Abstract
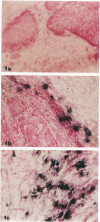
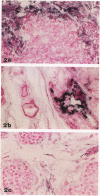
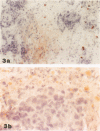
Degranulation of eosinophils has been observed in a variety of human tumors and in other diseases but has not been previously described in breast cancer. To determine whether eosinophil degranulation also occurs in breast carcinomas, we performed immunohistological studies on cryostat sections obtained from 26 breast cancer biopsies and from 2 benign breast tissues using a monoclonal antibody specific for human eosinophil peroxidase (EPO). For control purposes, the tissues were also immunostained with a mouse IgG1 negative control antibody and with monoclonal mouse anti-human myeloperoxidase. Of the 26 breast cancer specimens, 14 (53%) had extensive, unsuspected deposition of EPO that was located primarily in the connective tissue stroma around and within the tumor. Only 3 of the breast cancer cases had no immunohistochemical evidence of EPO. Thus, 23 of 26 cases of breast cancer (88%) had EPO deposits detectable within or around the tumor. By contrast, none of the benign breast tissues had similar deposits of EPO, and substantial extracellular myeloperoxidase deposition was detectable in only 3 cases of breast cancer. From these studies we conclude that there is eosinophil degranulation and extensive occult deposition of EPO in a major subset of human breast cancers.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee R. N., Narang R. M. Haematological changes in malignancy. Br J Haematol. 1967 Nov;13(6):829–843. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett E. G., Baker J. R., de Souza P. A light microscopical study of healing incised dermal wounds in rats, with special reference to eosinophil leucocytes and to the collagenous fibres of the periwound areas. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Dec;58(6):581–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightwell J., Tseng M. T. Peroxidase content in cell subpopulations of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary tumors in rats. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4562–4566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield J. H., Kephart G. M., Banks P. M., Gleich G. J. Extracellular deposition of eosinophil granule major basic protein in lymph nodes of patients with Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1250–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. K., Shyamala G. An evaluation of peroxidase as a marker for estrogen action in normal mammary glands of mice. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2202–2209. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collings J. R., Savage N. Peroxidase as a marker for oestrogen dependence in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1979 Sep;40(3):500–503. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSombre E. R., Lyttle C. R. Isolation and purification of rat mammary tumor peroxidase. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4086–4090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellon A. L., Hume R. B., Chretien P. B. Letter: Eosinophilia in bronchogenic carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 25;291(4):207–208. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407252910415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. J., O'Connell M., McDonnell L. Peroxidase activity as a marker for estrogen action in rat uteri and human mammary carcinomas. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1984;91:283–288. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-82188-2_41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Chandross R. J., Solic J. J., Weatherly N. F., Laszlo J., Moore J. O., Ottolenghi A. Medusa cells: cytostructure and cytochemistry of amoeboid eosinophils with pseudopod-like processes. Histochem J. 1981 Nov;13(6):905–919. doi: 10.1007/BF01002631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Chandross R. J., Weatherly N. F., Laszlo J., Moore J. O., Buckley R. H., Ottolenghi A. Medusa cells: the morphology and cytochemistry of common amoeboid variants of eosinophils. Histochem J. 1980 Nov;12(6):701–715. doi: 10.1007/BF01012025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEBANOFF S. J. INACTIVATION OF ESTROGEN BY RAT UTERINE PREPARATIONS. Endocrinology. 1965 Feb;76:301–311. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-2-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. J., Allen T. C., DeSombre E. R. Localization of uterine peroxidase activity in estrogen-treated rats. Biol Reprod. 1981 Nov;25(4):859–870. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.4.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiferman K. M., Ackerman S. J., Sampson H. A., Haugen H. S., Venencie P. Y., Gleich G. J. Dermal deposition of eosinophil-granule major basic protein in atopic dermatitis. Comparison with onchocerciasis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 1;313(5):282–285. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508013130502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyttle C. R., DeSombre E. R. Generality of oestrogen stimulation of peroxidase activity in growth responsive tissues. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):337–339. doi: 10.1038/268337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Román L., Medeiros L. J., Kingma D. W., Zárate-Osorno A., Nguyen V., Samoszuk M., Jaffe E. S. Malignant lymphomas of B-cell lineage with marked tissue eosinophilia. A report of five cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994 Apr;18(4):347–356. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199404000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Kephart G. M., Colby T. V., Gleich G. J. Tissue eosinophilia and eosinophil degranulation in syndromes associated with fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):521–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastrnák A., Jansa P. Local eosinophilia in stroma of tumors related to prognosis. Neoplasma. 1984;31(3):323–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Ramesh K. S., Wyler D. J. Eosinophils stimulate fibroblast DNA synthesis. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):572–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. P., Boohaker E. A., Pitts A. M., Macfadyen A. J., Bradley E. L., Jr, Pretlow T. G., 2nd Heterogeneity and subcompartmentalization in the distribution of eosinophils in human colonic carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1984 Aug;116(2):207–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M. K., Anderson A. L., Ramzi E., Wang F., Braunstein P., Lutsky J., Majmundar H., Slater L. M. Radioimmunodetection of Hodgkin's disease and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas with monoclonal antibody to eosinophil peroxidase. J Nucl Med. 1993 Aug;34(8):1246–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M. K., Nathwani B. N., Lukes R. J. Extensive deposition of eosinophil peroxidase in Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):426–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M. K., Nguyen V., Thomas C. T., Jacobson D. M. Effects of sonicated eosinophils on the in vitro sensitivity of human lymphoma cells to glucose oxidase. Cancer Res. 1994 May 15;54(10):2650–2653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samoszuk M., Sholly S., Epstein A. L. Eosinophil peroxidase is detectable with a monoclonal antibody in collagen bands of nodular sclerosis Hodgkin's disease. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):394–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strum J. M., Becci P. J. Analysis of mammary tumors for cytochemical evidence of endogenous mammary peroxidase. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1979 Oct;31(2):135–142. doi: 10.1007/BF02889931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Holt M. E., Denny P., Gibbs A. R., Williams B. D., Spry C. J. Deposition of eosinophil cationic protein in granulomas in allergic granulomatosis and vasculitis: the Churg-Strauss syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Aug 18;289(6442):400–402. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6442.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Crombrugge P., Pauwels R., Van der Straeten M. Thyroid carcinoma and eosinophilia. Ann Clin Res. 1983 Jun;15(3):128–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]