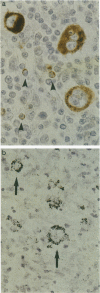
Abstract
Reed-Sternberg (RS) and Hodgkin's (H) cells are considered to be the neoplastic cells in Hodgkin's disease. Although most data suggest a lymphoid origin, the nature of these cells still remains the subject of considerable controversy. Recently, monoclonal antibodies became available, directed against granzyme B, a serine protease specifically expressed by activated cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) and natural killer (NK) cells. Using two granzyme B-specific antibodies directed against different epitopes, we studied the expression of granzyme B in a well characterized group of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive and EBV-negative cases of Hodgkin's disease. Granzyme B expression was found in part of the H-RS cells in 11 out of 61 tested cases (18%, 9 of 46 cases of nodular sclerosing and 1 of 12 mixed cellularity Hodgkin's disease). In none of these cases did H-RS cells express B-cell markers, whereas in four cases, expression of either the T-cell marker CD3 or CD8 was found in a small minority of H-RS cells. The percentage of granzyme B-positive H-RS cells ranged from < 10% to > 50%. Granzyme B-positive H-RS cells were present in 6 of 26 EBV-positive cases and in 5 of 35 EBV-negative cases, indicating no relationship with the presence of EBV. Moreover, no significant differences were found regarding either stage at presentation or clinical outcome. We conclude that in a restricted number of cases of Hodgkin's disease, the H-RS cells express granzyme B, and therefore might be considered the neoplastic equivalent of either activated CTLs or NK cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Nagler-Anderson C., O'Brien C., Levine H., Watkins S., Slayter H. S., Blue M. L., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with a 15-kDa cytoplasmic granule-associated protein defines a subpopulation of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):574–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai M. C., Jiwa N. M., Horstman A., Vos W., Kluin P. H., Van der Valk P., Mullink H., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Decreased expression of cellular markers in Epstein-Barr virus-positive Hodgkin's disease. J Pathol. 1994 Sep;174(1):49–55. doi: 10.1002/path.1711740108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone P. P., Kaplan H. S., Musshoff K., Smithers D. W., Tubiana M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin's Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971 Nov;31(11):1860–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu W. S., Abbondanzo S. L., Frizzera G. Inconsistency of the immunophenotype of Reed-Sternberg cells in simultaneous and consecutive specimens from the same patients. A paraffin section evaluation in 56 patients. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):11–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daus H., Trümper L., Roth J., von Bonin F., Möller P., Gause A., Pfreundschuh M. Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells do not carry T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements: evidence from single-cell polymerase chain reaction examination. Blood. 1995 Mar 15;85(6):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabie J., Tierens A., Wu G., Weisenburger D. D., Chan W. C. Lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin's disease: lineage and clonality determination using a single-cell assay. Blood. 1994 Nov 15;84(10):3291–3298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H. G. Recent results on the biology of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. I. Biopsy material. Leuk Lymphoma. 1992 Nov;8(4-5):283–313. doi: 10.3109/10428199209051008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H. G. Recent results on the biology of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. II. Continuous cell lines. Leuk Lymphoma. 1993 Jan;9(1-2):1–25. doi: 10.3109/10428199309148499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanz J. A., MacDonald H. R., Jenne D. E., Tschopp J., Nabholz M. Cell specificity of granzyme gene expression. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3111–3118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hameed A., Lowrey D. M., Lichtenheld M., Podack E. R. Characterization of three serine esterases isolated from human IL-2 activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3142–3147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hell K., Pringle J. H., Hansmann M. L., Lorenzen J., Colloby P., Lauder I., Fischer R. Demonstration of light chain mRNA in Hodgkin's disease. J Pathol. 1993 Oct;171(2):137–143. doi: 10.1002/path.1711710211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Wesselschmidt R. L., Shresta S., Russell J. H., Ley T. J. Cytotoxic lymphocytes require granzyme B for the rapid induction of DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in allogeneic target cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):977–987. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90376-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Kanavaros P., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Horstman A., Vos W., Mullink H., Meijer C. J. Expression of c-myc and bcl-2 oncogene products in Reed-Sternberg cells independent of presence of Epstein-Barr virus. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Mar;46(3):211–217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Oudejans J. J., Dukers D. F., Vos W., Horstman A., van der Valk P., Middledorp J. M., Walboomers J. M., Meijer C. J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of different latent membrane protein-1 epitopes of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphoproliferative diseases. J Clin Pathol. 1995 May;48(5):438–442. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krähenbühl O., Rey C., Jenne D., Lanzavecchia A., Groscurth P., Carrel S., Tschopp J. Characterization of granzymes A and B isolated from granules of cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3471–3477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummer J. A., Kamp A. M., Tadema T. M., Vos W., Meijer C. J., Hack C. E. Localization and identification of granzymes A and B-expressing cells in normal human lymphoid tissue and peripheral blood. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Apr;100(1):164–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummer J. A., Kamp A. M., van Katwijk M., Brakenhoff J. P., Radosević K., van Leeuwen A. M., Borst J., Verweij C. L., Hack C. E. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies raised against recombinant human granzymes A and B and showing cross reactions with the natural proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jul 6;163(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küppers R., Rajewsky K., Zhao M., Simons G., Laumann R., Fischer R., Hansmann M. L. Hodgkin disease: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells picked from histological sections show clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangements and appear to be derived from B cells at various stages of development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10962–10966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Rafii S., Granelli-Piperno A., Trapani J. A., Young J. D. Perforin and serine esterase gene expression in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2105–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poe M., Bennett C. D., Biddison W. E., Blake J. T., Norton G. P., Rodkey J. A., Sigal N. H., Turner R. V., Wu J. K., Zweerink H. J. Human cytotoxic lymphocyte tryptase. Its purification from granules and the characterization of inhibitor and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13215–13222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Daus H., Trümper L., Gause A., Salamon-Looijen M., Pfreundschuh M. Detection of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene rearrangement at the single-cell level in malignant lymphomas: no rearrangement is found in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jun 15;57(6):799–804. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiver J. W., Su L., Henkart P. A. Cytotoxicity with target DNA breakdown by rat basophilic leukemia cells expressing both cytolysin and granzyme A. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90359-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taatjes D. J., Mount S. L., Trainer T. D., Tindle B. H. Localization of anti-Leu-M1 (CD15) binding sites in Hodgkin's disease by immunoelectron microscopic examination. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 Feb;101(2):140–148. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.2.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Kummer J. A., Hack C. E., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Erkelens G. W., Meinders A. E., Kluin P. M., Breedveld F. C. Granzyme-positive cytotoxic cells are specifically increased in early rheumatoid synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Dec;37(12):1735–1743. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaru J., Hummel M., Zemlin M., Kalvelage B., Stein H. Hodgkin's disease with a B-cell phenotype often shows a VDJ rearrangement and somatic mutations in the VH genes. Blood. 1994 Aug 1;84(3):708–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velotti F., Palmieri G., D'Ambrosio D., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. Differential expression of granzyme A and granzyme B proteases and their secretion by fresh rat natural killer cells (NK) and lymphokine-activated killer cells with NK phenotype (LAK-NK). Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):1049–1053. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., Munroe M., Ariniello P., Anderson P. Identification of tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes expressing PEN5, a mucin-like glycoprotein selectively expressed on natural killer cells. Am J Pathol. 1995 Feb;146(2):409–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. C., Kummer J. A., van der Valk P., van Heerde P., Kluin P. M., Willemze R., Ossenkoppele G. J., Radaszkiewicz T., Meijer C. J. Granzyme B-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas: neoplastic equivalents of activated cytotoxic T cells with preference for mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue localization. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3785–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]