Abstract
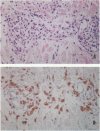
Immunohistochemical studies were performed to determine the presence and distribution of polypeptide transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta 1, a cytokine with macrophage-suppressing activity, in skin biopsies from 41 patients with different clinical forms of leprosy. We used an anti-TGF-beta 1 polyclonal antibody and the avidinbiotin-peroxidase (ABC complex) method. The results demonstrated that the lesions of the lepromatous and borderline lepromatous forms presented intense cytoplasm staining for TGF-beta 1 in the cells of the dermal infiltrate. A reaction of moderate intensity was observed in the cells of granulomas from borderline borderline cases, whereas no detectable immunoreaction was observed in granuloma cells from the tuberculoid and borderline tuberculoid forms. Considering that in the lepromatous leprosy form Mycobacterium leprae multiplies in the cytoplasm of macrophages and the lesions are diffuse and consist of poorly differentiated young macrophages, we believe that these alternations may be explained at least in part by the presence of TGF-beta 1 in the dermal infiltrate. Production of the cytokine may be induced by the presence of the bacillus itself and of its constituents, causing a mechanism of parasite evasion. Similarly, the absence of TGF-beta 1 in tuberculoid leprosy, which progresses with a specific immune response to M. leprae, may explain the intense differentiation of macrophage cells with the formation of well defined epithelioid granulomas capable of eliminating most of the bacilli.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnoldi J., Gerdes J., Flad H. D. Immunohistologic assessment of cytokine production of infiltrating cells in various forms of leprosy. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):749–753. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barral-Netto M., Barral A., Brownell C. E., Skeiky Y. A., Ellingsworth L. R., Twardzik D. R., Reed S. G. Transforming growth factor-beta in leishmanial infection: a parasite escape mechanism. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.1636092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Covaro G., Remington J. Infection of murine macrophages with Toxoplasma gondii is associated with release of transforming growth factor beta and downregulation of expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4126–4130. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4126-4130.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E. Production of transforming growth factor-beta by Mycobacterium avium-infected human macrophages is associated with unresponsiveness to IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1838–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Mehra V. Immunological unresponsiveness in leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Nathan C. Modulation of macrophage function by transforming growth factor beta, interleukin-4, and interleukin-10. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 23;685:713–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Paik J., Vodovotz Y., Nathan C. Contrasting mechanisms for suppression of macrophage cytokine release by transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23301–23308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantry D., Turner M., Abney E., Feldmann M. Modulation of cytokine production by transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4295–4300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A., Nathan C. F., Graycar J., Derynck R., Stuehr D. J., Srimal S. Macrophage deactivating factor and transforming growth factors-beta 1 -beta 2 and -beta 3 inhibit induction of macrophage nitrogen oxide synthesis by IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):940–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Taylor A., Kim S. J., Fauci A. S. Transforming growth factor-beta is a potent negative regulator of human lymphocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;628:345–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb17267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni A. B., Huh C. G., Becker D., Geiser A., Lyght M., Flanders K. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Ward J. M., Karlsson S. Transforming growth factor beta 1 null mutation in mice causes excessive inflammatory response and early death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. M., Rich S. Differential activation of CD8+ T cells by transforming growth factor-beta 1. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):668–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley J., Haregewoin A., Yemaneberhan T., Warndorff van Diepen T., Nsibami J., Knowles D., Smith K. A., Godal T. In vivo responses to Mycobacterium leprae: antigen presentation, interleukin-2 production, and immune cell phenotypes in naturally occurring leprosy lesions. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1985 Sep;53(3):385–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Seth P. TGF beta and HIV infection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 23;685:501–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney-Francis N., Mizel D., Wong H., Wahl L., Wahl S. TGF-beta regulates production of growth factors and TGF-beta by human peripheral blood monocytes. Growth Factors. 1990;4(1):27–35. doi: 10.3109/08977199009011007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Brenner M. B., Krangel M. S., Duby A. D., Bloom B. R. T-cell receptors of human suppressor cells. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):541–545. doi: 10.1038/329541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Horwitz D. A., Husmann L. A., Gillis S., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ identification of cells in human leprosy granulomas with monoclonal antibodies to interleukin 2 and its receptor. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3085–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Meyer P. R., Sharma O. P., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ demonstration of T lymphocyte subsets in granulomatous inflammation: leprosy, rhinoscleroma and sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):430–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. T lymphocyte subsets in the skin lesions of patients with leprosy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 Feb;8(2):182–189. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(83)70021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Kato H., Mehra V., Nelson E. E., Fan X. D., Rea T. H., Pattengale P. K., Bloom B. R. Genetically restricted suppressor T-cell clones derived from lepromatous leprosy lesions. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):459–461. doi: 10.1038/322459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Mehra V., Wong L., Fujimiya Y., Chang W. C., Horwitz D. A., Bloom B. R., Rea T. H., Pattengale P. K. Suppressor T lymphocytes from lepromatous leprosy skin lesions. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2831–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Melancon-Kaplan J., Young S. M., Pirmez C., Kino H., Convit J., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R. Learning from lesions: patterns of tissue inflammation in leprosy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R. B., Bhutani L. K., Sharma A. K., Nath I. T cell subsets in leprosy lesions: in situ characterization using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):421–429. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Analysis of cytoskeletal structures using blot-purified monospecific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:467–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salgame P., Abrams J. S., Clayberger C., Goldstein H., Convit J., Modlin R. L., Bloom B. R. Differing lymphokine profiles of functional subsets of human CD4 and CD8 T cell clones. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull M. M., Ormsby I., Kier A. B., Pawlowski S., Diebold R. J., Yin M., Allen R., Sidman C., Proetzel G., Calvin D. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):693–699. doi: 10.1038/359693a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. S., Twardzik D. R., Reed S. G. Regulation of Trypanosoma cruzi infections in vitro and in vivo by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):539–545. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor-beta: recent progress and new challenges. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1017–1021. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunawaki S., Sporn M., Ding A., Nathan C. Deactivation of macrophages by transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):260–262. doi: 10.1038/334260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Kaplan G., Sarno E. N., Horwitz M. A., Steinman R. M., Levis W. R., Nogueira N., Hair L. S., Gattass C. R., Arrick B. A. The cutaneous infiltrates of leprosy: cellular characteristics and the predominant T-cell phenotypes. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 23;307(26):1593–1597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212233072601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volc-Platzer B., Stemberger H., Luger T., Radaszkiewicz T., Wiedermann G. Defective intralesional interferon-gamma activity in patients with lepromatous leprosy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):235–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in inflammation: a cause and a cure. J Clin Immunol. 1992 Mar;12(2):61–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00918135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura M., Uyemura K., Deans R. J., Weinberg K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Defining protective responses to pathogens: cytokine profiles in leprosy lesions. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):277–279. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]