Abstract
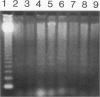
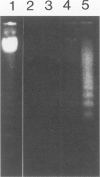
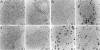
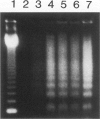
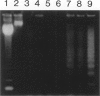
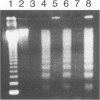
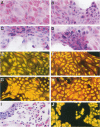
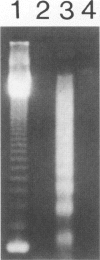
Apoptosis occurs naturally in the liver and increases in specific pathogenic processes. We previously described the use of a chemically defined medium supplemented with epidermal growth factor and dimethylsulfoxide to maintain rat hepatocytes in a highly differentiated state for more than 30 days (long-term culture). In this study, we showed that hepatocytes in long-term dimethylsulfoxide culture have definite advantages over using cells in short-term culture (cells in culture for 2 to 4 days) to study apoptosis. We demonstrated that treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha induced apoptosis (detected morphologically and by formation of an oligonucleosomal DNA ladder) only in hepatocytes that had been subjected to dimethylsulfoxide removal. Neither treatment with TNF-alpha alone or dimethylsulfoxide removal alone induced apoptosis. Apoptosis could be induced by concentrations as low as 500 U of TNF-alpha/ml. Although a DNA ladder was not detected by 12 hours after TNF-alpha treatment, it was easily identified by 24 hours. We conclude that this system can be used 1) to examine the underlying mechanism by which TNF-alpha causes apoptosis in hepatocytes and 2) to study induction of apoptosis in hepatocytes by other agents.
Full text
PDF


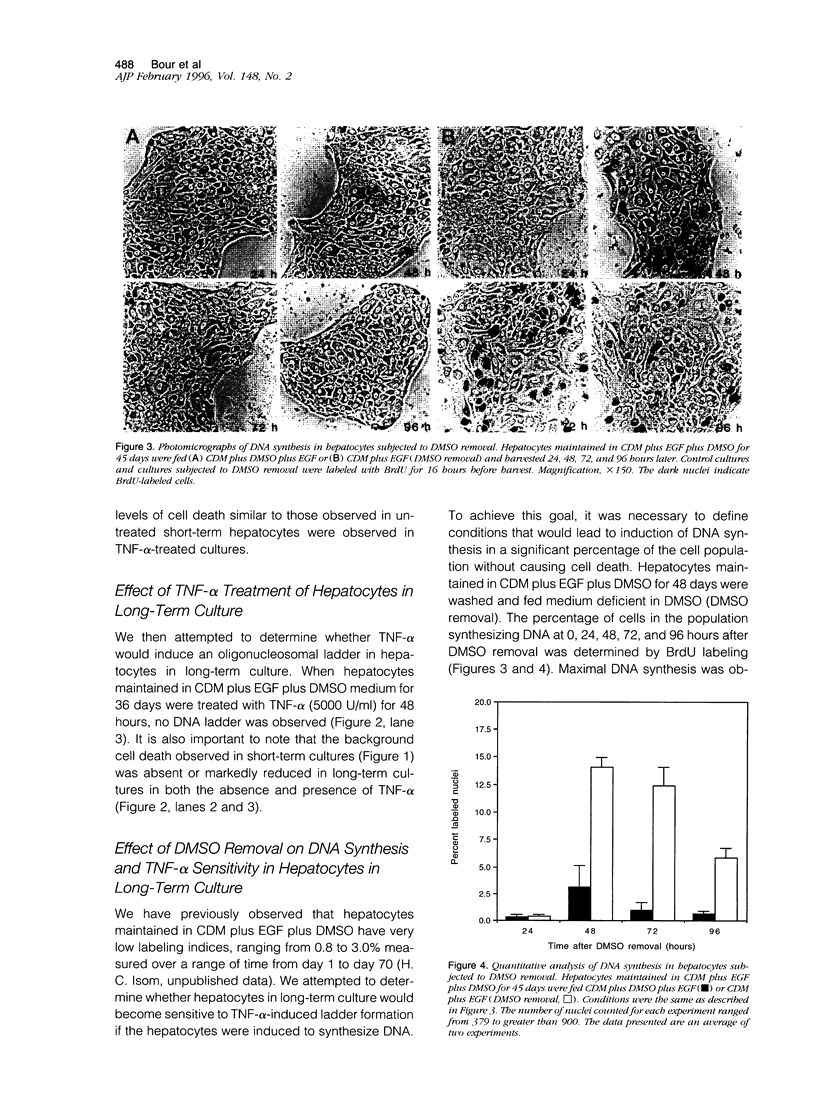
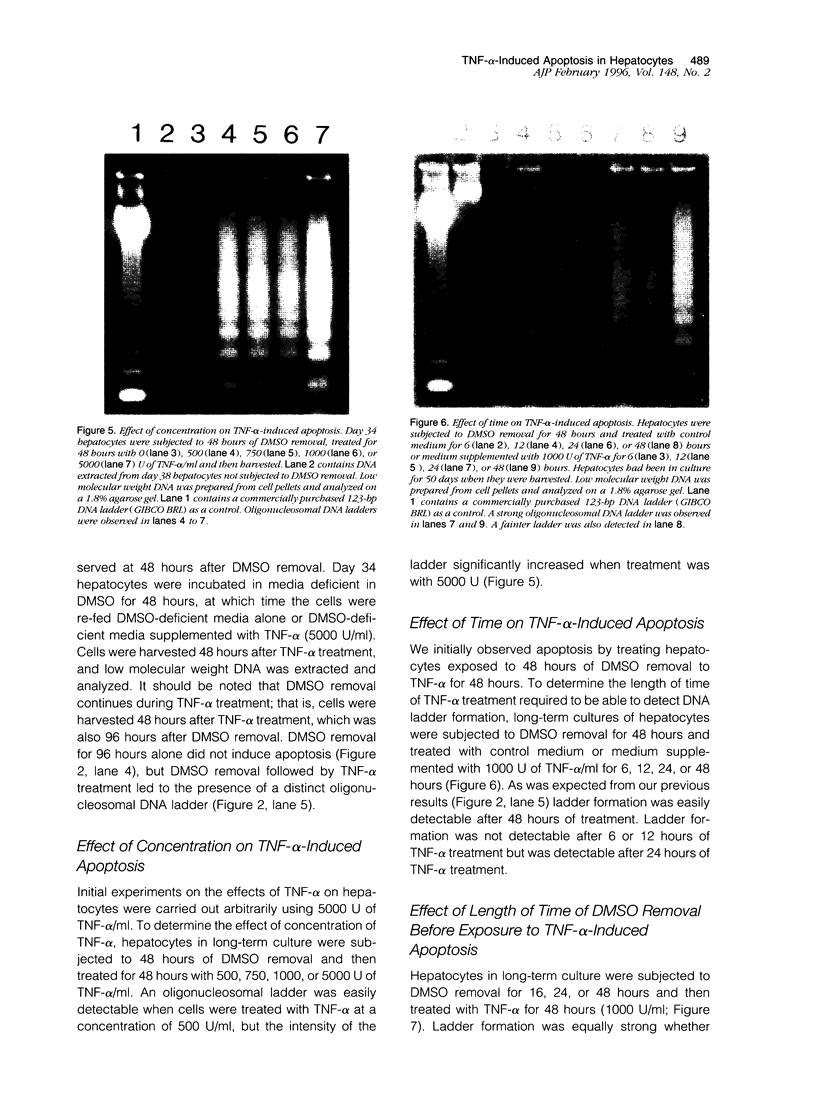
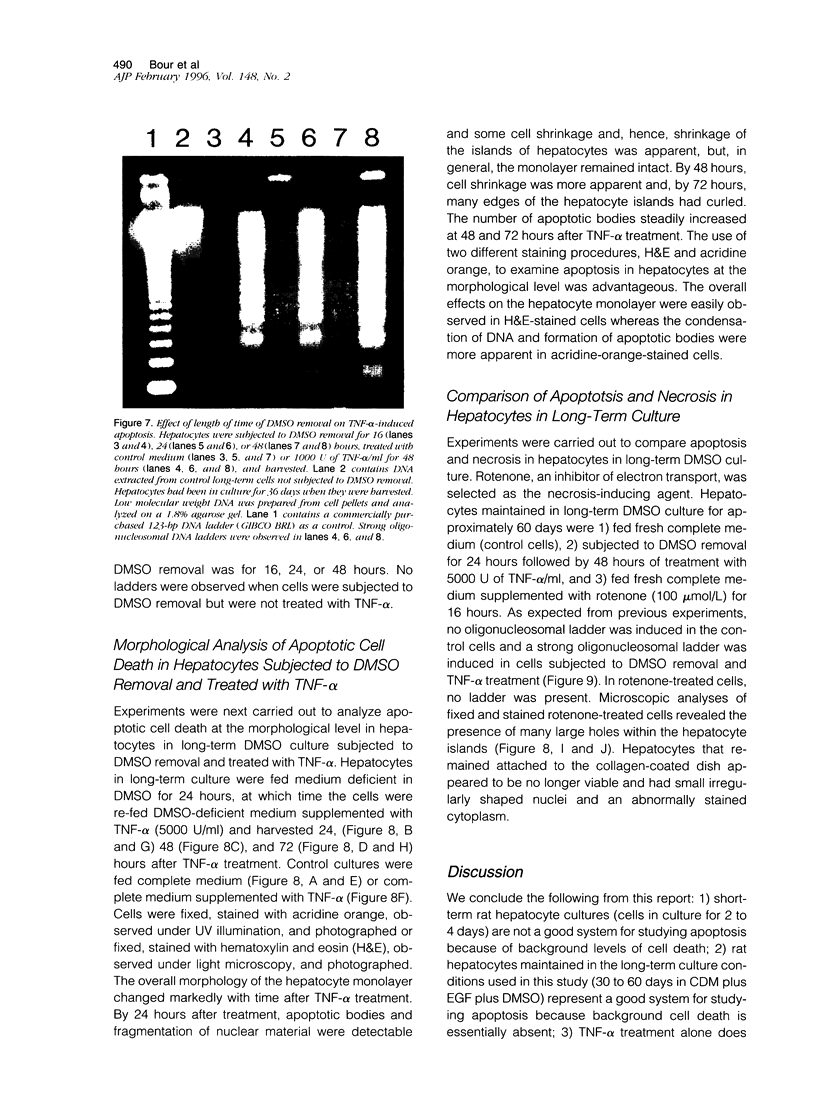
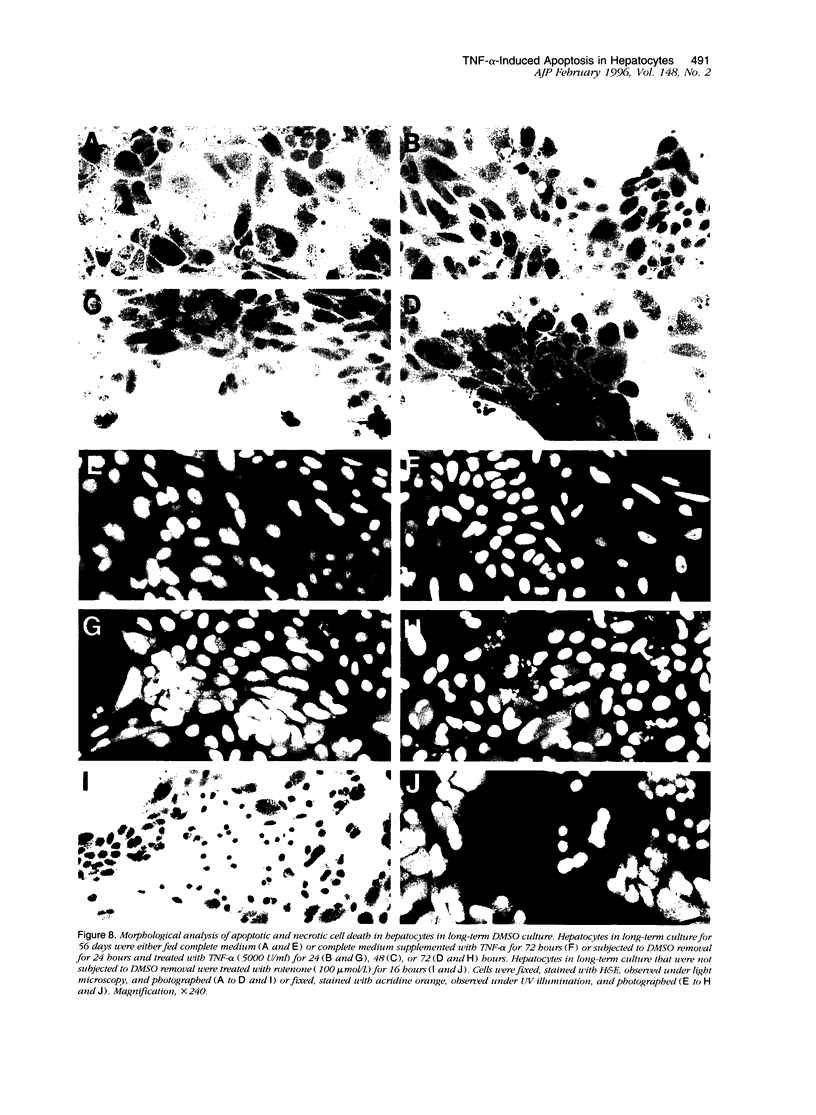




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alison M. R., Sarraf C. E. Liver cell death: patterns and mechanisms. Gut. 1994 May;35(5):577–581. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baribault H., Marceau N. Dexamethasone and dimethylsulfoxide as distinct regulators of growth and differentiation of cultured suckling rat hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Oct;129(1):77–84. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Düsterberg B., Schulte-Hermann R. Growth, regression and cell death in rat liver as related to tissue levels of the hepatomitogen cyproterone acetate. Arch Toxicol. 1986 Dec;59(4):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00290542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Lauer B., Timmermann-Trosiener I., Barthel G., Schuppler J., Schulte-Hermann R. Controlled death (apoptosis) of normal and putative preneoplastic cells in rat liver following withdrawal of tumor promoters. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Apr;5(4):453–458. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Oberhammer F., Jirtle R. L., Askari M., Sedivy R., Grasl-Kraupp B., Purchio A. F., Schulte-Hermann R. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 as a signal for induction of cell death by apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 1993 Mar;67(3):531–536. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Taper H. S., Lauer B., Schulte-Hermann R. Quantitative histological and histochemical studies on the occurrence and stages of controlled cell death (apoptosis) during regression of rat liver hyperplasia. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1985;50(2):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF02889898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøe R., Gjertsen B. T., Vintermyr O. K., Houge G., Lanotte M., Døskeland S. O. The protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid induces morphological changes typical of apoptosis in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90523-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K., Kost D. P., Michalopoulos G. Multiple sequential periods of DNA synthesis and quiescence in primary hepatocyte cultures maintained on the DMSO-EGF on/off protocol. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):584–590. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Programmed cell death in the immune system. Adv Immunol. 1991;50:55–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Columbano A., Ledda-Columbano G. M., Coni P. P., Faa G., Liguori C., Santa Cruz G., Pani P. Occurrence of cell death (apoptosis) during the involution of liver hyperplasia. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):670–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Vega F. M., Mendoza-Figueroa T. Dimethyl sulfoxide enhances lipid synthesis and secretion by long-term cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Biochimie. 1991 May;73(5):621–624. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90033-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbas M., White E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):546–554. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsdale T., Bard J. Collagen substrata for studies on cell behavior. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):626–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldhoff R. C., Taylor J. M., Jefferson L. S. Synthesis and secretion of rat albumin in vivo, in perfused liver, and in isolated hepatocytes. Effects of hypophysectomy and growth hormone treatment. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3611–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Cell death mechanisms and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 1991 Jun;121:29–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang A. T., Cohen K. J., Barrett J. F., Bergstrom D. A., Dang C. V. Participation of cyclin A in Myc-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6875–6879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. M., Camper S. A., Tilghman S. M., Miller T., Georgoff I., Serra R., Isom H. C. Functional analyses of albumin expression in a series of hepatocyte cell lines and in primary hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Sep;3(9):577–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom H. C. DNA synthesis in isolated hepatocytes infected with herpesviruses. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):199–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom H. C., Secott T., Georgoff I., Woodworth C., Mummaw J. Maintenance of differentiated rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3252–3256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom I., Georgoff I., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Persistence of liver-specific messenger RNA in cultured hepatocytes: different regulatory events for different genes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2877–2885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong T. C., Jeong H. G., Yang K. H. Induction of cytochrome P-450 by dimethyl sulfoxide in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett. 1992 Jul;61(2-3):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(92)90154-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Selby P. Tumour necrosis factor: clinical relevance. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(4):817–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F. Shrinkage necrosis: a distinct mode of cellular death. J Pathol. 1971 Sep;105(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/path.1711050103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoruts A., Stahnke L., McClain C. J., Logan G., Allen J. I. Circulating tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 concentrations in chronic alcoholic patients. Hepatology. 1991 Feb;13(2):267–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klion F. M., Schaffner F. The ultrastructure of acidophilic "Councilman-like" bodies in the liver. Am J Pathol. 1966 May;48(5):755–767. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist M., Gantner F., Bohlinger I., Germann P. G., Tiegs G., Wendel A. Murine hepatocyte apoptosis induced in vitro and in vivo by TNF-alpha requires transcriptional arrest. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 15;153(4):1778–1788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist M., Gantner F., Bohlinger I., Tiegs G., Germann P. G., Wendel A. Tumor necrosis factor-induced hepatocyte apoptosis precedes liver failure in experimental murine shock models. Am J Pathol. 1995 May;146(5):1220–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay C. K., Chenery R. J., Hawksworth G. M. Primary culture of rat hepatocytes in the presence of dimethyl sulphoxide. A system to investigate the regulation of cytochrome P450 IA. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 11;42 (Suppl):S17–S25. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90387-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. A. Reciprocal regulation of adult rat hepatocyte growth and functional activities in culture by dimethyl sulfoxide. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Dec;137(3):497–504. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muakkassah-Kelly S. F., Bieri F., Waechter F., Bentley P., Stäubli W. Long-term maintenance of hepatocytes in primary culture in the presence of DMSO: further characterization and effect of nafenopin, a peroxisome proliferator. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muakkassah-Kelly S. F., Bieri F., Waechter F., Bentley P., Stäubli W. The use of primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes to study induction of enzymes and DNA synthesis: effect of nafenopin and electroporation. Experientia. 1988 Oct 15;44(10):823–827. doi: 10.1007/BF01941178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F. A., Pavelka M., Sharma S., Tiefenbacher R., Purchio A. F., Bursch W., Schulte-Hermann R. Induction of apoptosis in cultured hepatocytes and in regressing liver by transforming growth factor beta 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5408–5412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F., Fritsch G., Pavelka M., Froschl G., Tiefenbacher R., Purchio T., Schulte-Hermann R. Induction of apoptosis in cultured hepatocytes and in the regressing liver by transforming growth factor-beta 1 occurs without activation of an endonuclease. Toxicol Lett. 1992 Dec;64-65 Spec No:701–704. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(92)90250-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., Jacobson M. D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):695–700. doi: 10.1126/science.8235590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. W., Jr Death in embryonic systems. Science. 1966 Nov 4;154(3749):604–612. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3749.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Hermann R., Bursch W., Kraupp-Grasl B., Oberhammer F., Wagner A., Jirtle R. Cell proliferation and apoptosis in normal liver and preneoplastic foci. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Dec;101 (Suppl 5):87–90. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101s587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwall R. H., Robbins K., Jardieu P., Chang L., Lai C., Terrell T. G. Activin induces cell death in hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro. Hepatology. 1993 Aug;18(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(93)90018-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Lau J., Daniels H., Goka J., Eddleston A., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Increased production of tumour necrosis factor alpha in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 1991 Mar;12(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90945-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa T., Yoshioka K., Kakumu S., Wakita T., Ishikawa T., Itoh Y., Takayanagi M. Apoptosis in cultured rat hepatocytes: the effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma. J Pathol. 1991 Nov;165(3):247–253. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.7878464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilg H. The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of chronic liver diseases. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1993;23(4):179–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02592306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilg H., Wilmer A., Vogel W., Herold M., Nölchen B., Judmaier G., Huber C. Serum levels of cytokines in chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jul;103(1):264–274. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91122-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth C. A., Thomas P. Liver endocytosis and Kupffer cells. Hepatology. 1992 Jul;16(1):255–266. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor: a pleiotropic cytokine and therapeutic target. Annu Rev Med. 1994;45:491–503. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.45.1.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukidate K., Yamamoto K., Snyder J. W., Farber J. L. Microtubule antagonists activate programmed cell death (apoptosis) in cultured rat hepatocytes. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):918–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa P., Arioli P., Guaitani A. Mechanism of maintenance of liver-specific functions by DMSO in cultured rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1991 May;194(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90146-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Isom H. C. Regulation of albumin gene expression in a series of rat hepatocyte cell lines immortalized by simian virus 40 and maintained in chemically defined medium. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3740–3748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Isom H. C. Transformation of differentiated rat hepatocytes with adenovirus and adenovirus DNA. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3570–3579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3570-3579.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C., Secott T., Isom H. C. Transformation of rat hepatocytes by transfection with simian virus 40 DNA to yield proliferating differentiated cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):4018–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Morris R. G., Smith A. L., Dunlop D. Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: association with condensed chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis. J Pathol. 1984 Jan;142(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]