Abstract
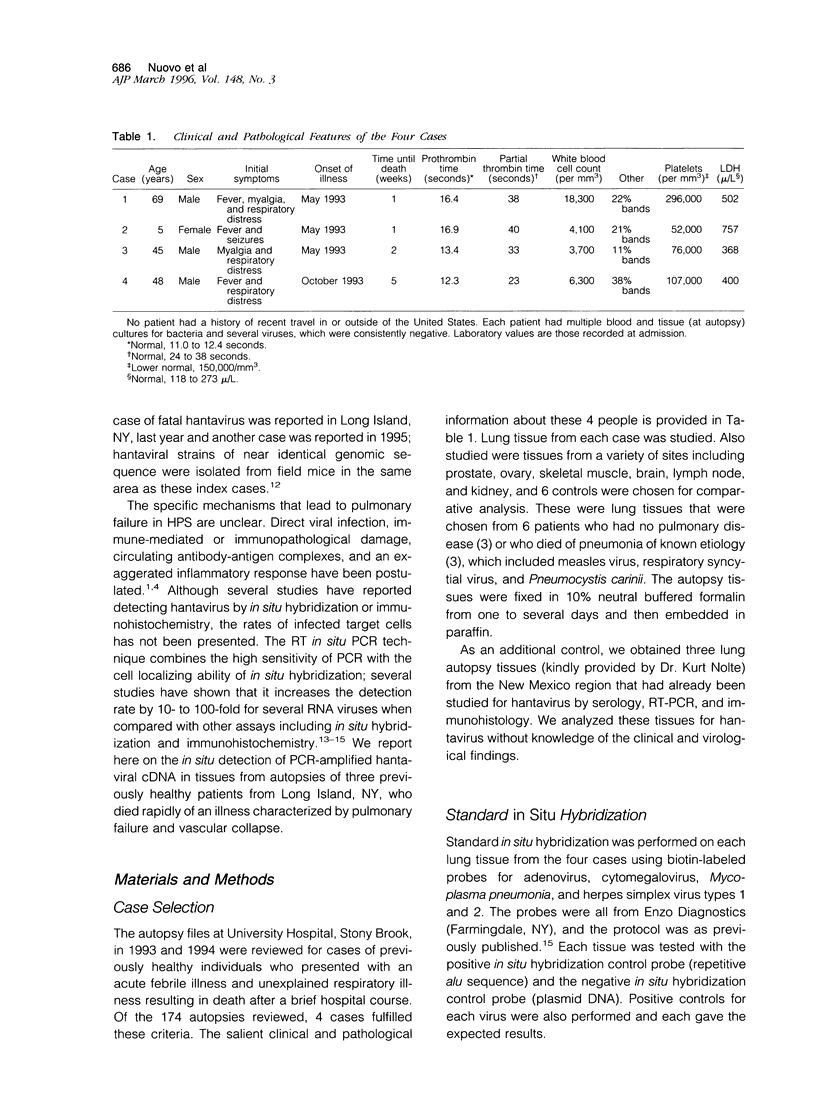
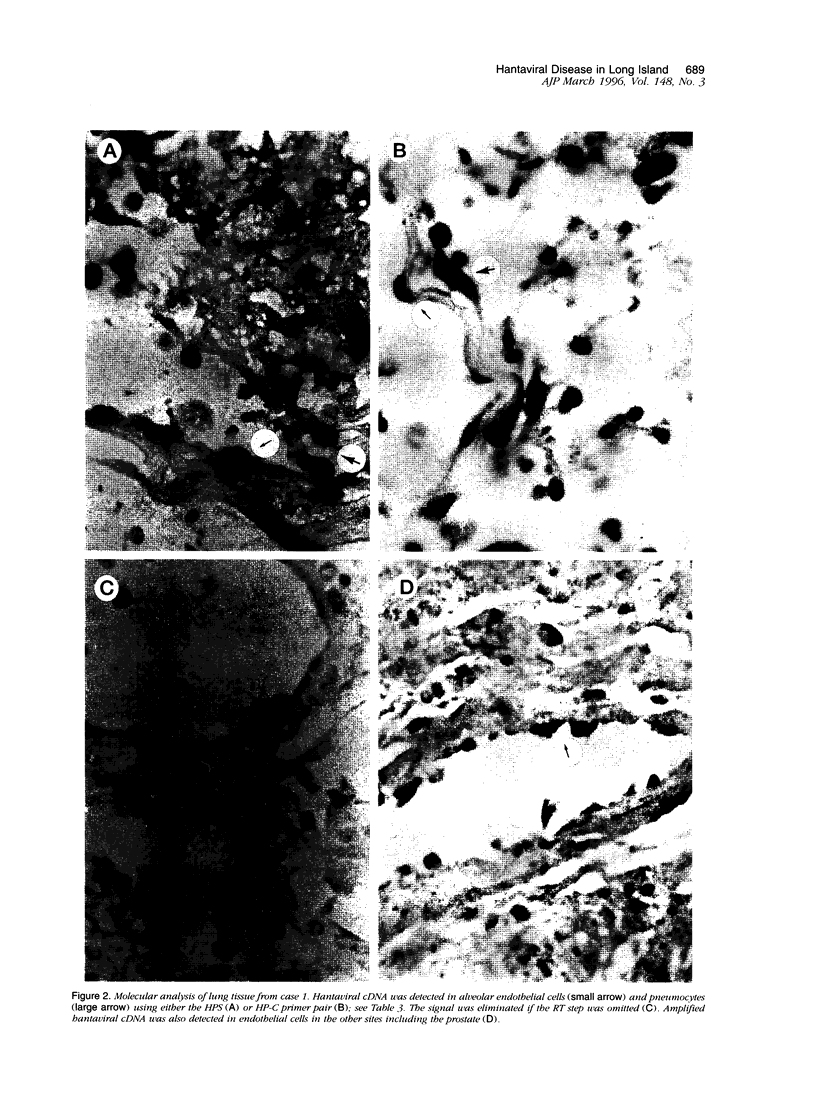
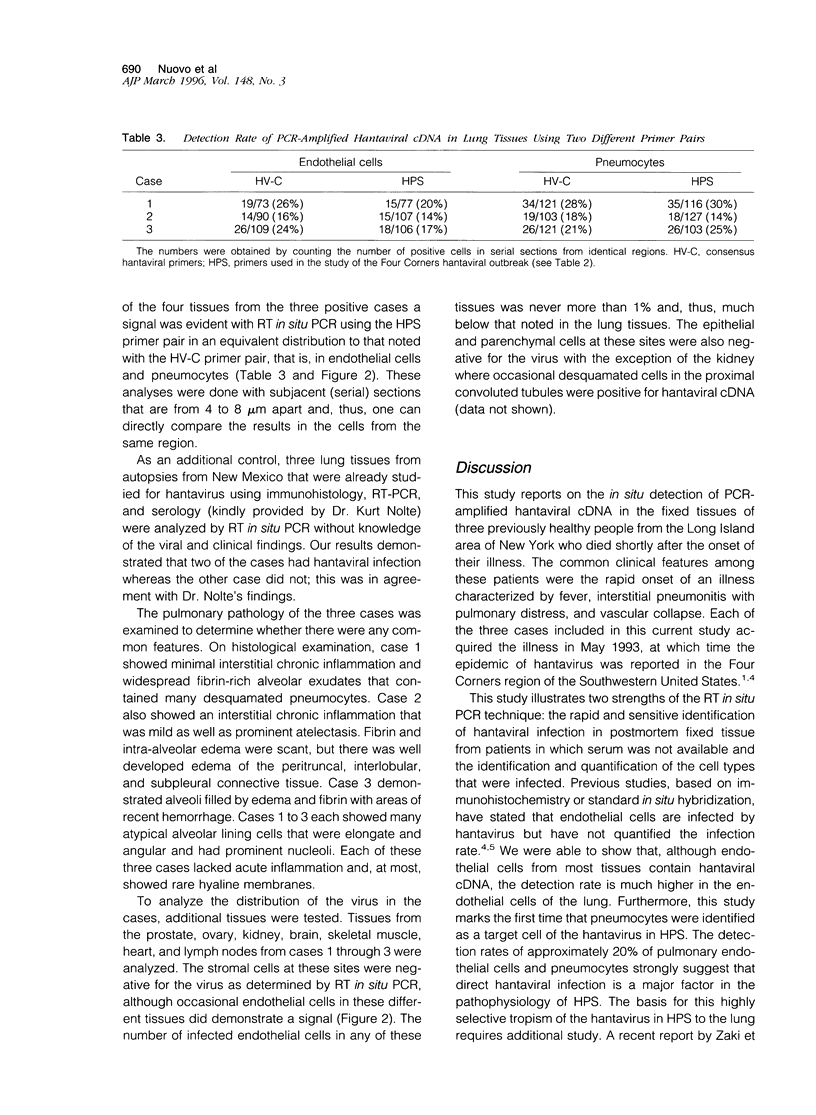
The purpose of this study was to analyze the histological distribution of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified hantaviral cDNA in three cases of fatal hantaviral infection that occurred 2 years ago in Long Island, NY. The three otherwise healthy patients had a rapid death characterized by fever and pulmonary failure and were identified from the autopsy files at University Hospital, Stony Brook. Six autopsy controls with either no pulmonary disease (three) or fatal pneumonitis of known etiology (three) were also studied. PCR-amplified hantaviral cDNA was detected in the lung tissue of the three cases and none of the six controls using the reverse transcriptase in situ PCR technique. In the positive cases, viral RNA was detected in approximately 20% of pneumocytes and alveolar endothelial cells as determined with a consensus and Four Corners-specific primer pair. Infected endothelial cells were identified in a wide variety of other sites, but at rates much lower than in the lungs. The selective localization of the viral RNA in many pneumocytes and pulmonary endothelial cells using a highly sensitive PCR-based test demonstrates a correlation between direct viral infection in the lung and the disease process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruno P., Hassell L. H., Brown J., Tanner W., Lau A. The protean manifestations of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. A retrospective review of 26 cases from Korea. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 1;113(5):385–391. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-5-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchin J. S., Koster F. T., Peters C. J., Simpson G. L., Tempest B., Zaki S. R., Ksiazek T. G., Rollin P. E., Nichol S., Umland E. T. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome: a clinical description of 17 patients with a newly recognized disease. The Hantavirus Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1994 Apr 7;330(14):949–955. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199404073301401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelle B., Jenison S., Torrez-Martinez N., Yamada T., Nolte K., Zumwalt R., MacInnes K., Myers G. A novel hantavirus associated with an outbreak of fatal respiratory disease in the southwestern United States: evolutionary relationships to known hantaviruses. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):592–596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.592-596.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggins J. W., Hsiang C. M., Cosgriff T. M., Guang M. Y., Smith J. I., Wu Z. O., LeDuc J. W., Zheng Z. M., Meegan J. M., Wang Q. N. Prospective, double-blind, concurrent, placebo-controlled clinical trial of intravenous ribavirin therapy of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1119–1127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol S. T., Spiropoulou C. F., Morzunov S., Rollin P. E., Ksiazek T. G., Feldmann H., Sanchez A., Childs J., Zaki S., Peters C. J. Genetic identification of a hantavirus associated with an outbreak of acute respiratory illness. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):914–917. doi: 10.1126/science.8235615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Gallery F., MacConnell P., Braun A. In situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha RNA in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):659–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Gorgone G. A., MacConnell P., Margiotta M., Gorevic P. D. In situ localization of PCR-amplified human and viral cDNAs. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 Nov;2(2):117–123. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Lidonnici K., MacConnell P., Lane B. Intracellular localization of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified hepatitis C cDNA. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993 Jul;17(7):683–690. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199307000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthavathana P., Lee H. W., Kang C. Y. Typing of Hantaviruses from five continents by polymerase chain reaction. Virus Res. 1992 Oct;26(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90142-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J. W., Baek L. J., Gajdusek D. C., Yanagihara R., Gavrilovskaya I., Luft B. J., Mackow E. R., Hjelle B. Isolation of pathogenic hantavirus from white-footed mouse (Peromyscus leucopus) Lancet. 1994 Dec 10;344(8937):1637–1637. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiropoulou C. F., Morzunov S., Feldmann H., Sanchez A., Peters C. J., Nichol S. T. Genome structure and variability of a virus causing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):715–723. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S. Y., Chu Y. K., Knauert F. K., Lofts R., Dalrymple J. M., LeDuc J. W. Comparison of hantavirus isolates using a genus-reactive primer pair polymerase chain reaction. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):567–573. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaki S. R., Greer P. W., Coffield L. M., Goldsmith C. S., Nolte K. B., Foucar K., Feddersen R. M., Zumwalt R. E., Miller G. L., Khan A. S. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. Pathogenesis of an emerging infectious disease. Am J Pathol. 1995 Mar;146(3):552–579. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]