Abstract
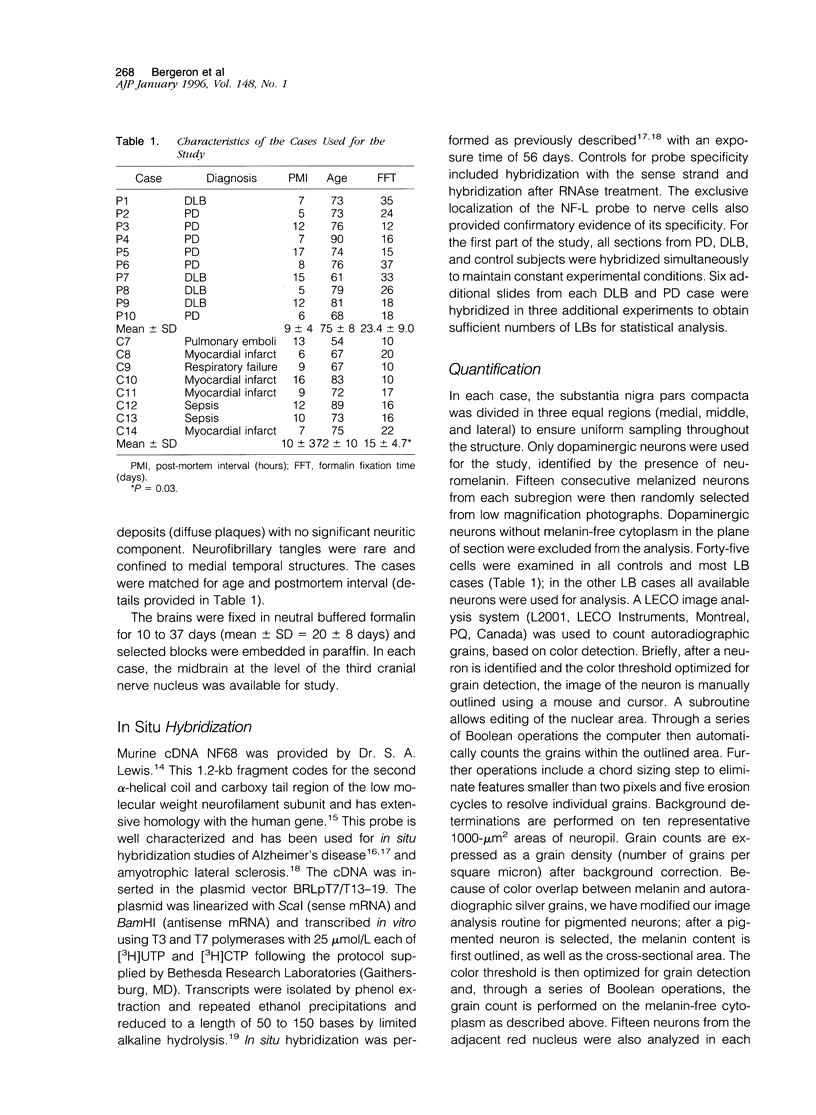
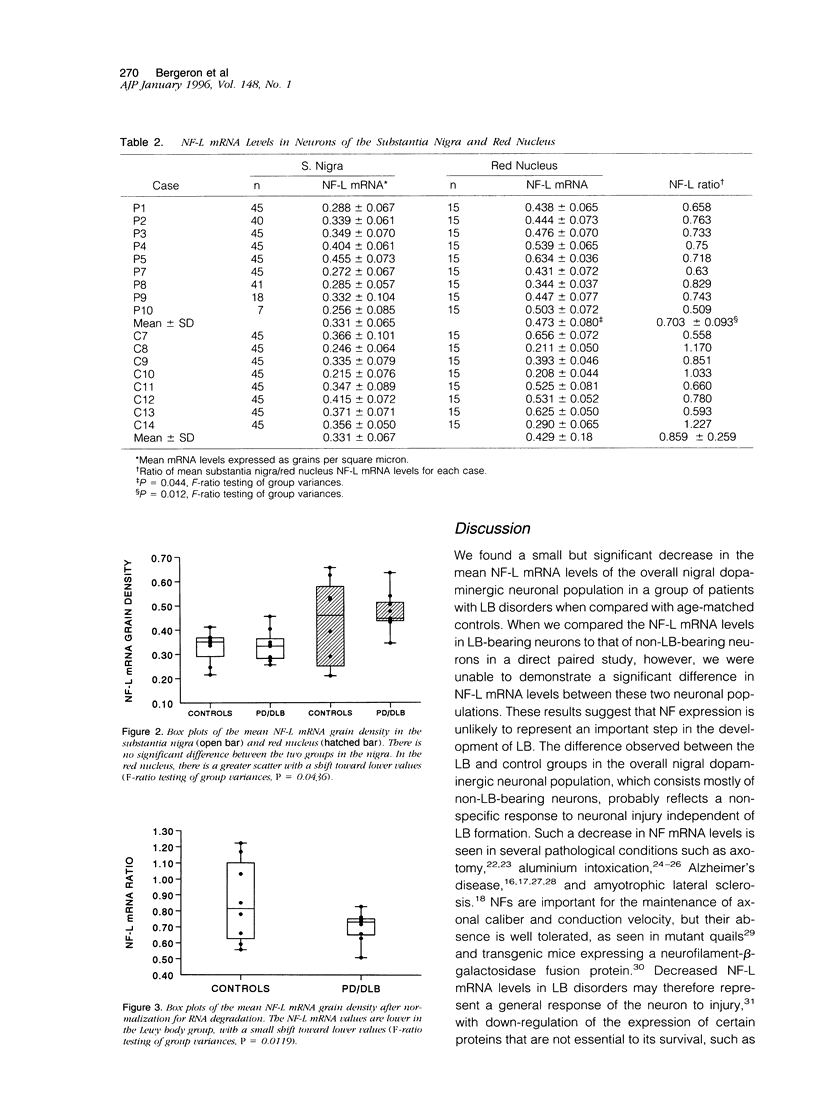
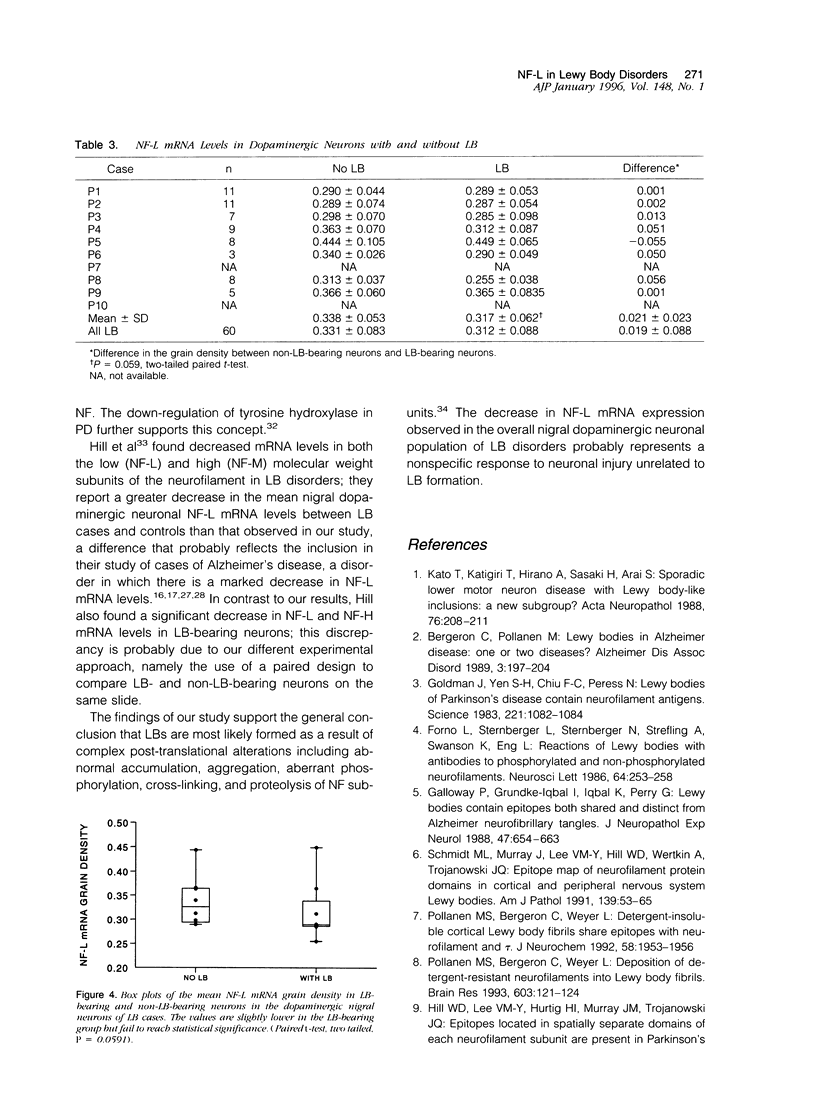
Lewy bodies (LBs) are cytoskeletal alterations found in several neurodegenerative disorders. Although neurofilaments are the main constituent of the LB, the precise mechanisms that underlie their formation remain speculative. To examine the pathogenesis of this inclusion, we measured the mRNA level of the low molecular weight neurofilament subunit in the nigral dopaminergic neurons of patients with LB disorders and neurologically normal controls. We found a small but significant decrease in the mean mRNA values in the LB group as compared with controls. However, a comparison of LB-bearing and non-LB-bearing neurons on the same section showed no significant difference between these two neuronal populations. We conclude that altered neurofilament expression is not a major contributory event in the pathogenesis of the LB. The decrease in neurofilament mRNA expression observed in the overall nigral dopaminergic neuronal population of LB disorders probably represents a nonspecific response to neuronal injury independent of LB formation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancher C., Lassmann H., Budka H., Jellinger K., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Wiche G., Seitelberger F., Wisniewski H. M. An antigenic profile of Lewy bodies: immunocytochemical indication for protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Jan;48(1):81–93. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198901000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton A. J., Pearson R. C., Najlerahim A., Harrison P. J. Pre- and postmortem influences on brain RNA. J Neurochem. 1993 Jul;61(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron C., Beric-Maskarel K., Muntasser S., Weyer L., Somerville M. J., Percy M. E. Neurofilament light and polyadenylated mRNA levels are decreased in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor neurons. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994 May;53(3):221–230. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199405000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron C., Pollanen M. Lewy bodies in Alzheimer disease--one or two diseases? Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1989 Winter;3(4):197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Krekoski C. A., Parhad I. M., Liston D., Julien J. P., Hoar D. I. Altered expression of genes for amyloid and cytoskeletal proteins in Alzheimer cortex. Ann Neurol. 1989 Apr;25(4):331–339. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyer J., Peterson A. Neurofilament-deficient axons and perikaryal aggregates in viable transgenic mice expressing a neurofilament-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):389–405. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forno L. S., Sternberger L. A., Sternberger N. H., Strefling A. M., Swanson K., Eng L. F. Reaction of Lewy bodies with antibodies to phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated neurofilaments. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Mar 14;64(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Perry G. Lewy bodies contain epitopes both shared and distinct from Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;47(6):654–663. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway P. G., Mulvihill P., Perry G. Filaments of Lewy bodies contain insoluble cytoskeletal elements. Am J Pathol. 1992 Apr;140(4):809–822. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Yen S. H., Chiu F. C., Peress N. S. Lewy bodies of Parkinson's disease contain neurofilament antigens. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1082–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.6308771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette J. G., Wong L., Crapper McLachlan D. R., Lewis P. N. Characterization of messenger RNA from the cerebral cortex of control and Alzheimer-afflicted brain. J Neurochem. 1986 Sep;47(3):987–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Pearson R. C. In situ hybridization histochemistry and the study of gene expression in the human brain. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;34(4):271–312. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. D., Arai M., Cohen J. A., Trojanowski J. Q. Neurofilament mRNA is reduced in Parkinson's disease substantia nigra pars compacta neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Mar 15;329(3):328–336. doi: 10.1002/cne.903290304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Cleveland D. W. Neurofilament and tubulin expression recapitulates the developmental program during axonal regeneration: induction of a specific beta-tubulin isotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Pollock S. C., Striph G. G. Altered gene expression after optic nerve transection: reduced neurofilament expression as a general response to axonal injury. Exp Neurol. 1993 Jan;119(1):32–36. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1993.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javoy-Agid F., Hirsch E. C., Dumas S., Duyckaerts C., Mallet J., Agid Y. Decreased tyrosine hydroxylase messenger RNA in the surviving dopamine neurons of the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease: an in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience. 1990;38(1):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90389-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Grosveld F., Yazdanbaksh K., Flavell D., Meijer D., Mushynski W. The structure of a human neurofilament gene (NF-L): a unique exon-intron organization in the intermediate filament gene family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 6;909(1):10–20. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Katagiri T., Hirano A., Sasaki H., Arai S. Sporadic lower motor neuron disease with Lewy body-like inclusions: a new subgroup? Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(2):208–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00688105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Genetics, evolution, and expression of the 68,000-mol-wt neurofilament protein: isolation of a cloned cDNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):843–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love S., Saitoh T., Quijada S., Cole G. M., Terry R. D. Alz-50, ubiquitin and tau immunoreactivity of neurofibrillary tangles, Pick bodies and Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Jul;47(4):393–405. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198807000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., McDermott H., Landon M., Mayer R. J., Wilkinson K. D. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase (PGP 9.5) is selectively present in ubiquitinated inclusion bodies characteristic of human neurodegenerative diseases. J Pathol. 1990 Jun;161(2):153–160. doi: 10.1002/path.1711610210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muma N. A., Troncoso J. C., Hoffman P. N., Koo E. H., Price D. L. Aluminum neurotoxicity: altered expression of cytoskeletal genes. Brain Res. 1988 Apr;427(2):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parhad I. M., Krekoski C. A., Mathew A., Tran P. M. Neuronal gene expression in aluminum myelopathy. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1989 Mar;9(1):123–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00711449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollanen M. S., Bergeron C., Weyer L. Deposition of detergent-resistant neurofilaments into Lewy body fibrils. Brain Res. 1993 Feb 12;603(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91307-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollanen M. S., Bergeron C., Weyer L. Detergent-insoluble cortical Lewy body fibrils share epitopes with neurofilament and tau. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1953–1956. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollanen M. S., Dickson D. W., Bergeron C. Pathology and biology of the Lewy body. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 May;52(3):183–191. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199305000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. L., Murray J., Lee V. M., Hill W. D., Wertkin A., Trojanowski J. Q. Epitope map of neurofilament protein domains in cortical and peripheral nervous system Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):53–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville M. J., Percy M. E., Bergeron C., Yoong L. K., Grima E. A., McLachlan D. R. Localization and quantitation of 68 kDa neurofilament and superoxide dismutase-1 mRNA in Alzheimer brains. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jan;9(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90123-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong M. J., Mao K., Nerurkar V. R., Wakayama I., Yanagihara R., Garruto R. M. Dose-dependent selective suppression of light (NFL) and medium (NFM) but not heavy (NFH) molecular weight neurofilament mRNA levels in acute aluminum neurotoxicity. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1994 Aug;5(4):319–326. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1994.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetzlaff W., Alexander S. W., Miller F. D., Bisby M. A. Response of facial and rubrospinal neurons to axotomy: changes in mRNA expression for cytoskeletal proteins and GAP-43. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2528–2544. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Bennett G. S., Itakura C., Mizutani M. Defective expression of neurofilament protein subunits in hereditary hypotrophic axonopathy of quail. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):734–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]