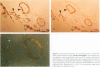
Abstract
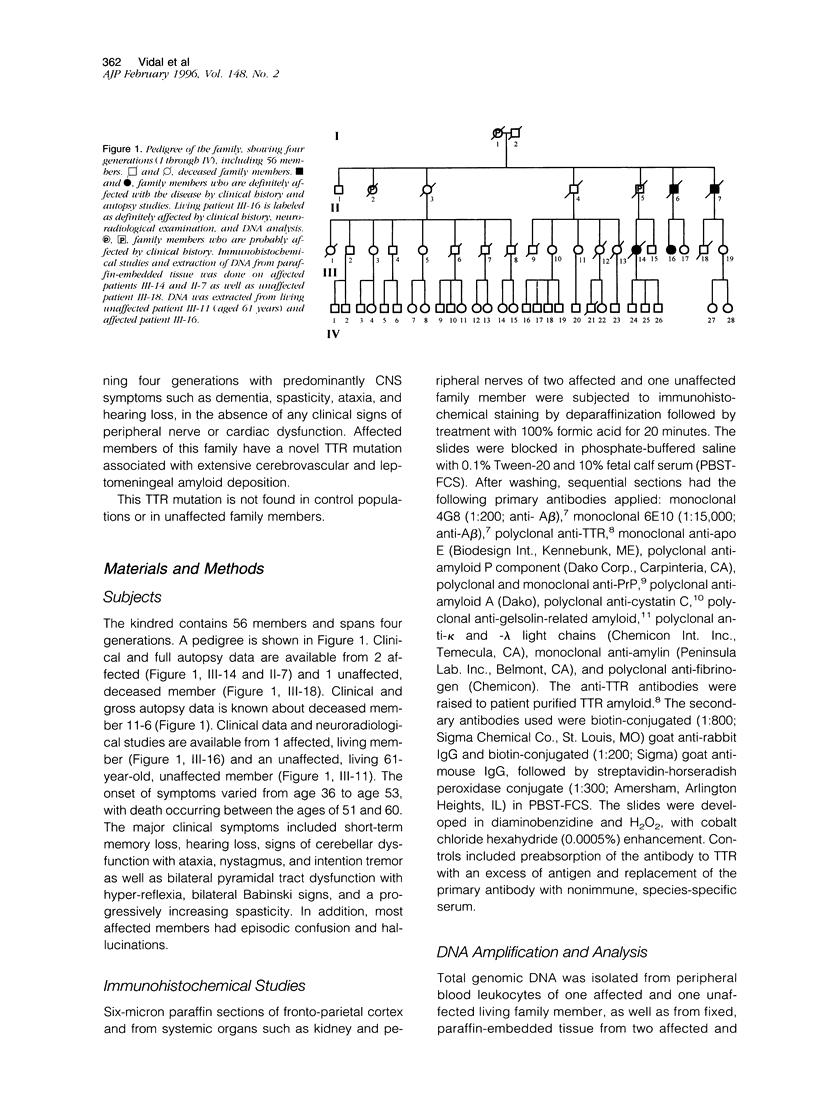
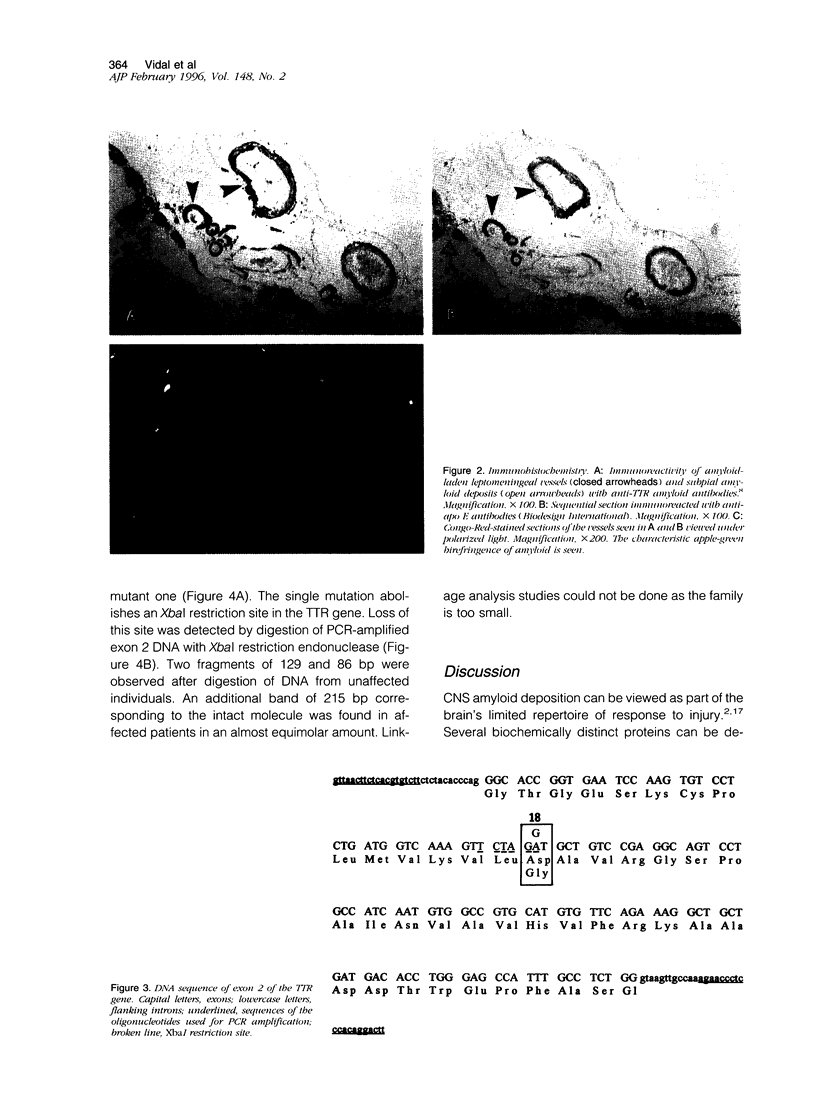
We describe a novel transthyretin mutation at codon 18 where Asp is replaced by Gly (D18G) in a Hungarian kindred. This mutation is associated with meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis, producing dementia, ataxia, and spasticity. Fifty different transthyretin mutations are related to amyloid deposition, typically producing a peripheral neuropathy or cardiac dysfunction. These symptoms are absent in this family. Up to now, amyloid-beta (A beta), cystatin C, and prion proteins have been known to be deposited as amyloid in the brain, leading to stroke or dementia. With this report we establish that transthyretin amyloid deposition can also produce central nervous system dysfunction as the major clinical symptom.
Full text
PDF



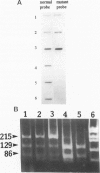
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake C. C., Geisow M. J., Swan I. D., Rerat C., Rerat B. Strjcture of human plasma prealbumin at 2-5 A resolution. A preliminary report on the polypeptide chain conformation, quaternary structure and thyroxine binding. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E., Prelli F., Larrondo-Lillo M., van Duinen S., Shelanski M. L., Frangione B. Isolation and characterization of amyloid P component from Alzheimer's disease and other types of cerebral amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Etiology and pathogenesis of prion diseases. Am J Pathol. 1995 Apr;146(4):785–811. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya H., Yoshioka K., Sasaki H., Sakaki Y., Nakazato M., Matsuo H., Nakadai A., Ikeda S., Yanagisawa N. Molecular analysis of a variant type of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy showing cerebellar ataxia and pyramidal tract signs. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1706–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI113261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti B., Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Bugiani O., Frangione B., Farlow M. R., Dlouhy S. R. Familial Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease with neurofibrillary tangles. Mol Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;8(1):41–48. doi: 10.1007/BF02778006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Jensson O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibrils in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis of Icelandic type is a variant of gamma-trace basic protein (cystatin C). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Unifying features of systemic and cerebral amyloidosis. Mol Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;8(1):49–64. doi: 10.1007/BF02778007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumoto S., Younger D., Hays A. P., Martone R. L., Smith R. T., Herbert J. Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy presenting with carpal tunnel syndrome and a new transthyretin mutation, asparagine 70. Neurology. 1992 Nov;42(11):2094–2102. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.11.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kametani F., Ikeda S., Yanagisawa N., Ishi T., Hanyu N. Characterization of a transthyretin-related amyloid fibril protein from cerebral amyloid angiopathy in type I familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J Neurol Sci. 1992 Apr;108(2):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90048-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Maeda S., Shimada K., Araki S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human prealbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):558–564. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen R. B., Tabaton M., Chen S. G., Monari L., Richardson S. L., Lynch T., Manetto V., Lanska D. J., Markesbery W. R., Lynches T [corrected to Lynch T. ]. Familial progressive subcortical gliosis: presence of prions and linkage to chromosome 17. Neurology. 1995 Jun;45(6):1062–1067. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.6.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Prelli F., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Primary structure of an amyloid prealbumin variant in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):539–542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva M. J. Transthyretin mutations in health and disease. Hum Mutat. 1995;5(3):191–196. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380050302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Anderton B. H. Dorothy Russell Memorial Lecture. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease: are we any closer to understanding the neurodegenerative process? Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1994 Aug;20(4):322–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1994.tb00977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Prelli F., Porro M., Rossi G., Giaccone G., Farlow M. R., Dlouhy S. R., Ghetti B., Bugiani O., Frangione B. Amyloid fibrils in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana and Swedish kindreds) express only PrP peptides encoded by the mutant allele. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiyama M., Ikeda S., Yanagisawa N. Transthyretin-type cerebral amyloid angiopathy in type I familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(5):524–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00310133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinters H. V., Nishimura G. S., Secor D. L., Pardridge W. M. Immunoreactive A4 and gamma-trace peptide colocalization in amyloidotic arteriolar lesions in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):233–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Sletten K., Johansson B., Cornwell G. G., 3rd Fibril in senile systemic amyloidosis is derived from normal transthyretin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2843–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Alzheimer's disease and soluble A beta. Neurobiol Aging. 1994 Mar-Apr;15(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(94)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Haltia M., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Lewy bodies are immunoreactive with antibodies raised to gelsolin related amyloid-Finnish type. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1077–1083. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]