Abstract
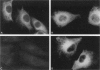
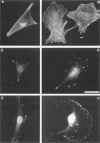
Intermediate filaments have been used as cell-type-specific markers in differentiation and pathology; however, recent reports have demonstrated the coexpression of vimentin (a mesenchymal marker) and keratins (epithelial markers) in numerous neoplasms, including melanoma, which has been linked to metastatic disease. To test the hypothesis that coexpression of vimentin and keratins by melanoma cells contributes to a more migratory and invasive phenotype, we co-transfected a vimentin-positive human melanoma cell line, A375P (of low invasive ability), with cDNAs for keratins 8 and 18. The resultant stable transfectants expressed vimentin- and keratin-positive intermediate filaments showed a two- to threefold increase in their invasion of basement membrane matrix and migration through gelatin in vitro. These findings were further corroborated by video cinematography. During attachment and spreading on fibronectin, the transfectants containing vimentin and keratins 8 and 18 demonstrated an increase in focal adhesions that stained positive for beta 1 integrin and phosphotyrosine, along with enhanced membrane ruffling and actin stress fiber formation. From these data, we postulate that coexpression of vimentin and keratins results in increased cytoskeletal interactions at focal contacts within extracellular matrices involving integrin cell signaling events, which contributes to a more migratory behavior.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Zöller M., Raz A. Differential expression of intermediate filament proteins in metastatic and nonmetastatic variants of the BSp73 tumor. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):785–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Turner C. E., Romer L. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):893–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Masur S. K., Lazega D., Waxman S., Ossowski L. Induction of cell migration by pro-urokinase binding to its receptor: possible mechanism for signal transduction in human epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):259–270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu Y. W., Runyan R. B., Oshima R. G., Hendrix M. J. Expression of complete keratin filaments in mouse L cells augments cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4261–4265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Intermediate filaments and disease: mutations that cripple cell strength. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):511–516. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Goldman R. D. Evidence for an interaction between the cell surface and intermediate filaments in cultured fibroblasts. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1986;6(4):389–405. doi: 10.1002/cm.970060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. J., Seftor E. A., Chu Y. W., Seftor R. E., Nagle R. B., McDaniel K. M., Leong S. P., Yohem K. H., Leibovitz A. M., Meyskens F. L., Jr Coexpression of vimentin and keratins by human melanoma tumor cells: correlation with invasive and metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Feb 5;84(3):165–174. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.3.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Haskill S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):577–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Liotta L. A., Robey P. G., Tryggvason K., Martin G. R. Isolation and characterization of type IV procollagen, laminin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the EHS sarcoma. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6188–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Bachant J. B., Domingo A. Functions of intermediate filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(3):309–331. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L. J., Earp H. S., Turner C. E., Prockop C., Juliano R. L. Signal transduction by integrins: increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation caused by clustering of beta 1 integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L., Earp H. S., Parsons J. T., Schaller M., Juliano R. L. Cell adhesion or integrin clustering increases phosphorylation of a focal adhesion-associated tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23439–23442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku N. O., Omary M. B. Identification of the major physiologic phosphorylation site of human keratin 18: potential kinases and a role in filament reorganization. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):161–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Hogan B. L., Kurkinen M., Garrels J. I. Co-expression of vimentin and cytokeratins in parietal endoderm cells of early mouse embryo. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):701–704. doi: 10.1038/303701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Franssila K. Immunohistochemical spectrum of malignant melanoma. The common presence of keratins. Lab Invest. 1989 Dec;61(6):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuckolls G. H., Romer L. H., Burridge K. Microinjection of antibodies against talin inhibits the spreading and migration of fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1992 Aug;102(Pt 4):753–762. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate filaments: cell-type-specific markers in differentiation and pathology. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Intermediate filament molecular biology. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90067-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta V., Jones J. C. The internal affairs of an integrin. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):2–4. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90046-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Haag D., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P. H., Vooijs G. P. Coexpression of keratin- and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human metastatic carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2618–2622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond W. A., Leong A. S. Vimentin--a new prognostic parameter in breast carcinoma? J Pathol. 1989 Jun;158(2):107–114. doi: 10.1002/path.1711580205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romer L. H., McLean N., Turner C. E., Burridge K. Tyrosine kinase activity, cytoskeletal organization, and motility in human vascular endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Mar;5(3):349–361. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.3.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. The Walter Herbert Lecture. Control of cell motility and tumour invasion by extracellular matrix interactions. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):239–242. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. E., Horwitz A. F., Lauffenburger D. A., Sheetz M. P. Integrin-cytoskeletal interactions in migrating fibroblasts are dynamic, asymmetric, and regulated. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):977–991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seftor R. E., Seftor E. A., Gehlsen K. R., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Ruoslahti E., Hendrix M. J. Role of the alpha v beta 3 integrin in human melanoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1557–1561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Goldman R. D. Recent insights into the assembly, dynamics, and function of intermediate filament networks. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;19(2):67–79. doi: 10.1002/cm.970190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Liem R. K. Intermediate filament dynamics. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90651-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. W., Paik S., Brünner N., Sommers C. L., Zugmaier G., Clarke R., Shima T. B., Torri J., Donahue S., Lippman M. E. Association of increased basement membrane invasiveness with absence of estrogen receptor and expression of vimentin in human breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):534–544. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Butler J. P., Ingber D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1124–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.7684161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Orlando R. A., Cheresh D. A. Integrins alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 contribute to cell attachment to vitronectin but differentially distribute on the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):919–929. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner T. M., Liu E. T., Craven R. J., Cance W. G. Expression of focal adhesion kinase gene and invasive cancer. Lancet. 1993 Oct 23;342(8878):1024–1025. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92881-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbo R. J., Gown A. M., Nagle R. B., Visscher D. W., Crissman J. D. Anomalous cytokeratin expression in malignant melanoma: one- and two-dimensional western blot analysis and immunohistochemical survey of 100 melanomas. Mod Pathol. 1990 Jul;3(4):494–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]