Abstract
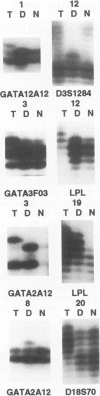
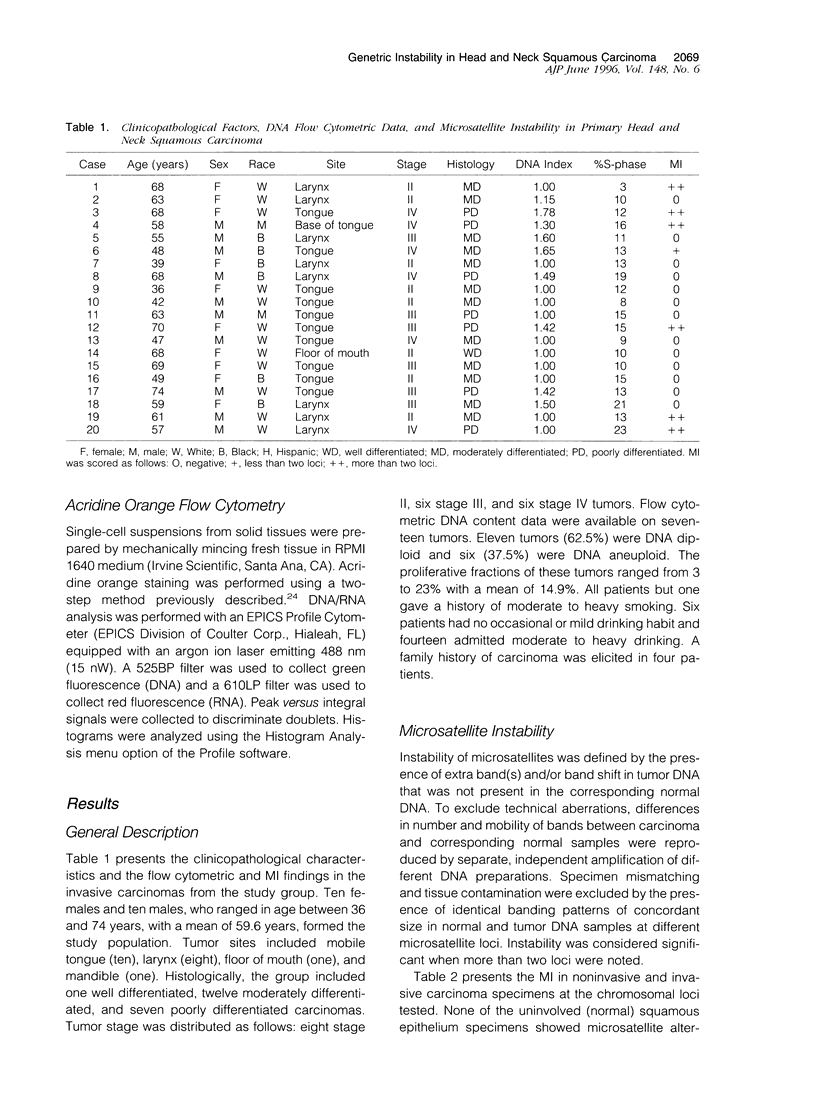
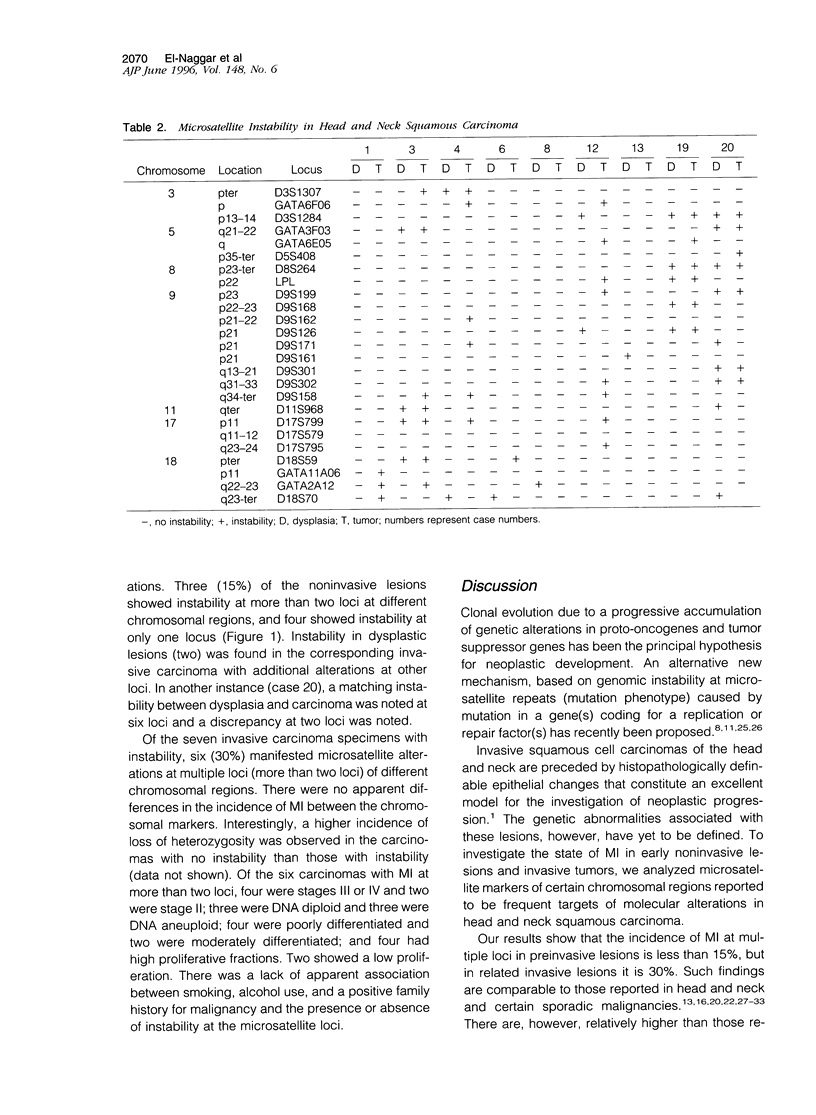
To investigate the extent and significance of microsatellite instability in head and neck carcinogenesis we analyzed DNA extracted from normal squamous epithelium, severe dysplasia, and corresponding carcinoma specimens from 20 patients by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Loci on chromosomes 3p, 5p, 5q, 8p, 9p, 9q, 11q, 17p, 17q, 18p, 18q were selected for analysis. Our results show that three of the dysplasias (15.0%) and six of the invasive carcinoma (30.0%) manifested instability at multiple loci. Two of the dysplastic lesions had identical alterations in the corresponding carcinomas and one showed instability differences in only two of eight loci. Normal squamous epithelium lacked microsatellite instability. No apparent association between smoking, alcohol use, or family history of cancer and instability was found in this small cohort. Invasive carcinomas with instability were relatively more poorly differentiated and had a higher stage and a high proliferative fraction. Our study indicates that microsatellite instability is 1) noted in a small subset of dysplastic lesions of head and neck squamous epithelium and 2) present in approximately one-third of invasive lesions, usually with aggressive characteristics, and may clinically be a late event associated with tumor progression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen L. A., Peltomäki P., Leach F. S., Sistonen P., Pylkkänen L., Mecklin J. P., Järvinen H., Powell S. M., Jen J., Hamilton S. R. Clues to the pathogenesis of familial colorectal cancer. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):812–816. doi: 10.1126/science.8484121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Weber J. L. Survey of human and rat microsatellites. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):627–631. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90285-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya N. P., Skandalis A., Ganesh A., Groden J., Meuth M. Mutator phenotypes in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks R. T., Kessis T. D., Cho K. R., Hedrick L. Microsatellite instability in endometrial carcinoma. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1163–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. Pathology of squamous carcinomas of the head and neck. Curr Opin Oncol. 1992 Jun;4(3):485–490. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199206000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. K., Kiaris H., Howard P., Vaughan E. D., Spandidos D. A., Jones A. S. Microsatellite instability in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Br J Cancer. 1995 May;71(5):1065–1069. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R., Lescoe M. K., Rao M. R., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Garber J., Kane M., Kolodner R. The human mutator gene homolog MSH2 and its association with hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong K. M., Zimmerman P. V., Smith P. J. Microsatellite instability and other molecular abnormalities in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 Jan 1;55(1):28–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honchel R., Halling K. C., Schaid D. J., Pittelkow M., Thibodeau S. N. Microsatellite instability in Muir-Torre syndrome. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1159–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Yeh P. L., Martin M. B., Straub R. E., Gilliam T. C., Caldwell C. W., Skibba J. L. Genetic alterations of microsatellites on chromosome 18 in human breast carcinoma. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1995 Mar;4(1):66–72. doi: 10.1097/00019606-199503000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionov Y., Peinado M. A., Malkhosyan S., Shibata D., Perucho M. Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):558–561. doi: 10.1038/363558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Thilly W. G. Fidelity of DNA polymerases in DNA amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9253–9257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Nucleotide repeats. Slippery DNA and diseases. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):207–208. doi: 10.1038/365207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Microsatellite instability: marker of a mutator phenotype in cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 1;54(19):5059–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao L., Lee D. J., Tockman M. S., Erozan Y. S., Askin F., Sidransky D. Microsatellite alterations as clonal markers for the detection of human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9871–9875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer S. J., Yin J., Manin B., Rhyu M. G., Cottrell J., Hudson E., Redd J. L., Krasna M. J., Abraham J. M., Reid B. J. Microsatellite instability occurs frequently and in both diploid and aneuploid cell populations of Barrett's-associated esophageal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3379–3382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström-Lahti M., Parsons R., Sistonen P., Pylkkänen L., Aaltonen L. A., Leach F. S., Hamilton S. R., Watson P., Bronson E., Fusaro R. Mismatch repair genes on chromosomes 2p and 3p account for a major share of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer families evaluable by linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;55(4):659–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R., Li G. M., Longley M. J., Fang W. H., Papadopoulos N., Jen J., de la Chapelle A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Modrich P. Hypermutability and mismatch repair deficiency in RER+ tumor cells. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90331-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltomäki P., Lothe R. A., Aaltonen L. A., Pylkkänen L., Nyström-Lahti M., Seruca R., David L., Holm R., Ryberg D., Haugen A. Microsatellite instability is associated with tumors that characterize the hereditary non-polyposis colorectal carcinoma syndrome. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 15;53(24):5853–5855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prolla T. A., Pang Q., Alani E., Kolodner R. D., Liskay R. M. MLH1, PMS1, and MSH2 interactions during the initiation of DNA mismatch repair in yeast. Science. 1994 Aug 19;265(5175):1091–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.8066446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn A. G., Healy E., Rehman I., Sikkink S., Rees J. L. Microsatellite instability in human non-melanoma and melanoma skin cancer. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Mar;104(3):309–312. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12664612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyu M. G., Park W. S., Meltzer S. J. Microsatellite instability occurs frequently in human gastric carcinoma. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risinger J. I., Berchuck A., Kohler M. F., Watson P., Lynch H. T., Boyd J. Genetic instability of microsatellites in endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5100–5103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schantz S. P. Basic science advances in head and neck oncology: the past decade. Semin Surg Oncol. 1995 May-Jun;11(3):272–279. doi: 10.1002/ssu.2980110313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seruca R., Santos N. R., David L., Constância M., Barroca H., Carneiro F., Seixas M., Peltomäki P., Lothe R., Sobrinho-Simões M. Sporadic gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability display a particular clinicopathologic profile. Int J Cancer. 1995 Feb 20;64(1):32–36. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910640108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D., Peinado M. A., Ionov Y., Malkhosyan S., Perucho M. Genomic instability in repeated sequences is an early somatic event in colorectal tumorigenesis that persists after transformation. Nat Genet. 1994 Mar;6(3):273–281. doi: 10.1038/ng0394-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidransky D. Molecular genetics of head and neck cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 1995 May;7(3):229–233. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199505000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyrk T. C. Colon cancer connections. Cancer syndrome meets molecular biology meets histopathology. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jul;145(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., Prolla T. A., Liskay R. M., Petes T. D. Destabilization of tracts of simple repetitive DNA in yeast by mutations affecting DNA mismatch repair. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):274–276. doi: 10.1038/365274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. DNA repeats--a treasury of human variation. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jul 21;331(3):191–193. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199407213310310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Harpaz N., Tarmin L., Yin J., Jiang H. Y., Bell J. D., Hontanosas M., Groisman G. M., Abraham J. M., Meltzer S. J. Microsatellite instability in ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal dysplasias and cancers. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4841–4844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeau S. N., Bren G., Schaid D. Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):816–819. doi: 10.1126/science.8484122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traganos F., Darzynkiewicz Z., Sharpless T., Melamed M. R. Simultaneous staining of ribonucleic and deoxyribonucleic acids in unfixed cells using acridine orange in a flow cytofluorometric system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jan;25(1):46–56. doi: 10.1177/25.1.64567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Wada C., Wang C., Ishida H., Egawa S., Yokoyama E., Ohtani H., Koshiba K. Microsatellite instability in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 2;10(5):1019–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada C., Shionoya S., Fujino Y., Tokuhiro H., Akahoshi T., Uchida T., Ohtani H. Genomic instability of microsatellite repeats and its association with the evolution of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1994 Jun 15;83(12):3449–3456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooster R., Cleton-Jansen A. M., Collins N., Mangion J., Cornelis R. S., Cooper C. S., Gusterson B. A., Ponder B. A., von Deimling A., Wiestler O. D. Instability of short tandem repeats (microsatellites) in human cancers. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):152–156. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]