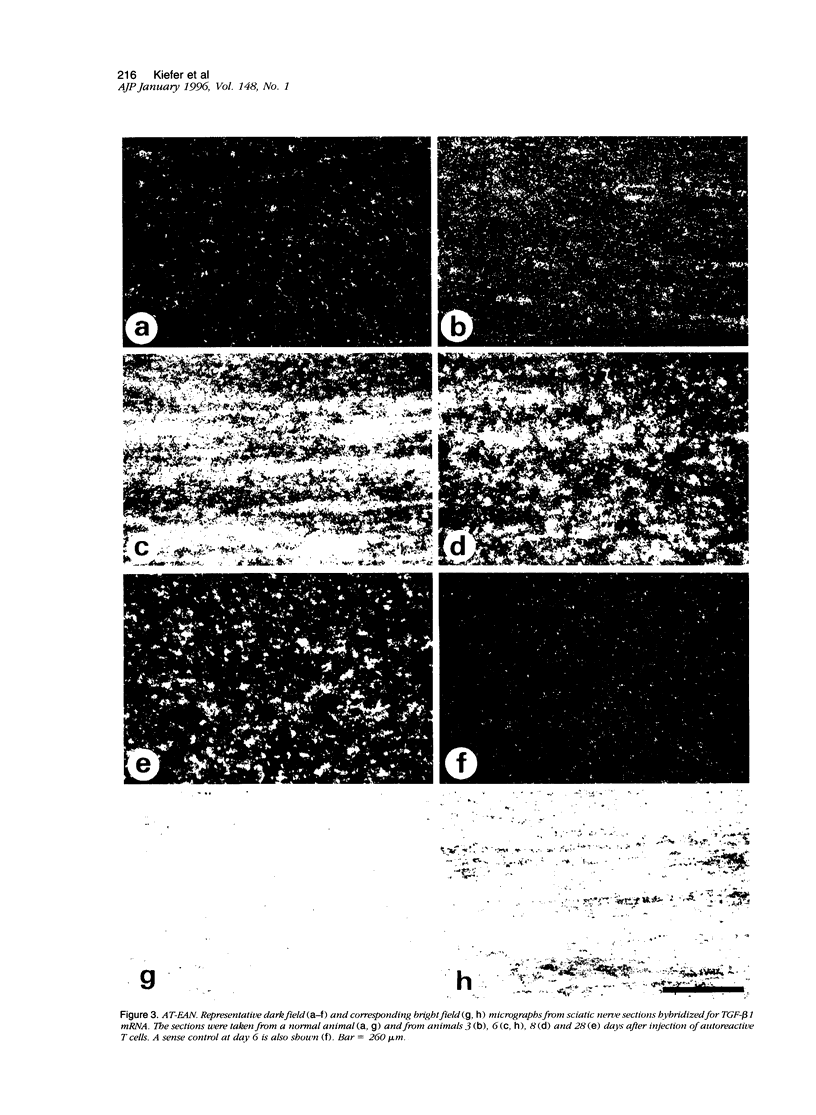
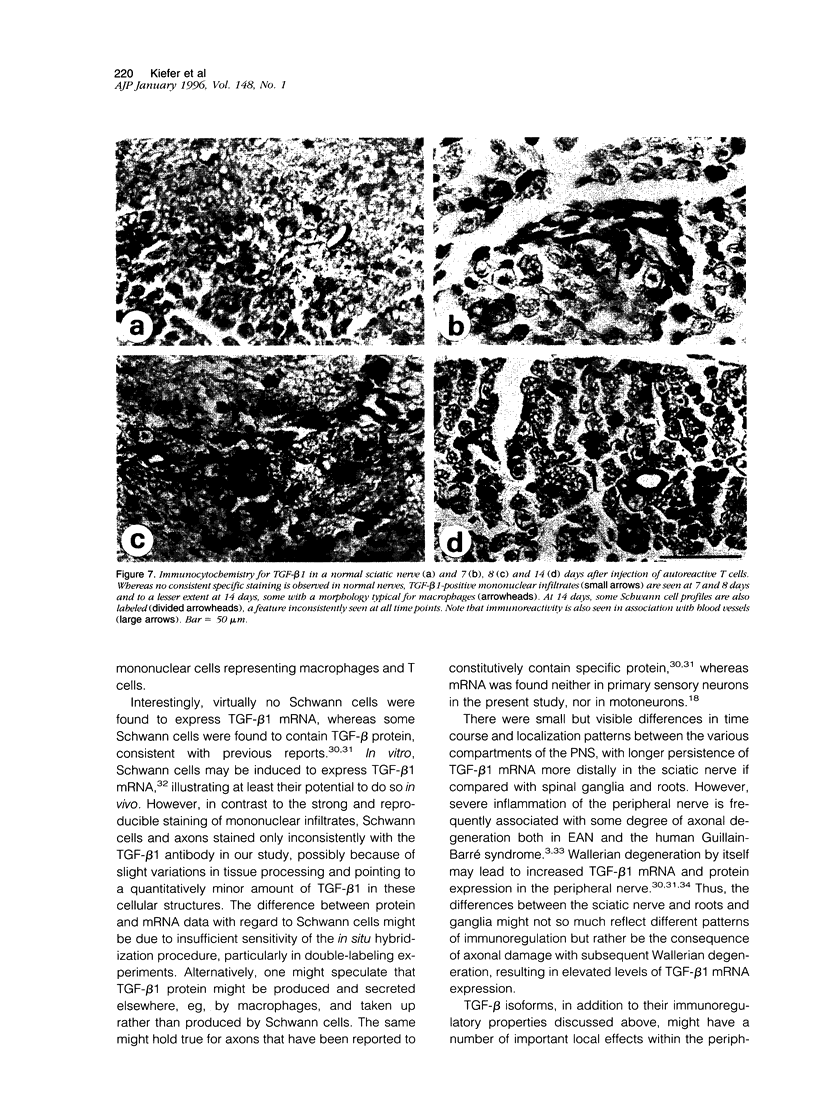
Experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN) is a monophasic inflammatory disorder of the peripheral nervous system that resolves spontaneously by molecular mechanisms as yet unknown. We have investigated whether the immunosuppressive cytokine transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) might be endogenously expressed in the peripheral nervous system of Lewis rats with actively induced and adoptive transfer EAN. TGF-beta 1 mRNA was upregulated to high levels in sensory and motor roots, spinal ganglia, and sciatic nerve as revealed by quantitative Northern blot analysis and in situ hybridization histochemistry, with peak levels just preceding the first signs of clinical recovery. TGF-beta 1 mRNA was localized to scattered round cells and dense cellular infiltrates, but only rarely to Schwann cell profiles. Double labeling studies revealed macrophages and subpopulations of T cells as the major cellular source of TGF-beta 1 mRNA. TGF-beta 1 protein was visualized immunocytochemically and localized to infiltrating mononuclear cells with peak expression around the same time as mRNA, in addition to some constitutive expression in axons and Schwann cells. Our studies suggest that the spontaneous recovery observed in Lewis rat EAN might be mediated by the endogenous elaboration of TGF-beta 1 within the peripheral nerve, and that macrophages might control their own cytotoxicity by expressing TGF-beta 1.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Manthey C. L., Hand A. R., Ohura K., Ellingsworth L., Wahl S. M. Rapid onset synovial inflammation and hyperplasia induced by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):231–247. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalazonitis A., Kalberg J., Twardzik D. R., Morrison R. S., Kessler J. A. Transforming growth factor beta has neurotrophic actions on sensory neurons in vitro and is synergistic with nerve growth factor. Dev Biol. 1992 Jul;152(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90162-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston P. A., Jessen K. R., Mirsky R. Transforming growth factor-beta and gamma-interferon have dual effects on growth of peripheral glia. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Dec;24(4):524–530. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregorian S. K., Lee W. P., Beck L. S., Rostami A., Amento E. P. Regulation of experimental autoimmune neuritis by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Cell Immunol. 1994 Jun;156(1):102–112. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Heininger K., Schäfer B., Fierz W., Toyka K. V. Immune mechanisms in inflammatory polyneuropathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:122–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Pollard J. D., Harvey G. K., Toyka K. V. Immunopathogenesis and treatment of the Guillain-Barré syndrome--Part II. Muscle Nerve. 1995 Feb;18(2):154–164. doi: 10.1002/mus.880180203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Schäfer B., Diamantstein T., Fierz W., Heininger K., Toyka K. V. Suppression of P2-T cell line-mediated experimental autoimmune neuritis by interleukin-2 receptor targeted monoclonal antibody ART 18. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 5;489(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Schäfer B., van der Meide P. H., Fierz W., Heininger K., Toyka K. V. The role of interferon-gamma in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune disease of the peripheral nervous system. Ann Neurol. 1990 Mar;27(3):247–257. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heininger K., Stoll G., Linington C., Toyka K. V., Wekerle H. Conduction failure and nerve conduction slowing in experimental allergic neuritis induced by P2-specific T-cell lines. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jan;19(1):44–49. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns L. D., Flanders K. C., Ranges G. E., Sriram S. Successful treatment of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with transforming growth factor-beta 1. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1792–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns L. D., Sriram S. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: neutralizing antibody to TGF beta 1 enhances the clinical severity of the disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Aug;47(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Krämer S., Schluesener H. J., Hünig T., Toyka K., Hartung H. P. Prevention and therapy of experimental autoimmune neuritis by an antibody against T cell receptors-alpha/beta. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3768–3775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Schluesener H. J., Schmidt B., Fontana A., Toyka K. V., Hartung H. P. Therapeutic effect of transforming growth factor-beta 2 on actively induced EAN but not adoptive transfer EAN. Immunology. 1994 Dec;83(4):545–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpus W. J., Swanborg R. H. CD4+ suppressor cells inhibit the function of effector cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through a mechanism involving transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1163–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. K., Torrance D. S., Picha K. S., Mohler K. M. Analysis of cytokine mRNA expression in the central nervous system of mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis reveals that IL-10 mRNA expression correlates with recovery. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2496–2505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer R., Gold R., Gehrmann J., Lindholm D., Wekerle H., Kreutzberg G. W. Transforming growth factor beta expression in reactive spinal cord microglia and meningeal inflammatory cells during experimental allergic neuritis. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Nov 1;36(4):391–398. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490360405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer R., Kreutzberg G. W. Gamma interferon-like immunoreactivity in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):725–734. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90103-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer R., Lindholm D., Kreutzberg G. W. Interleukin-6 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 mRNAs are induced in rat facial nucleus following motoneuron axotomy. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Jul 1;5(7):775–781. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer R., Streit W. J., Toyka K. V., Kreutzberg G. W., Hartung H. P. Transforming growth factor-beta 1: a lesion-associated cytokine of the nervous system. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1995 Jun-Jul;13(3-4):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(94)00074-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni A. B., Huh C. G., Becker D., Geiser A., Lyght M., Flanders K. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Ward J. M., Karlsson S. Transforming growth factor beta 1 null mutation in mice causes excessive inflammatory response and early death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruvilla A. P., Shah R., Hochwald G. M., Liggitt H. D., Palladino M. A., Thorbecke G. J. Protective effect of transforming growth factor beta 1 on experimental autoimmune diseases in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2918–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Hengerer B., Zafra F., Thoenen H. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 stimulates expression of nerve growth factor in the rat CNS. Neuroreport. 1990 Sep;1(1):9–12. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199009000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Heumann R., Meyer M., Thoenen H. Interleukin-1 regulates synthesis of nerve growth factor in non-neuronal cells of rat sciatic nerve. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):658–659. doi: 10.1038/330658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Izumo S., Suzuki M., Uyemura K., Meyermann R., Wekerle H. A permanent rat T cell line that mediates experimental allergic neuritis in the Lewis rat in vivo. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1946–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Lassmann H., Ozawa K., Kosin S., Mongan L. Cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin supergene family as tissue-specific autoantigens: induction of experimental allergic neuritis (EAN) by P0 protein-specific T cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1813–1817. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou J. C., Le Van Thai A., Valette A., Weber M. J. Transforming growth factor beta 1 is a potent survival factor for rat embryo motoneurons in culture. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Mar 1;52(1-2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90233-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Attisano L., Wrana J. L. The TGF-beta family and its composite receptors. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):172–178. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mews M., Meyer M. Modulation of Schwann cell phenotype by TGF-beta 1: inhibition of P0 mRNA expression and downregulation of the low affinity NGF receptor. Glia. 1993 Jul;8(3):208–217. doi: 10.1002/glia.440080308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Lider O., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Weiner H. L. Suppressor T cells generated by oral tolerization to myelin basic protein suppress both in vitro and in vivo immune responses by the release of transforming growth factor beta after antigen-specific triggering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):421–425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan L., Jessen K. R., Mirsky R. Negative regulation of the P0 gene in Schwann cells: suppression of P0 mRNA and protein induction in cultured Schwann cells by FGF2 and TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2 and TGF beta 3. Development. 1994 Jun;120(6):1399–1409. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson A., Miyazono K., Kanzaki T., Colosetti P., Engström U., Heldin C. H. Transforming growth factor-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 secreted by a human glioblastoma cell line. Identification of small and different forms of large latent complexes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19482–19488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Cannella B., Albert P., Sporn M., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Evidence of endogenous regulatory function of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Int Immunol. 1992 May;4(5):615–620. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Dhib-Jalbut S., Cannella B., Albert P. S., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Prevention and treatment of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by transforming growth factor-beta 1. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3012–3017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Davis J. B., Stroobant P., Land H. Transforming growth factors-beta 1 and beta 2 are mitogens for rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3419–3424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rufer M., Flanders K., Unsicker K. Presence and regulation of transforming growth factor beta mRNA and protein in the normal and lesioned rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Nov 1;39(4):412–423. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490390408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad B., Constam D. B., Ortmann R., Moos M., Fontana A., Schachner M. Astrocyte-derived TGF-beta 2 and NGF differentially regulate neural recognition molecule expression by cultured astrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):473–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S. S., Kamholz J., Jakowlew S. B. Axons modulate the expression of transforming growth factor-betas in Schwann cells. Glia. 1993 Aug;8(4):265–276. doi: 10.1002/glia.440080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull M. M., Ormsby I., Kier A. B., Pawlowski S., Diebold R. J., Yin M., Allen R., Sidman C., Proetzel G., Calvin D. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):693–699. doi: 10.1038/359693a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta: recent progress and new challenges. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1017–1021. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll G., Jung S., Jander S., van der Meide P., Hartung H. P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in immune-mediated demyelination and Wallerian degeneration of the rat peripheral nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jun;45(1-2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunawaki S., Sporn M., Ding A., Nathan C. Deactivation of macrophages by transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):260–262. doi: 10.1038/334260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A. D., Whitham R., Swain S. L., Morrison W. J., Wyrick G., Hoy C., Vandenbark A. A., Offner H. Transforming growth factor-beta enhances the in vivo effector function and memory phenotype of antigen-specific T helper cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2109–2117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettl U. K., Gold R., Hartung H. P., Toyka K. V. Apoptotic cell death of T-lymphocytes in experimental autoimmune neuritis of the Lewis rat. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Jul 18;176(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90875-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]